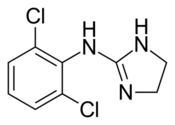
Chemistry:Clonidine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈklɒnədiːn/ |
| Trade names | Catapres, Kapvay, Nexiclon, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682243 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, epidural, intravenous (IV), transdermal, topical |
| Drug class | Centrally acting α2A-agonist hypotensive agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 70–80% (oral),[1][2] 60–70% (transdermal)[3] |
| Protein binding | 20–40%[4] |
| Metabolism | Liver to inactive metabolites,[4] 2/3 CYP2D6[8] |
| Onset of action | IR: 30–60 minutes after an oral dose[5] |
| Elimination half-life | IR: 12–16 hours; 41 hours in kidney failure,[6][7] 48 hours for repeated dosing[3] |
| Excretion | Urine (72%)[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H9Cl2N3 |
| Molar mass | 230.09 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2-adrenergic agonist[9] medication used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, drug withdrawal (alcohol, opioids, or nicotine), menopausal flushing, diarrhea, spasticity, and certain pain conditions.[10] It is used orally (by mouth), by injection, or as a transdermal skin patch.[10] Onset of action is typically within an hour with the effects on blood pressure lasting for up to eight hours.[10]
Common side effect include dry mouth, dizziness, headaches, hypotension, and sleepiness.[10] Severe side effects may include hallucinations, heart arrhythmias, and confusion.[11] If rapidly stopped, withdrawal effects may occur.[10] Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended.[11] Clonidine lowers blood pressure by stimulating α2 receptors in the brain, which results in relaxation of many arteries.[10]
Clonidine was patented in 1961 and came into medical use in 1966.[12][13][14] It is available as a generic medication.[10] In 2020, it was the 75th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 9 million prescriptions.[15][16]
Medical uses
Clonidine is used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (alcohol, opioids, or smoking), menopausal flushing, diarrhea, and certain pain conditions. It also sees some use off-label for episodic insomnia, restless-legs syndrome, and anxiety, among other uses.[10]
Resistant hypertension
Clonidine may be effective for lowering blood pressure in people with resistant hypertension.[17]
Clonidine works by slowing the pulse rate and exerts a reduction of serum concentrations of renin, aldosterone, and catecholamines.[18]
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Clonidine may improve symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in some people but causes many adverse effects and the beneficial effect is modest.[19] In Australia , clonidine is an accepted but not approved use for ADHD by the TGA.[20] Clonidine, along with methylphenidate, has been studied for treatment of ADHD.[21][22][23] While not as effective as methylphenidate in treating ADHD, clonidine does offer some benefit;[21] it can also be useful in combination with stimulant medications.[24] Some studies show clonidine to be more sedating than guanfacine, which may be better at bedtime along with an arousing stimulant in the morning.[25][26] Clonidine has been used to reduce sleep disturbances in ADHD, including to help offset stimulant-associated insomnia.[27][28][29][30] Unlike stimulant medications, clonidine is regarded as having no abuse potential, and may even be used to reduce abuse of drugs including nicotine and cocaine.[31]
Drug withdrawal
Clonidine may be used to ease drug withdrawal symptoms associated with abruptly stopping the long-term use of opioids, alcohol, benzodiazepines and nicotine.[32] It can alleviate opioid withdrawal symptoms by reducing the sympathetic nervous system response such as tachycardia and hypertension, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), hot and cold flashes, and akathisia.[33] It may also be helpful in aiding smokers to quit.[34] The sedation effect can also be useful. Clonidine may also reduce severity of neonatal abstinence syndrome in infants born to mothers that are using certain drugs, particularly opioids.[35] In infants with neonatal withdrawal syndrome, clonidine may improve the neonatal intensive care unit Network Neurobehavioral Score.[36]
Clonidine has also been suggested as a treatment for rare instances of dexmedetomidine withdrawal.[37]
