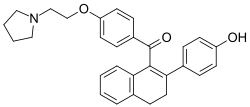
Chemistry:Trioxifene
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LY-133,314 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H31NO3 |
| Molar mass | 453.582 g·mol−1 |
Trioxifene (INN; developmental code LY-133,314), or as the salt trioxifene mesylate (USAN), is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with competitive binding activity against estradiol for the ERα and antagonistic activity against ERα-mediated gene expression, that was under preclinical and clinical development by Eli Lilly and Company for breast cancer and prostate cancer,[1] but was abandoned.[2]:11[3][4] Its affinity for the rat estrogen receptor was reported to be 20% relative to estradiol.[5][6]
References
- ↑ "The selective estrogen receptor modulator trioxifene (LY133314) inhibits metastasis and extends survival in the PAIII rat prostatic carcinoma model". Cancer Research 63 (18): 6056–62. September 2003. PMID 14522935.
- ↑ "Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer.". Milestones in Drug Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media. 2013. ISBN 978-3-03-480664-0.
- ↑ The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 1252–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA1252.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 281–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA281.
- ↑ "The biological evaluation of novel antioestrogens for the treatment of breast cancer". Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 15 (3): 243–69. December 1993. doi:10.1016/1040-8428(93)90044-5. PMID 8142059.
- ↑ "Endocrine Disruptors: Effects on Sex Steroid Hormone Receptors and Sex Development". Drug Toxicity in Embryonic Development II: Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of Birth Defects: Mechanistics Understanding of Human Development Toxicants. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 437–. ISBN 978-3-642-60447-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=vcHsCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA437.
 |

