Chemistry:Quipazine
Quipazine, also known as 1-(2-quinolinyl)piperazine (2-QP), is a serotonergic drug of the arylpiperazine family and an analogue of 1-(2-pyridinyl)piperazine which is used in scientific research.[1][2][3][4][5] It was first described in the 1960s and was originally intended as an antidepressant but was never developed or marketed for medical use.[1][6][4] The effects of quipazine in humans include nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal disturbances, diarrhea, and, at higher doses, psychedelic effects.[1][7][3] Quipazine may represent the prototype of a novel structural class of psychedelic drugs.[1][8][9]
Use and effects
The effects and side effects of quipazine in humans have been described.[7][1] At a dose of 25 mg orally, they included nausea, flatulence, gastrointestinal discomfort, and diarrhea, with no LSD-like subjective effects.[7] Higher doses were not assessed due to serotonin 5-HT3 receptor-mediated side effects of nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort.[7][3] An anecdotal report in one or more subjects, in which the dose of quipazine was said to be 0.5 mg (sic), described quipazine as producing low-dose mescaline-like effects followed by onset of dysphoria and nausea.[7][1][10]
It was suggested by Jerrold C. Winter in 1994 that serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists like ondansetron could allow for use of higher doses of quipazine and assessment of whether it produces clear psychedelic effects or not.[7] Alexander Shulgin subsequently reported in The Shulgin Index (2011), based on an anonymous report dated to 2007, that quipazine in combination with a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, presumably ondansetron, produced a "full psychedelic response".[3][11][1][12]
Interactions
Serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists like ondansetron have been reported to block the nausea and vomiting induced by quipazine.[3][11][1][12] Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonists like ketanserin have been reported to block the psychedelic-like effects of quipazine in animals.[1][3]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Target | Affinity (Ki, nM) |
|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 230–>10,000 |
| 5-HT1B | 1,000 |
| 5-HT1D | 1,000–3,720 |
| 5-HT1E | ND |
| 5-HT1F | ND |
| 5-HT2A | 59–2,780 (Ki) 309 (EC50) 62–71% (Emax) |
| 5-HT2B | 49–178 (Ki) 178 (EC50) 17% (Emax) |
| 5-HT2C | 54–1,344 (Ki) 339 (EC50) 57–69% (Emax) |
| 5-HT3 | 1.23–4.0 (Ki) 1.0 (EC50) ND (Emax) |
| 5-HT4 | >10,000 (guinea pig) |
| 5-HT5A | >10,000 (mouse) |
| 5-HT6 | 3,600 |
| 5-HT7 | 3,033 |
| α1 | >10,000 (rat) |
| α2 | 5,000 (rat) |
| β1 | 5,600 |
| β2 | 2,900 (rat) |
| D1 | >10,000 |
| D2 | >10,000 |
| D2-like | 3,920 (rat) |
| mACh | >10,000 (rat) |
| TAAR1 | >10,000 (human) (EC50) |
| SERT | 30–143 |
| NET | ND |
| DAT | ND |
| Notes: The smaller the value, the more avidly the drug binds to the site. All proteins are human unless otherwise specified. Refs: [14][15][13][16][17][18][19][20][21] | |
Quipazine is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor agonist and to a lesser extent a serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor agonist as well as serotonin reuptake inhibitor.[1][2][17][14][15] It also shows affinity for serotonin 5-HT1 receptors, including the serotonin 5-HT1B receptor and to a lesser extent the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor.[22] Activation of the serotonin 5-HT3 is implicated in inducing nausea and vomiting as well as anxiety, which has limited the potential clinical usefulness of quipazine.[1][2][3]
Quipazine produces a head-twitch response and other psychedelic-consistent effects in animal studies including in mice, rats, and monkeys.[1][3][23][24][25] These effects appear to be mediated by activation of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, as they are blocked by serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonists like ketanserin.[1][3][25] The head twitches induced by quipazine are potentiated by the monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) pargyline.[25][26] Based on this, it has been suggested that quipazine may act as a serotonin releasing agent and that it may induce the head twitch response by a dual action of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonism and induction of serotonin release.[25][26]