Spasticity
Clonidine has some role in the treatment of spasticity, acting principally by inhibiting excessive sensory transmission below the level of injury. Its use, however, is mainly as a second or third line agent, due to side effects such as hypotension, bradycardia, and drowsiness.[38]
Other uses
Clonidine also has several off-label uses, and has been prescribed to treat psychiatric disorders including stress, sleep disorders,[27] hyperarousal caused by post-traumatic stress disorder, borderline personality disorder, and other anxiety disorders.[39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46] Clonidine is also a mild sedative, and can be used as premedication before surgery or procedures.[47] It has also been studied as a way to calm acute manic episodes.[48] Its epidural use for pain during heart attack, and postoperative and intractable pain has also been studied extensively.[49] Clonidine can be used in restless legs syndrome.[50] It can also be used to treat facial flushing and redness associated with rosacea.[51] It has also been successfully used topically in a clinical trial as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy.[52] Clonidine can also be used for migraine headaches and hot flashes associated with menopause.[53][54] Clonidine has also been used to treat refractory diarrhea associated with irritable bowel syndrome, fecal incontinence, diabetes, diarrhea associated with opioid withdrawal, intestinal failure, neuroendocrine tumors, and cholera.[55] Clonidine can be used in the treatment of Tourette syndrome (specifically for tics).[56] Clonidine has also had some success in clinical trials for helping to remove or ameliorate the symptoms of hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD).[57]
Injection of α2 receptor agonists into the knee joint space, including clonidine, may reduce the severity of knee pain after arthroscopic knee surgery.[58]
Light-activated derivatives of clonidine (adrenoswitches) have been developed for research purposes and shown to control pupillary reflex with light in blind mice by topical application.[59]
Clonidine suppression test
The reduction in circulating norepinephrine by clonidine was used in the past as an investigatory test for phaeochromocytoma, which is a catecholamine-synthesizing tumor, usually found in the adrenal medulla.[60] In a clonidine suppression test, plasma catecholamine levels are measured before and 3 hours after a 0.3 mg oral test dose has been given to the patient. A positive test occurs if there is no decrease in plasma levels.[60]
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
It is classified by the TGA of Australia as pregnancy category B3, which means that it has shown some detrimental effects on fetal development in animal studies, although the relevance of this to human beings is unknown.[61] Clonidine appears in high concentration in breast milk; a nursing infant's serum clonidine concentration is approximately 2/3 of the mother's.[62] Caution is warranted in women who are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding.[63]
Adverse effects
The principal adverse effects of clonidine are sedation, dry mouth, and hypotension (low blood pressure).[4]
Very common (>10% frequency):
- Dizziness
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Somnolence (dose-dependent)
- Dry mouth
- Headache (dose-dependent)
- Fatigue
- Skin reactions (if given transdermally)
- Hypotension
Common (1–10% frequency):
- Anxiety
- Constipation
- Sedation (dose-dependent)
- Nausea/vomiting
- Malaise
- Abnormal LFTs
- Rash
- Weight gain/loss
- Pain below the ear (from salivary gland)
- Erectile dysfunction
Uncommon (0.1–1% frequency):
- Delusional perception
- Hallucination
- Nightmare
- Paresthesia
- Sinus bradycardia
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Pruritus
- Urticaria
Rare (<0.1% frequency):
- Gynaecomastia
- Impaired ability to cry
- Atrioventricular block
- Nasal dryness
- Colonic pseudo-obstruction
- Alopecia
- Hyperglycemia
Withdrawal
Because clonidine suppresses sympathetic outflow, resulting in lower blood pressure, sudden discontinuation can result in acute hypertension due to a rebound in sympathetic outflow. In extreme cases, this can result in a hypertensive crisis, which is a medical emergency.[65]
