Chemistry:Eterobarb
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
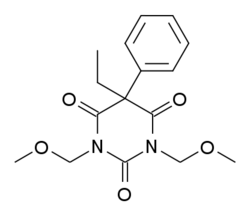
| Formula | C16H20N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 320.345 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Eterobarb (Antilon) is a barbiturate derivative. It has mainly anticonvulsant action with less sedative effects than the closely related compound phenobarbital. It saw reasonable success in clinical trials, but is not in widespread medical use.[1][2]
Synthesis
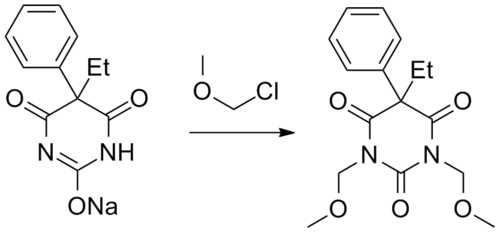
Eterobarb can be synthesized by reacting phenobarbital with chloromethyl methyl ether in presence of a base.[3]
References
- ↑ "Clinical evaluation of eterobarb, a new anticonvulsant drug". Neurology 25 (5): 399–404. May 1975. doi:10.1212/wnl.25.5.399. PMID 1094318.
- ↑ "A comparison of the toxicity effects of the anticonvulsant eterobarb (antilon, DMMP) and phenobarbital in normal human volunteers". Epilepsia 27 (2): 149–55. 1986. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03518.x. PMID 3956454.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsants. 2. Acyloxymethyl and halomethyl derivatives of barbituric acid and diphenylhydantoin". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 14 (3): 187–9. March 1971. doi:10.1021/jm00285a002. PMID 5552206.
| GABAergics |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel modulators |
| ||||||
| Others |
| ||||||
| |||||||
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
 | 0.00      (0 votes) (0 votes) |
