Chemistry:Mexiletine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mexitil, NaMuscla |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607064 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 50–60% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6 and 1A2-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 10–12 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
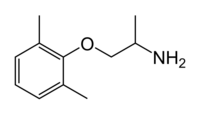
| Formula | C11H17NO |
| Molar mass | 179.263 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Mexiletine (INN) (sold under the brand names Mexitil and Namuscla) is a medication used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, chronic pain, and some causes of muscle stiffness. Common side effects include abdominal pain, chest discomfort, drowsiness, headache, and nausea. It works as a non-selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker and belongs to the Class IB group of anti-arrhythmic medications.[1]
Medical uses
Mexiletine has several uses including the treatment of abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias, chronic pain, and myotonia.
In general when treating arrhythmias, mexiletine is reserved for use in dangerous heart rhythm disturbances such as ventricular tachycardia.[2] It is of particular use when treating arrhythmias caused by long QT syndrome.[3] The LQT3 form of long QT syndrome is amenable to treatment with mexiletine as this form is caused by defective sodium channels that continue to release a sustained current rather than fully inactivating, however other forms of long QT syndrome can also be treated with this medication.[3]
Mexiletine has been used to treat chronic pain and may also be used to treat muscle stiffness resulting from myotonic dystrophy (Steinert's disease) or nondystrophic myotonias such as myotonia congenita (Thomsen syndrome or Becker syndrome).[4][5]
Adverse effects
Common side effects of mexiletine include abdominal pain, chest discomfort, drowsiness, headache, nausea and skin reactions.[6] Uncommon or rare side effects include seizures and liver dysfunction.[6]
Pharmacology
Mexiletine is an oral analogue of lidocaine.[5] It is a class IB antiarrhythmic which shorten the refractory period and action potential duration (APD). Decrease in APD more than that of ERP so there is increase ERP/APD ratio.[2] The drug has a bioavailability of 90%, and peak plasma concentrations are seen after 2–4 hours.[2] The mean drug half-life is approximately 11 hours.[2] Mexiletine is predominantly metabolised by the liver. The pharmacokinetics of mexiletine are preserved with even moderate to severe renal impairment, but dose adjustment may be required when creatinine clearance falls below 10 mL/minute.[2]
Synthesis

Society and culture
Mexiletine is available for human use in the US, and has been reintroduced in the UK as a licensed product, having previously only been available as a 'named patient' import. The drug is sold under the trade name Mexitil for use in arrhythmias and NaMuscla for use in myotonia.[8][9]
Veterinary uses
Mexiletine is available to veterinarians in the US for the treatment of heart disease in dogs and cats. It is commonly used for the treatment of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) in Boxer dogs in combination with sotalol.
References
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Mexiletine: pharmacology and therapeutic use". Clinical Cardiology 13 (5): 349–59. May 1990. doi:10.1002/clc.4960130509. PMID 2189614.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "The role of mexiletine in the management of long QT syndrome". Journal of Electrocardiology 51 (6): 1061–1065. November 2018. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2018.08.035. PMID 30497731.
- ↑ "Mexiletine Usage in a Chronic Pain Clinic: Indications, Tolerability, and Side Effects". Pain Physician 21 (5): E573–E579. September 2018. doi:10.36076/ppj.2018.5.E573. PMID 30282405.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Martindale: The complete drug reference (33rd ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. 2002. ISBN 0-85369-499-0.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Mexiletine". British National Formulary. NICE. https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drug/mexiletine.html.
- ↑ Koppe R, Kummer W, "1-(2{40 ,6{40 -Dimethyl-phenoxy)-2-amino-alkanes and salts thereof", US patent 3954872, issued 1976, assigned to Boehringer Sohn Ingelheim.
- ↑ "Mexiletine". https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00379.
- ↑ "Lupin announces launch of NaMuscla" (in en). https://www.biospectrumindia.com/news/43/12704/lupin-announces-launch-of-namuscla.html.
Further reading
- Pharmacology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. 2004. ISBN 0-521-68794-2.
External links
- "Mexiletine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/mexiletine.
 |