Clonidine therapy should generally be gradually tapered when discontinuing therapy to avoid rebound effects from occurring. Treatment of clonidine withdrawal hypertension depends on the severity of the condition. Reintroduction of clonidine for mild cases, alpha and beta blockers for more urgent situations. Beta blockers never should be used alone to treat clonidine withdrawal as alpha vasoconstriction would still continue.[66][67]
Pharmacology
| Site | Ki (nM) | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| NET | >1,000 | Human | [68] |
| 5-HT1B | >10,000 | Rat | [69] |
| 5-HT2A | >10,000 | Human | [70] |
| α1A | 316.23 | Human | [68] |
| α1B | 316.23 | Human | [68] |
| α1D | 125.89 | Human | [68] |
| α2A | 35.48 - 61.65 | Human | [68][71] |
| α2B | 69.18 - 309.0 | Human | [71][68] |
| α2C | 134.89 - 501.2 | Human | [71][68] |
| D1 | > 10,000 | Rat | [72] |
| I1 | 31.62 | Bovine | [68] |
| I2 (cortex) | >1,000 | Rat | [68] |
| MAO-A | >1,000 | Rat | [68] |
| MAO-B | >1,000 | Rat | [68] |
| σ | >10,000 | Guinea Pig | [73] |
| The Ki refers to a drug's affinity for a receptor. The smaller the Ki, the higher the affinity for that receptor.[74] Reported imidazoline-2 binding is measured in the cortex - I2 receptor bindings measured in stomach membranes are much lower.[75] | |||
Mechanism of action
Clonidine crosses the blood–brain barrier.[6]
High blood pressure
Clonidine treats high blood pressure by stimulating α2 receptors in the brainstem, which decreases peripheral vascular resistance, lowering blood pressure. It has specificity towards the presynaptic α2 receptors in the vasomotor center in the brainstem. This binding has a sympatholytic effect, suppresses release of norepinephrine, ATP, renin, and neuropeptide Y which if released would increase vascular resistance.[9]:201–203
Clonidine also acts as an agonist at imidazoline-1 (I1) receptors in the brain, and it is hypothesized that this effect may contribute to reducing blood pressure by reducing signaling in the sympathetic nervous system; this effect acts upstream of the central α2 agonist effect of clonidine.[9]:201–203[76]
Clonidine may also cause bradycardia, theoretically by increasing signaling through the vagus nerve. When given intravenously, clonidine can temporarily increase blood pressure by stimulating α1 receptors in smooth muscles in blood vessels.[77] This hypertensive effect is not usual when clonidine is given orally or by the transdermal route.[9]:201–203
Plasma concentration of clonidine exceeding 2.0 ng/mL does not provide further blood pressure reduction.[78]
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder

In the setting of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), clonidine's molecular mechanism of action occurs due to its agonism at the α2A adrenergic receptor, the subtype of the adrenergic receptor that is most principally found in the brain. Within the brain, the α2A adrenergic receptors are found within the prefrontal cortex (PFC), among other areas. The α2A adrenergic receptors are found on the presynaptic cleft of a given neuron, and, when activated by an agonist, the effect on downstream neurons is inhibitory. The inhibition is accomplished by preventing the secretion of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. Thus, clonidine's agonism on α2A adrenergic receptors in the PFC inhibits the action of downstream neurons by preventing the secretion of norepinephrine.[79]
This mechanism is similar to the brain's physiological inhibition of PFC neurons by the locus ceruleus (LC), which secretes norepinephrine into the PFC. Although norepinephrine can also bind to target adrenergic receptors on the downstream neuron (otherwise inducing a stimulatory effect), norepinephrine also binds to α2A adrenergic receptors (akin to clonidine's mechanism of action), inhibiting the release of norepinephrine by that neuron and inducing an inhibitory effect. Because the PFC is required for working memory and attention, it is thought that clonidine's inhibition of PFC neurons helps to eliminate irrelevant attention (and subsequent behaviors), improving the person's focus and correcting deficits in attention.[79]
Growth hormone test
Clonidine stimulates release of GHRH hormone from the hypothalamus, which in turn stimulates pituitary release of growth hormone.[80] This effect has been used as part of a "growth hormone test," which can assist with diagnosing growth hormone deficiency in children.[81]
