Chemistry:7α-Methylestradiol
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 7α-Methyl-E2; 7α-Me-E2; 7α-Methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol |
| Drug class | Estrogen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 286.415 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
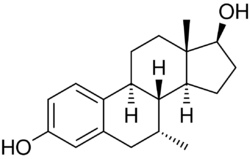
7α-Methylestradiol (7α-Me-E2), also known as 7α-methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is a synthetic estrogen and an active metabolite of the androgen/anabolic steroids trestolone/Methandienone.[1][2][3] It is considered to be responsible for the estrogenic activity of trestolone.[2][3] The compound shows about the same affinity for the estrogen receptor as estradiol.[1]
| Compound | PR | AR | ER | GR | MR | SHBG | CBG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estradiol | 2.6 | 7.9 | 100 | 0.6 | 0.13 | 8.7 | <0.1 | |
| 7α-Methylestradiol | 1–3 | 15–25 | 101 | <1 | <1 | ? | ? | |
| Trestolone | 50–75 | 100–125 | ? | <1 | ? | ? | ? | |
| Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were progesterone for the PR, testosterone for the AR, E2 for the ER, DEXA for the GR, aldosterone for the MR, DHT for SHBG, and cortisol for CBG. | ||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Receptor Binding as a Tool in the Development of New Bioactive Steroids". Drug Design. 1979. pp. 169–214. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-060308-4.50010-X. ISBN 9780120603084. https://books.google.com/books?id=bhAlBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA169.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Comparison of 7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone effectiveness alone or combined with progestins on androgen receptor mediated-transactivation". Reproduction 143 (2): 211–219. February 2012. doi:10.1530/REP-11-0171. PMID 22065861.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Dimethandrolone (7alpha,11beta-dimethyl-19-nortestosterone) and 11beta-methyl-19-nortestosterone are not converted to aromatic A-ring products in the presence of recombinant human aromatase". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 110 (3–5): 214–222. June 2008. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.11.009. PMID 18555683.
- ↑ "Towards the mapping of the progesterone and androgen receptors". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 27 (1–3): 255–269. 1987. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(87)90317-7. PMID 3695484.
- ↑ "Unique steroid congeners for receptor studies". Cancer Research 38 (11 Pt 2): 4186–4198. November 1978. PMID 359134. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/38/11_Part_2/4186.short.
- ↑ "Steroid hormone receptors and pharmacology". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 12: 143–157. January 1980. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(80)90264-2. PMID 7421203.
 |

