Biology:Common gamma chain
 Generic protein structure example |
The common gamma chain (γc) (or CD132), also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL-2RG, is a cytokine receptor sub-unit that is common to the receptor complexes for at least six different interleukin receptors: IL-2, IL-4,[1] IL-7,[2] IL-9, IL-15[3] and interleukin-21 receptor. The γc glycoprotein is a member of the type I cytokine receptor family expressed on most lymphocyte (white blood cell) populations, and its gene is found on the X-chromosome of mammals.
This protein is located on the surface of immature blood-forming cells in bone marrow. One end of the protein resides outside the cell where it binds to cytokines and the other end of the protein resides in the interior of the cell where it transmits signals to the cell's nucleus. The common gamma chain partners with other proteins to direct blood-forming cells to form lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The receptor also directs the growth and maturation of lymphocyte subtypes: T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells. These cells kill viruses, make antibodies, and help regulate the entire immune system.
Gene
Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL-2RG is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL2RG gene.[4] The human IL2RG gene is located on the long (q) arm of the X chromosome at position 13.1, from base pair 70,110,279 to base pair 70,114,423.
Structure
The γc chain is an integral membrane protein that contains extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains.
Function
Lymphocytes expressing the common gamma chain can form functional receptors for these cytokine proteins, which transmit signals from one cell to another and direct programs of cellular differentiation.
Ligands
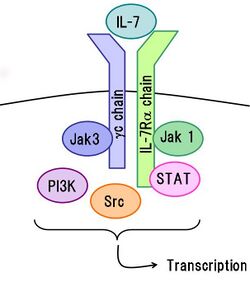
The γc chain partners with other ligand-specific receptors to direct lymphocytes to respond to cytokines including IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21.[5]
Signalling
IL2RG has been shown to interact with Janus kinase 3.[6][7]
Clinical significance
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency is caused by mutations in the IL2RG gene. More than 200 different mutations in the IL2RG gene have been identified in people with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).[8] Most of these mutations involve changes in one or a few nucleotides (DNA building blocks) in the gene. These changes lead to the production of a nonfunctional version of the common gamma chain protein [citation needed] or no production of protein.[9] Without the common gamma chain, important chemical signals are not relayed to the nucleus and lymphocytes cannot develop normally. A lack of functional mature lymphocytes disrupts the immune system's ability to protect the body from infection. Affected people have no functional immunity and can die within months after birth without successful bone marrow transplantation or alternatively, isolation from exposure to pathogens. Without important developmental signals from IL-7 and IL-15, T-cell and NK cell populations respectively fail to develop.
Experiments in animal models have shown X-SCID to occur similarly in dogs, but not in mice.[10]
Schizophrenia
Alterations in the immune response are involved in pathogenesis of many neuropsychiatric disorders including schizophrenia. Distinct gene variants of a number of pro-inflammatory and chemotactic cytokines together with their receptors associate with this disorder. IL2RG represents an important signaling component of many interleukin receptors and so far, no data on the functional state of this receptor in schizophrenia have been reported. Over-expression of the IL2RG gene may be implicated in altered immune response in schizophrenia and contribute to the pathogenesis of this disorder.[11]
References
- ↑ "Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-4 receptor". Science 262 (5141): 1880–3. December 1993. doi:10.1126/science.8266078. PMID 8266078. Bibcode: 1993Sci...262.1880R. https://zenodo.org/record/1231251.
- ↑ "Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-7 receptor". Science 262 (5141): 1877–80. December 1993. doi:10.1126/science.8266077. PMID 8266077. Bibcode: 1993Sci...262.1877N. https://zenodo.org/record/1231251.
- ↑ "Identification and cloning of a novel IL-15 binding protein that is structurally related to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor". EMBO J. 14 (15): 3654–63. August 1995. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00035.x. PMID 7641685.
- ↑ "Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor". Science 257 (5068): 379–82. July 1992. doi:10.1126/science.1631559. PMID 1631559. Bibcode: 1992Sci...257..379T.
- ↑ "Cutting edge: the common gamma-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex". J. Immunol. 167 (1): 1–5. July 2001. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.1. PMID 11418623.
- ↑ "Functional activation of Jak1 and Jak3 by selective association with IL-2 receptor subunits". Science 266 (5187): 1045–7. November 1994. doi:10.1126/science.7973659. PMID 7973659. Bibcode: 1994Sci...266.1045M.
- ↑ "Interaction of IL-2R beta and gamma c chains with Jak1 and Jak3: implications for XSCID and XCID". Science 266 (5187): 1042–5. November 1994. doi:10.1126/science.7973658. PMID 7973658. Bibcode: 1994Sci...266.1042R. https://zenodo.org/record/1231239.