Pharmacokinetics
After being ingested, clonidine is absorbed into the blood stream rapidly with an overall bioavailability around 70–80%.[1] Peak concentrations in human plasma occur within 60–90 minutes for the "Immediate Release" (IR) version of the drug, which is shorter than the "Extended Release" (ER/XR) version.[82] Clonidine is fairly lipid soluble with the logarithm of its partition coefficient (log P) equal to 1.6;[83][82] to compare, the optimal log P to allow a drug that is active in the human central nervous system to penetrate the blood brain barrier is 2.0.[84] Less than half of the absorbed portion of an orally administered dose will be metabolized by the liver into inactive metabolites, with roughly the other half being excreted unchanged by the kidneys.[82] About one-fifth of an oral dose will not be absorbed, and is thus excreted in the feces.[82] Work with liver microsomes shows in the liver clonidine is primarily metabolized by CYP2D6 (66%), CYP1A2 (10–20%), and CYP3A (0–20%) with negligible contributions from the less abundant enzymes CYP3A5, CYP1A1, and CYP3A4.[8] 4-hydroxyclonidine, the main metabolite of clonidine, is also an α2A agonist but is non lipophilic and is not believed to contribute to the effects of clonidine since it does not cross the blood–brain barrier.[85][86]
Measurements of the half-life of clonidine vary widely, between 6 and 23 hours, with the half-life being greatly affected by and prolonged in the setting of poor kidney function.[82] Variations in half-life may be partially attributable to CYP2D6 genetics.[8] Some research has suggested the half-life of clonidine is dose dependent and approximately doubles upon chronic dosing,[87] while other work contradicts this.[3] Following a 0.3 mg oral dose, a small study of five patients by Dollery et al. (1976) found half-lives ranging between 6.3 and 23.4 hours (mean 12.7).[88] A similar N=5 study by Davies et al. (1977) found a narrower range of half-lives, between 6.7 and 13 hours (average 8.6 hours),[1] while an N=8 study by Keraäen et al. that included younger patients found a somewhat shorter average half-life of 7.5 hours.[89]
History
Clonidine was introduced in 1966.[90] It was first used as a hypertension treatment under the trade name of Catapres.[91]
Society and culture
Brand names
As of June 2017, clonidine was marketed under many brand names worldwide: Arkamin, Aruclonin, Atensina, Catapin, Catapres, Catapresan, Catapressan, Chianda, Chlofazoline, Chlophazolin, Clonid-Ophtal, Clonidin, Clonidina, Clonidinã, Clonidine, Clonidine hydrochloride, Clonidinhydrochlorid, Clonidini, Clonidinum, Clonigen, Clonistada, Clonnirit, Clophelinum, Dixarit, Duraclon, Edolglau, Haemiton, Hypodine, Hypolax, Iporel, Isoglaucon, Jenloga, Kapvay, Klofelino, Kochaniin, Lonid, Melzin, Menograine, Normopresan, Paracefan, Pinsanidine, Run Rui, and Winpress.[92] It was marketed as a combination drug with chlortalidone as Arkamin-H, Bemplas, Catapres-DIU, and Clorpres, and in combination with bendroflumethiazide as Pertenso.[92]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships of intervenous and oral clonidine". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 21 (5): 593–601. May 1977. doi:10.1002/cpt1977215593. PMID 870272.
- ↑ "Catapres- clonidine hydrochloride tablet". 6 September 2016. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d7f569dc-6bed-42dc-9bec-940a9e6b090d. "The pharmacokinetics of clonidine is dose-proportional in the range of 100 to 600 µg.The absolute bioavailability of clonidine on oral administration is 70% to 80%. Peak plasma clonidine levels are attained in approximately 1 to 3 hours."
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Clinical pharmacokinetics of clonidine". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 14 (5): 287–310. May 1988. doi:10.2165/00003088-198814050-00002. PMID 3293868.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "clonidine (Rx) - Catapres, Catapres-TTS, more..". Medscape Reference. WebMD. http://reference.medscape.com/drug/catapres-tts-clonidine-342382.
- ↑ "Catapres- clonidine hydrochloride tablet". 6 September 2016. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d7f569dc-6bed-42dc-9bec-940a9e6b090d. "Catapres tablets act relatively rapidly. The patient’s blood pressure declines within 30 to 60 minutes after an oral dose, the maximum decrease occurring within 2 to 4 hours."