Besides the head-twitch response, quipazine fully substitutes for LSD and partially substitutes for mescaline in rodent drug discrimination tests.[7] In addition, quipazine substitutes for DOM in rodents and monkeys and this is blocked by serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonists like pizotyline and ketanserin.[1] When quipazine is used as the training drug, LSD, mescaline, and psilocybin all fully substitute for quipazine.[1] In monkeys, quipazine additionally produced LSD-like behavioral changes along with projectile vomiting.[7] In contrast to primates, rodents generally lack an emetic response, and hence the nausea and vomiting that quipazine can induce may not be a limiting factor in this order of animals.[1] Similarly to DOI, quipazine alters time perception in rodents.[27]
Quipazine can produce tachycardia, including positive chronotropic and positive inotropic effects, through activation of the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor.[2]
Although quipazine does not generalize to dextroamphetamine in drug discrimination tests of dextroamphetamine-trained rodents, dextroamphetamine and cathinone have been found to partially generalize to quipazine in assays of quipazine-trained rodents.[28][29] In relation to this, it has been suggested that quipazine might possess some dopaminergic activity, as the discriminative stimulus properties of amphetamine appear to be mediated by dopamine signaling.[28][29] Relatedly, quipazine has been said to act as a dopamine receptor agonist in addition to serotonin receptor agonist.[25] Conversely however, the generalization may be due to serotonergic activities of amphetamine and cathinone.[30] Fenfluramine has been found to fully generalize to quipazine, but levofenfluramine, in contrast to quipazine, did not generalize to dextroamphetamine.[28][24]
Quipazine is said to differ in its pharmacology and effects from other serotonergic arylpiperazines like TFMPP and mCPP.[1][3] Relatedly, unlike quipazine, neither TFMPP nor mCPP substitute for DOM in drug discrimination tests.[1][3] In addition, DOM and TFMPP mutually antagonize each others' stimulus effects.[1] In contrast to quipazine, TFMPP and mCPP show prominent bias or preference for the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor over the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[3]
Quipazine is a very weak agonist of the human trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1).[21]
Chemistry
Quipazine is a substituted piperazine and quinoline.[4] It is structurally related to 6-nitroquipazine, isoquipazine, 1-(2-naphthyl)piperazine (2-NP), and 1-(1-naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP).[4][3]
Novel analogues of quipazine with retained serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonism and reduced undesirable off-target activity such as serotonin 5-HT3 receptor agonism and associated adverse effects have been developed and characterized.[8][9][31] A doctoral thesis on novel psychedelic quipazine analogues was published by Yilun Yang at Columbia University in August 2025.[31] However, the thesis is embargoed until 2030.[31]
Synthesis
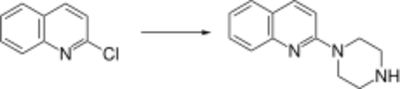
Quipazine is synthesized by reacting 2-chloroquinoline with piperazine.[32]
History
Quipazine was first described in the scientific literature by 1966.[4][33] It was described as an antidepressant-like agent by 1971.[6] The psychedelic-like effects of quipazine in animals were first described by 1977.[26]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 "Quipazine: Classical hallucinogen? Novel psychedelic?". Australian Journal of Chemistry 76 (5): 288–298. 2 May 2023. doi:10.1071/CH22256. ISSN 0004-9425.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "The interactions of the 5-HT3 receptor with quipazine-like arylpiperazine ligands: the journey track at the end of the first decade of the third millennium". Curr Top Med Chem 10 (5): 504–526. 2010. doi:10.2174/156802610791111560. PMID 20166948.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 "Psychedelic-like Properties of Quipazine and Its Structural Analogues in Mice". ACS Chem Neurosci 12 (5): 831–844. March 2021. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00291. PMID 33400504.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer US. 2014. p. 987. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA987. Retrieved 10 December 2024.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Netherlands. 2012. p. 244. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA244. Retrieved 10 December 2024.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Quipazine, a new type of antidepressant agent". Psychopharmacologia 21 (1): 89–100. 1971. doi:10.1007/BF00404000. PMID 5567294.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 "The stimulus effects of serotonergic hallucinogens in animals". NIDA Res Monogr 146: 157–182. 