- ↑ Primary immunodeficiency mutation databases. Advances in Genetics. 43. 2001. 103–88. doi:10.1016/s0065-2660(01)43005-7. ISBN 9780120176434.
- ↑ "Missense mutation in exon 7 of the common gamma chain gene causes a moderate form of X-linked combined immunodeficiency". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (3): 1169–73. March 1995. doi:10.1172/JCI117765. PMID 7883965.
- ↑ "IL-2R gamma gene microdeletion demonstrates that canine X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency is a homologue of the human disease". Genomics 23 (1): 69–74. September 1994. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1460. PMID 7829104.
- ↑ "Chronic schizophrenia is associated with over-expression of the interleukin-2 receptor gamma gene". Psychiatry Res 217 (3): 158–62. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.03.020. PMID 24713359.
Further reading
- Buckley RH (2004). "Molecular defects in human severe combined immunodeficiency and approaches to immune reconstitution". Annu Rev Immunol 22: 625–55. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104614. PMID 15032591.
- "Mutations in genes required for T-cell development: IL7R, CD45, IL2RG, JAK3, RAG1, RAG2, ARTEMIS, and ADA and severe combined immunodeficiency: HuGE review". Genet Med 6 (1): 16–26. 2004. doi:10.1097/01.GIM.0000105752.80592.A3. PMID 14726805.
- "Alternate signalling pathways from the interleukin-2 receptor". Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13 (1): 27–40. 2002. doi:10.1016/S1359-6101(01)00023-5. PMID 11750878.
- "Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor". Science 257 (5068): 379–82. July 1992. doi:10.1126/science.1631559. PMID 1631559. Bibcode: 1992Sci...257..379T.
- "Association of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 with the multichain high-affinity interleukin 2 receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (18): 7329–33. September 1990. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.18.7329. PMID 1976256. Bibcode: 1990PNAS...87.7329B.
- "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 produces immune defects in CD4+ T lymphocytes by inhibiting interleukin 2 mRNA". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (6): 2379–83. March 1990. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.6.2379. PMID 2315327. Bibcode: 1990PNAS...87.2379O.
- "Lymphocyte activation by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein". Nature 335 (6189): 445–8. September 1988. doi:10.1038/335445a0. PMID 2843775. Bibcode: 1988Natur.335..445K. https://zenodo.org/record/1233075.
- "The interleukin-2 and interleukin-4 receptors studied by molecular modelling". Structure 2 (9): 839–51. 1995. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(94)00085-9. PMID 7529123.
- "Screening for mutations causing X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in the IL-2R gamma chain gene by single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis". Hum. Genet. 96 (4): 427–32. October 1995. doi:10.1007/BF00191801. PMID 7557965.
- "Two mutational hotspots in the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene causing human X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 57 (3): 564–71. September 1995. PMID 7668284.
- "Functional analysis of the human interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain gene promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (13): 7479–86. March 1995. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.13.7479. PMID 7706294.
- "Female germ line mosaicism as the origin of a unique IL-2 receptor gamma-chain mutation causing X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (2): 895–9. February 1995. doi:10.1172/JCI117740. PMID 7860773.
- "Defective human interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain in an atypical X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency with peripheral T cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (20): 9466–70. September 1994. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.20.9466. PMID 7937790. Bibcode: 1994PNAS...91.9466D.
- "Interaction of IL-2R beta and gamma c chains with Jak1 and Jak3: implications for XSCID and XCID". Science 266 (5187): 1042–5. November 1994. doi:10.1126/science.7973658. PMID 7973658. Bibcode: 1994Sci...266.1042R. https://zenodo.org/record/1231239.
- "Impairment of ligand binding and growth signaling of mutant IL-2 receptor gamma-chains in patients with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency". J. Immunol. 153 (3): 1310–7. August 1994. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.153.3.1310. PMID 8027558.
- "Soluble IL-2 receptor beta and gamma subunits: ligand binding and cooperativity". Eur. Cytokine Netw. 5 (1): 23–34. 1994. PMID 8049354.
- "Detection of three nonsense mutations and one missense mutation in the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain gene in SCIDX1 that differently affect the mRNA processing". Genomics 21 (1): 291–3. May 1994. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1265. PMID 8088810.
- "Sharing of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor gamma chain between receptors for IL-2 and IL-4". Science 262 (5141): 1874–7. December 1993. doi:10.1126/science.8266076. PMID 8266076. Bibcode: 1993Sci...262.1874K.
External links
- Interleukin+Receptor+Common+gamma+Subunit at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P31785 (Human Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma) at the PDBe-KB.
 |