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Catapres- clonidine hydrochloride tablet". 6 September 2016. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d7f569dc-6bed-42dc-9bec-940a9e6b090d. "Following intravenous administration, clonidine displays biphasic disposition with a distribution half-life of about 20 minutes and an elimination half-life ranging from 12 to 16 hours. The half-life increases up to 41 hours in patients with severe impairment of renal function. Clonidine crosses the placental barrier. It has been shown to cross the blood–brain barrier in rats."
- ↑ "Kapvay". http://www.rxlist.com/kapvay-drug/clinical-pharmacology.htm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "CYP2D6 mediates 4-hydroxylation of clonidine in vitro: implication for pregnancy-induced changes in clonidine clearance". Drug Metabolism and Disposition 38 (9): 1393–1396. September 2010. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.033878. PMID 20570945.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "Chapter 12:Adrenergic Agonists and Antagonists" (in en). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (13th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education / Medical. 2017. ISBN 9781259584732.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 "Clonidine Monograph for Professionals" (in en). American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/clonidine.html.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 144. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ "Clonidine: clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use in pain management". Current Clinical Pharmacology 6 (4): 280–287. November 2011. doi:10.2174/157488411798375886. PMID 21827389.
- ↑ "A historical perspective: development of clonidine". Best Practice & Research Clinical Anaesthesiology 14 (2): 237–246. June 2000. doi:10.1053/bean.2000.0079.
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 550. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA550. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Clonidine - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Clonidine.
- ↑ "Hypertension Update: Resistant Hypertension". FP Essent 469: 20–25. June 2018. PMID 29863319.
- ↑ "CATAPRES- clonidine hydrochloride tablet". 6 September 2016. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d7f569dc-6bed-42dc-9bec-940a9e6b090d. "Slowing of the pulse rate has been observed in most patients given clonidine, but the drug does not alter normal hemodynamic response to exercise. Other studies in patients have provided evidence of a reduction in plasma renin activity and in the excretion of aldosterone and catecholamines."
- ↑ "A meta-analysis of clonidine for symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 38 (12): 1551–1559. December 1999. doi:10.1097/00004583-199912000-00017. PMID 10596256.
- ↑ Rossi, S, ed (2013). Australian Medicines Handbook (2013 ed.). Adelaide: The Australian Medicines Handbook Unit Trust. ISBN 978-0-9805790-9-3.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Clonidine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: I. Efficacy and tolerability outcomes". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 47 (2): 180–188. February 2008. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31815d9af7. PMID 18182963.
- ↑ "Clonidine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: II. ECG changes and adverse events analysis". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 47 (2): 189–198. February 2008. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31815d9ae4. PMID 18182964.
- ↑ "Effects of FDA advisories on the pharmacologic treatment of ADHD, 2004-2008". Psychiatric Services 64 (4): 339–346. April 2013. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201200147. PMID 23318985.
- ↑ "Clonidine extended-release tablets as add-on therapy to psychostimulants in children and adolescents with ADHD". Pediatrics 127 (6): e1406–e1413. June 2011. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1260. PMID 21555501.
- ↑ "Guanfacine, but not clonidine, improves planning and working memory performance in humans". Neuropsychopharmacology 20 (5): 460–470. May 1999. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00127-4. PMID 10192826.
- ↑ "Clonidine and Guanfacine IR vs ER: Old Drugs With "New" Formulations". Mental Health Clinician 4: 22–26. 2014. doi:10.9740/mhc.n186955. http://cpnp.org/resource/mhc/2014/01/clonidine-and-guanfacine-ir-vs-er-old-drugs-new-formulations. Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "A review of the use of clonidine as a sleep aid in the child and adolescent population". Clinical Pediatrics 53 (3): 211–216. March 2014. doi:10.1177/0009922813502123. PMID 24027233.
- ↑ "Assessment and treatment of disturbed sleep in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 4 (2): 307–316. March 2004. doi:10.1586/14737175.4.2.307. PMID 15853572.
- ↑ "Pharmacological Treatment of Attention-Deficit/HyperactivityDisorder". Handbook of Disruptive Behavior Disorders. Springer US. 1999. pp. 221–254. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-4881-2_10. ISBN 978-1-4613-7214-1.
