Chemistry:Teflurane
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
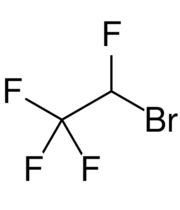
| Formula | C2HBrF4 |
| Molar mass | 180.928 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Teflurane (INN, USAN, code name Abbott 16900) is a halocarbon drug which was investigated as an inhalational anesthetic but was never marketed.[1][2] Its clinical development was terminated due to a high incidence of cardiac arrhythmias in patients, similarly to the cases of halopropane and norflurane.[3]
Chemistry
Teflurane is 2-bromo-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, a haloalkane. It is a gas at standard conditions.[4] The compound is chiral.
See also
References
- ↑ A glossary of anesthesia and related terminology. Springer-Verlag. 1993. ISBN 978-0-387-97831-4. https://archive.org/details/glossaryofanesth0000klei.
- ↑ Practical anesthesiology. Mosby. 1962. ISBN 9780608393322. https://books.google.com/books?id=hGtsAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Anesthesia, The Heart and the Vascular System: Annual Utah Postgraduate Course in Anesthesiology 1987. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 185–. ISBN 978-94-009-3295-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=s3OhBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT185.
- ↑ "2-Bromo-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane". Chem Spider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.21235115.html.
 |