1994. PMID 8742798. https://archives.nida.nih.gov/sites/default/files/monograph146.pdf#page=162.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Psychedelic Alpha (20 March 2024). "Notes from the International Society for Research on Psychedelics' 2024 Conference in New Orleans (Guest Contribution)". https://psychedelicalpha.com/news/notes-from-the-international-society-for-research-on-psychedelics-2024-conference-in-new-orleans-guest-contribution. "Dr. Jason Younkin, a postdoctoral researcher at Virginia Commonwealth University and adjunct professor at Virginia State University, gave a talk and displayed interesting findings with quipazine analogs during the poster session. Quipazine is a unique psychedelic as its chemical structure includes a piperazine group. While it produces psychedelic effects, it is not used as frequently as other serotonergic psychedelics due to its effects on the gastrointestinal tract via 5-HT3 receptor activation. The goal of this study was to find analogs of quipazine that do not produce these negative side effects or the hallucination-like effects of all classical psychedelics using a battery of molecular and pharmacological techniques. [Photograph]"
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Jason Younkin (16 February 2024). "Pharmacological characterization of quipazine analogs as a new structural class of psychedelic 5-HT2A receptor agonists". International Society for Research on Psychedelics.
- ↑ "Quipazine-induced stimulus control in the rat". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 60 (3): 265–269. February 1979. doi:10.1007/BF00426666. PMID 108704. "As yet, no report of the effects of quipazine in human subjects has been published. The implications of the present findings and those of White et al. (1977) for the clinical pharmacology of quipazine are obvious. One would expect the drug to produce at least a portion of the mescaline-LSD syndrome. In a preliminary clinical investigation (H. Daumier, personal communication) normal human subjects reported 'low dose mescaline-like' effects at a dose of 0.5 mg. The study of higher doses was precluded by the onset of dysphoric effects including nausea.".
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Effect of Hallucinogens on Unconditioned Behavior". Behavioral Neurobiology of Psychedelic Drugs. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36. 2016. pp. 159–199. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_466. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. 1. Berkeley: Transform Press. 2011. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=68-huAAACAAJ. Retrieved 2 November 2024. "Quipazine [...] (11) This experimental antidepressant is an agonist to several 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. If taken with a 5-HT3 antagonist, quipazine (blocking nausea/vomiting) it produces a full psychedelic response (Anon., 2007)."
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Classical psychedelics' action on brain monoaminergic systems". Int J Biochem Cell Biol 176. November 2024. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2024.106669. PMID 39332625.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "PDSP Database" (in zu). https://pdsp.unc.edu/databases/pdsp.php?testFreeRadio=testFreeRadio&testLigand=Quipazine&kiAllRadio=all&doQuery=Submit+Query.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "BindingDB BDBM50014407 2-(piperazin-1-yl)quinoline::2-Piperazin-1-yl-quinoline::2-Piperazin-1-yl-quinoline (Quipazine)::2-Piperazin-1-yl-quinoline(Quipazine)::CHEMBL18772::QUIPAZINE". https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/chemsearch/marvin/MolStructure.jsp?monomerid=50014407.
- ↑ "Structure-activity relationships at 5-HT1A receptors: binding profiles and intrinsic activity". Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40 (4): 1041–1051. December 1991. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(91)90124-k. PMID 1816558.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Agonist high and low affinity state ratios predict drug intrinsic activity and a revised ternary complex mechanism at serotonin 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors". Synapse 35 (2): 144–150. February 2000. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(200002)35:2<144::AID-SYN7>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID 10611640.
- ↑ "Structure-affinity relationship studies on arylpiperazine derivatives related to quipazine as serotonin transporter ligands. Molecular basis of the selectivity SERT/5HT3 receptor". Bioorg Med Chem 13 (10): 3455–3460. May 2005. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.03.008. PMID 15848758.