- ↑ "Clonidine for sleep disturbances associated with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 33 (3): 424–426. 1994. doi:10.1097/00004583-199403000-00018. PMID 8169189.
- ↑ Clemow, DB; Walker, DJ (September 2014). "The potential for misuse and abuse of medications in ADHD: a review.". Postgraduate Medicine 126 (5): 64–81. doi:10.3810/pgm.2014.09.2801. PMID 25295651.
- ↑ "Elevated Norepinephrine may be a Unifying Etiological Factor in the Abuse of a Broad Range of Substances: Alcohol, Nicotine, Marijuana, Heroin, Cocaine, and Caffeine". Substance Abuse 7: 171–183. October 2013. doi:10.4137/SART.S13019. PMID 24151426.
- ↑ Drugs of Abuse (2nd ed.). Los Angeles: Practice Management Information. 1997.
- ↑ "Clonidine for smoking cessation". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008 (3): CD000058. 2004. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000058.pub2. PMID 15266422.
- ↑ "Role of Clonidine in Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: A Systematic Review". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 50 (4): 301–310. April 2016. doi:10.1177/1060028015626438. PMID 26783353.
- ↑ "Pharmacological Treatments for Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis". JAMA Pediatrics 173 (3): 234–243. March 2019. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.5044. PMID 30667476.
- ↑ "Two cases of acute dexmedetomidine withdrawal syndrome following prolonged infusion in the intensive care unit: Report of cases and review of the literature". Human & Experimental Toxicology 32 (1): 107–110. January 2013. doi:10.1177/0960327112454896. PMID 23111887.
- ↑ "A Review of Spasticity Treatments: Pharmacological and Interventional Approaches". Critical Reviews in Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 25 (1–2): 11–22. 2013. doi:10.1615/CritRevPhysRehabilMed.2013007945. PMID 25750484.
- ↑ "The drug treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder". Journal of Affective Disorders 13 (2): 203–213. September–October 1987. doi:10.1016/0165-0327(87)90024-3. PMID 2960712.
- ↑ "Pharmacotherapy for post-traumatic stress disorder". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America 17 (2): 409–423. June 1994. doi:10.1016/S0193-953X(18)30122-9. PMID 7937367.
- ↑ "Role of norepinephrine in the pathophysiology and treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder". Biological Psychiatry 46 (9): 1192–1204. November 1999. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00219-X. PMID 10560025.
- ↑ "Noradrenergic dysfunction and the psychopharmacology of posttraumatic stress disorder". Depression and Anxiety 25 (3): 260–271. 2008. doi:10.1002/da.20292. PMID 17354267.
- ↑ "Pharmacologic reduction of CNS noradrenergic activity in PTSD: the case for clonidine and prazosin". Journal of Psychiatric Practice 13 (2): 72–78. March 2007. doi:10.1097/01.pra.0000265763.79753.c1. PMID 17414682.
- ↑ "Neuropsychiatric consequences of cardiovascular medications". Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 9 (1): 29–45. 2007. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2007.9.1/jchuffman. PMID 17506224.
- ↑ "Post-traumatic stress disorder and its treatment in children and adolescents". Current Psychiatry Reports 10 (2): 104–108. April 2008. doi:10.1007/s11920-008-0019-0. PMID 18474199.
- ↑ "Clonidine improves hyperarousal in borderline personality disorder with or without comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 29 (2): 170–173. April 2009. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e31819a4bae. PMID 19512980.
- ↑ "A comparison of oral clonidine and oral midazolam as preanesthetic medications in the pediatric tonsillectomy patient". Anesthesia and Analgesia 92 (1): 56–61. January 2001. doi:10.1097/00000539-200101000-00011. PMID 11133600.
- ↑ "Clonidine in mania". Drug Development Research 3 (1): 101–105. 1983. doi:10.1002/ddr.430030112.
- ↑ "Epidural clonidine: a review of its pharmacology and efficacy in the management of pain during labour and postoperative and intractable pain". CNS Drugs 6 (6): 474–497. 1996. doi:10.2165/00023210-199606060-00007.
