Chemistry:CGS-20625
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 41% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
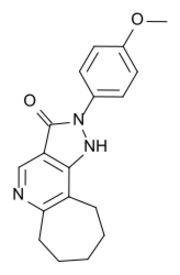
| Formula | C18H19N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 309.369 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
CGS-20625 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs,[1] but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.[2][3] It produces anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects, but with no sedative effects even at high doses, and no significant muscle relaxant effects.[4] It is orally active in humans, but with relatively low bioavailability.[5]
CGS-20625 is a positive allosteric modulator at several GABAA receptors types. Due to its alicyclic moiety potency at γ1 subunit, containing receptor types is more pronounced for CGS-20625 compared to benzodiazepines.[1] γ1 subunits are expressed at higher levels in the central amygdala.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Pharmacological properties of GABAA receptors containing gamma1 subunits". Mol. Pharmacol. 69 (2): 640–9. Feb 2006. doi:10.1124/mol.105.017236. PMID 16272224. https://phaidra.univie.ac.at/o:244857.
- ↑ Bennett DA (1987). "Pharmacology of the pyrazolo-type compounds: agonist, antagonist and inverse agonist actions". Physiol. Behav. 41 (3): 241–5. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(87)90360-X. PMID 2893398.
- ↑ "Determination of a potential anxiolytic drug (CGS 20625) in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography". J. Chromatogr. 568 (2): 487–93. Aug 1991. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(91)80188-I. PMID 1686029.
- ↑ "CGS 20625, a novel pyrazolopyridine anxiolytic". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248 (1): 89–96. Jan 1989. PMID 2563294. http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=2563294.
- ↑ "Oral absorption of CGS-20625, an insoluble drug, in dogs and man". J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 23 (1): 11–23. Feb 1995. doi:10.1007/BF02353783. PMID 8576841.
- ↑ "GABAA receptors containing gamma1 subunits contribute to inhibitory transmission in the central amygdala". J. Neurophysiol. 101 (1): 341–9. January 2009. doi:10.1152/jn.90991.2008. PMID 19004994.
 |