- ↑ "Synthesis, in vitro binding studies and docking of long-chain arylpiperazine nitroquipazine analogues, as potential serotonin transporter inhibitors". Eur J Med Chem 49: 200–210. March 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.01.012. PMID 22309909.
- ↑ "Functional characterization of agonists at recombinant human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors in CHO-K1 cells". Br J Pharmacol 128 (1): 13–20. September 1999. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702751. PMID 10498829.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Molecular basis of human trace amine-associated receptor 1 activation". Nat Commun 15 (1). January 2024. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-44601-4. PMID 38168118. Bibcode: 2024NatCo..15..108Z.
- ↑ "Central serotonin receptors as targets for drug research". J Med Chem 30 (1): 1–12. January 1987. doi:10.1021/jm00384a001. PMID 3543362. "Table II. Affinities of Selected Phenalkylamines for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 Binding Sites".
- ↑ "Classical Hallucinogens". Pharmacological Aspects of Drug Dependence. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 118. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1996. pp. 343–371. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-60963-3_10. ISBN 978-3-642-64631-7.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Site-Selective Serotonin Agonists as Discriminative Stimuli". Transduction Mechanisms of Drug Stimuli. Psychopharmacology Series. 4. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1988. pp. 15–31. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-73223-2_2. ISBN 978-3-642-73225-6.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 "Monoamine oxidase and head-twitch response in mice. Mechanisms of alpha-methylated substrate derivatives". Neurotoxicology 25 (1–2): 223–232. January 2004. doi:10.1016/S0161-813X(03)00101-3. PMID 14697897. Bibcode: 2004NeuTx..25..223N.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 "Quipazine-induced head-twitch in mice". Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6 (3): 325–329. March 1977. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(77)90032-6. PMID 140381.
- ↑ "The Role of the Serotonergic System in Time Perception: A Systematic Review". Int J Mol Sci 25 (24). December 2024. doi:10.3390/ijms252413305. PMID 39769070.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 "Discriminative stimulus properties of amphetamine and structurally related phenalkylamines". Med Res Rev 6 (1): 99–130. 1986. doi:10.1002/med.2610060105. PMID 3512936.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Speculations on the mechanism of action of hallucinogenic indolealkylamines". Neurosci Biobehav Rev 5 (2): 197–207. 1981. doi:10.1016/0149-7634(81)90002-6. PMID 7022271.
- ↑ "Comparative effects of cathinone and amphetamine on fixed-interval operant responding: a rate-dependency analysis". Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23 (3): 355–365. September 1985. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(85)90006-1. PMID 4048231.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Yang, Yilun. Design and Synthesis of Quipazine Analogs for Programmable Control of Psychedelic Effects. doi:10.7916/0K6K-YC03. https://academiccommons.columbia.edu/doi/10.7916/0k6k-yc03. "To better understand how to potentially regulate these effects, we focused on the design of compounds with programmable psychedelic intensity through fine-tuning the 5-HT2A receptor signaling efficacy. We turned to the source that drives the psychedelic effects of serotonergic psychedelics, the 5-HT2A receptor. By modifying the scaffold of quipazine, we aimed to control the psychedelic intensity by tuning different levels of 5-HT2A signaling efficacy within the quipazine analog series, and thus provide design guidelines for developing desirable pharmacological agents with varying degree of psychedelic effects.".
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Rodriguez R, DE patent 2006638, issued 1970 Chem. Abstr., 73: 98987g (1970).
- ↑ "Mechanism of action of quipazine maleate on the central nervous system". Bol Inst Estud Med Biol Univ Nac Auton Mex 24 (1): 191–205. 1966. PMID 5299393.
External links
- Quipazine - Isomer Design
- Quipazine: A Long-Standing Enigma in Psychedelic Research - Mario de la Fuente Revenga - Psychedelic Science Review (PSR)
- The Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor: From Mice to Humans - Ian Liddle - Psychedelic Science Review (PSR)
Template:Arylpiperazines Template:Chemical classes of psychoactive drugs
 |