- ↑ "Treatment and Management of RLS". WebMD LLC. https://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/522010_6.
- ↑ "Rosacea: a common, yet commonly overlooked, condition". American Family Physician 66 (3): 435–440. August 2002. PMID 12182520. http://www.aafp.org/afp/2002/0801/p435.html. Retrieved 12 February 2012.
- ↑ "Randomized control trial of topical clonidine for treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy". Pain 153 (9): 1815–1823. September 2012. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2012.04.014. PMID 22683276.
- ↑ "Clonidine Oral Uses". WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/drugs/drug-11754-Clonidine.aspx?drugid=11754&drugname=Clonidine.
- ↑ "Clonidine". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/clonidine.html.
- ↑ "What about clonidine for diarrhoea? A systematic review and meta-analysis of its effect in humans". Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology 9 (3): 282–301. May 2016. doi:10.1177/1756283X15625586. PMID 27134659.
- ↑ "Current pharmacotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of Tourette syndrome". Drugs of Today 50 (2): 159–179. February 2014. doi:10.1358/dot.2014.50.2.2097801. PMID 24619591.
- ↑ "Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder: Etiology, Clinical Features, and Therapeutic Perspectives". Brain Sciences 8 (3): 47. March 2018. doi:10.3390/brainsci8030047. PMID 29547576.
- ↑ "Intra-articular Alpha-2 Agonists as an Adjunct to Local Anesthetic in Knee Arthroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". J Knee Surg 32 (2): 138–145. February 2019. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1636909. PMID 29534270.
- ↑ Prischich, Davia; Gomila, Alexandre M. J.; Milla-Navarro, Santiago; Sangüesa, Gemma; Diez-Alarcia, Rebeca; Preda, Beatrice; Matera, Carlo; Batlle, Montserrat et al. (2020-12-21). "Adrenergic Modulation With Photochromic Ligands". Angewandte Chemie International Edition (Wiley) 60 (7): 3625–3631. doi:10.1002/anie.202010553. ISSN 1433-7851. PMID 33103317.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 "Biochemical diagnosis of pheochromocytoma: how to distinguish true- from false-positive test results". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 88 (6): 2656–2666. June 2003. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-030005. PMID 12788870.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 "CATAPRES® 150 TABLETS CATAPRES® AMPOULES" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Boehringer Ingelheim Pty Limited. 28 February 2013. https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-02400-3.
- ↑ "Clonidine". Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). National Library of Medicine (US). 2006. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501628/. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- ↑ "Clonidine". Prescription Marketed Drugs. www.drugsdb.eu. http://drugsdb.eu/drug.php?d=Clonidine&m=Physicians%20Total%20Care,%20Inc.&id=b65742b7-5db5-41cf-bf69-41700cdd2c59.xml.
- ↑ "Clonidine 25 mcg Tablets BP - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Sandoz Limited. 2 August 2012. http://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/21711/SPC/Clonidine+25mcg+Tablets+BP/.
- ↑ Brayfield, A, ed (13 January 2014). "Clonidine". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. http://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/martindale/current/ms-11308-l.htm.
- ↑ Goodman & Gilman's - the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. New York: McGraw-Hill. 2006. pp. 854–855. ISBN 978-0-07-142280-2. https://archive.org/details/goodmangilmansph00brun_116.
- ↑ "Understanding the Risk of Using Medications for ADHD with Respect to Physical Growth and Cardiovascular Function". Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 17 (2): 459–474, xi. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2007.11.010. PMID 18295156.
- ↑ 68.00 68.01 68.02 68.03 68.04 68.05 68.06 68.07 68.08 68.09 68.10 "S18616, a highly potent, spiroimidazoline agonist at alpha(2)-adrenoceptors: I. Receptor profile, antinociceptive and hypothermic actions in comparison with dexmedetomidine and clonidine". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 295 (3): 1192–1205. December 2000. PMID 11082457.
