Chemistry:Safranal
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
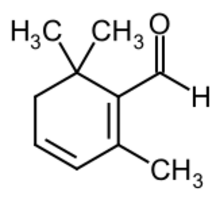
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6,6-Trimethylcyclohexa-1,3-diene-1-carbaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.21 g/mol |
| Density | 0.9734 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 70 °C (158 °F; 343 K) at 1 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Safranal is an organic compound isolated from saffron, the spice consisting of the stigmas of crocus flowers (Crocus sativus). It is the constituent primarily responsible for the aroma of saffron.
It is believed that safranal is a degradation product of the carotenoid zeaxanthin via the intermediate picrocrocin.
Pharmacology
Safranal is an effective anticonvulsant in animal models, shown to act as an agonist at GABAA receptors.[1][2] Safranal also exhibits high antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity,[3][4] along with cytotoxicity towards cancer cells in vitro.[5] One of its anticancer mechanisms of action involves disruption of the normal assembly dynamics of cellular microtubules.[6] It has also been shown to have antidepressant properties in animals and pilot studies in humans.[7][8]
Natural sources
Natural sources of safranal include:Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
- Centaurea sibthorpii [9]
- Centaurea amanicola[9]
- Centaurea consanguinea[9]
- Erodium cicutarium (common stork's-bill or pinweed)[9]
- Calycopteris floribunda (Ukshi)[9]
- Sambucus nigra (elderberry)[9]
- Citrus limon (lemon)[9]
- Achillea distans [9]
References
- ↑ Hosseinzadeh H; Talebzadeh F (December 2005). "Anticonvulsant evaluation of safranal and crocin from Crocus sativus in mice". Fitoterapia 76 (7–8): 722–4. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2005.07.008. PMID 16253437.
- ↑ Hosseinzadeh H; Sadeghnia HR (April 2007). "Protective effect of safranal on pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in the rat: involvement of GABAergic and opioids systems". Phytomedicine 14 (4): 256–62. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2006.03.007. PMID 16707256.
- ↑ Hosseinzadeh H; Sadeghnia HR (2005). "Safranal, a constituent of Crocus sativus (saffron), attenuated cerebral ischemia induced oxidative damage in rat hippocampus". Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 8 (3): 394–9. PMID 16401389. https://www.ualberta.ca/~csps/JPPS8(3)/H.Hosseinzadeh2/safranal.htm.
- ↑ Assimopoulou AN; Sinakos Z; Papageorgiou VP (November 2005). "Radical scavenging activity of Crocus sativus L. extract and its bioactive constituents". Phytotherapy Research 19 (11): 997–1000. doi:10.1002/ptr.1749. PMID 16317646.
- ↑ Escribano J; Alonso GL; Coca-Prados M; Fernandez JA (February 1996). "Crocin, safranal and picrocrocin from saffron (Crocus sativus L.) inhibit the growth of human cancer cells in vitro". Cancer Letters 100 (1–2): 23–30. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(95)04067-6. PMID 8620447.
- ↑ Cheriyamundath S, Choudhary S, and Lopus M (2017) Safranal inhibits HeLa cell viability by perturbing the reassembly potential of microtubules. Phytother Res, 32, 170-173. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5938. PMID 29024138
- ↑ Hosseinzadeh H; Karimi G; Niapoor M (2004). "Antidepressant effect of Crocus sativus L. stigma extracts and their constituents, crocin and safranal, in mice". Acta Horticulturae 650 (650): 435–45. doi:10.17660/ActaHortic.2004.650.54. http://www.actahort.org/books/650/650_54.htm.
- ↑ Akhondzadeh S; Fallah-Pour H; Afkham K; Jamshidi AH; Khalighi-Cigaroudi F (September 2004). "Comparison of Crocus sativus L. and imipramine in the treatment of mild to moderate depression: A pilot double-blind randomized trial ISRCTN45683816". BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 4: 12. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-4-12. PMID 15341662.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Ramin Rezaee; Hossein Hosseinzadeh (January 2013). "[Safranal: From an Aromatic Natural Product to a Rewarding Pharmacological Agent"]. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 16 (1): 12–26. PMID 23638289.
 |