- ↑ "Characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors in rat spinal cord via [125I]iodocyanopindolol binding and inhibition of [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine release". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 260 (2): 614–626. February 1992. PMID 1738111.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedPDSP - ↑ 71.0 71.1 71.2 "Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant alpha2 adrenergic receptors: agonist-mediated [35S]GTPgammaS binding". Biochemical Pharmacology 55 (7): 1035–1043. April 1998. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(97)00631-x. PMID 9605427.
- ↑ "Sodium-dependent isomerization of dopamine D-2 receptors characterized using [125I]epidepride, a high-affinity substituted benzamide ligand". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 252 (3): 1108–1116. March 1990. PMID 2138666.
- ↑ "1,3-Di(2-[5-3Htolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs"]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 83 (22): 8784–8788. November 1986. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. PMID 2877462. Bibcode: 1986PNAS...83.8784W.
- ↑ "Ligand-Receptor Binding and Tissue Response" (in en). Pharmacology. Elsevier. 2009. p. 65. ISBN 9780123695215. https://archive.org/details/pharmacologyprim00kena_186.
- ↑ "Characterization of I2 imidazoline and sigma binding sites in the rat and human stomach". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 285 (1): 170–177. April 1998. PMID 9536007.
- ↑ "The imidazoline receptor in control of blood pressure by clonidine and drugs". American Journal of Physiology 273 (5): R1569–R1571. 1997. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.1997.273.5.R1569. PMID 9374795.
- ↑ "Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: a review of current clinical applications" (in en-US). Anesthesia Progress 62 (1): 31–39. 2015. doi:10.2344/0003-3006-62.1.31. PMID 25849473.
- ↑ "CATAPRES- clonidine hydrochloride tablet". 6 September 2016. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d7f569dc-6bed-42dc-9bec-940a9e6b090d. "The antihypertensive effect is reached at plasma concentrations between about 0.2 and 2.0 ng/mL in patients with normal excretory function. A further rise in the plasma levels will not enhance the antihypertensive effect."
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 79.2 "Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Current Psychiatry Reports 12 (5): 366–373. October 2010. doi:10.1007/s11920-010-0136-4. PMID 20652773.
- ↑ "Growth hormone-releasing hormone: clinical studies and therapeutic aspects". Neuroendocrinology 53 (Suppl 1): 37–40. 1991. doi:10.1159/000125793. PMID 1901390.
- ↑ "Growth Hormone Test" (in en). Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/g/growth-hormone.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 82.4 "alpha-2 and imidazoline receptor agonists. Their pharmacology and therapeutic role". Anaesthesia 54 (2): 146–165. February 1999. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2044.1999.00659.x. PMID 10215710.
- ↑ Foye's principles of medicinal chemistry (6th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2008. p. 403. ISBN 9780781768795. https://archive.org/details/foyesprinciplesm00lemk.
- ↑ "Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs". NeuroRx 2 (4): 541–553. October 2005. doi:10.1602/neurorx.2.4.541. PMID 16489364.
- ↑ "Antinociceptive activity of clonidine in the mouse, rat and dog". Life Sciences 31 (11): 1123–1132. September 1982. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(82)90086-8. PMID 6128647.
- ↑ "Alpha adrenoceptor modulation of the jaw-opening reflex". Neuropharmacology 26 (7A): 649–655. July 1987. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(87)90224-3. PMID 2819761.
- ↑ "Clonidine kinetics in man--evidence for dose dependency and changed pharmacokinetics during chronic therapy". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 12 (5): 653–658. November 1981. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01284.x. PMID 7332729.
- ↑ "Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of clonidine". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 19 (1): 11–17. January 1976. doi:10.1002/cpt197619111. PMID 1245090.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and side-effects of clonidine". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 13 (2): 97–101. May 1978. doi:10.1007/BF00609752. PMID 658114.
- ↑ "A historical perspective: development of clonidine". Best Practice & Research Clinical Anaesthesiology 14 (2): 237–246. June 2000. doi:10.1053/bean.2000.0079.
- ↑ "Clonidine: Drug Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - Drugs.com" (in en-US). Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/clonidine.html.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Clonidine brand names". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/international/clonidine.html.
External links
- Alpha-2 agonists in ADHD
 |


