Chemistry:Carbromal
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Bromo-N-carbamoyl-2-ethylbutanamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | carbromal |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
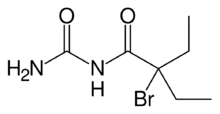
| C7H13BrN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 237.097 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 1.544 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 119 °C (246 °F; 392 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, ether, acetone, benzene |
| log P | 1.623 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.69 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.31 |
| Structure | |
| rhombic | |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | N05CM04 (WHO) |
| Related compounds | |
Related ureas
|
Bromisoval |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Carbromal is a hypnotic/sedative originally synthesized in 1909 by Bayer and subsequently marketed as Adalin.[1][2] The drug was later sold by Parke-Davis in combination with pentobarbital, under the name Carbrital.[3]
Synthesis
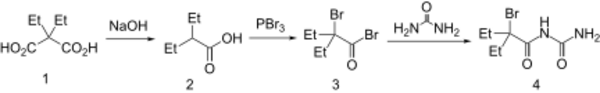
Diethylmalonic acid [510-20-3] (1) is decarboxylated to 2-ethylvaleric acid [20225-24-5] (2). The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction converts this to 2-Bromo-2-Ethylbutyryl Bromide [26074-53-3] (3). Reaction with urea with affords carbromal (4).
See also
References
- ↑ "A purpuric drug eruption caused by carbromal". British Medical Journal 1 (4914): 645–6. March 1955. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4914.645. PMID 13230580.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Verfahren dur Darstellung von Bromodiäthylacetylharnstoff [Method for the preparation of bromodiethylacetylurea]" DE patent 22571, published 1910-09-17
- ↑ Physicians' Desk Reference. (33 ed.). Oradell, N.J.: Medical Economics Co. 1979. pp. 1266. ISBN 0-87489-999-0. OCLC 4636066. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/4636066.
- ↑ Frdl. 10, 1160
- ↑ Chem. Zentralbl. 1910, II, 1008.
- ↑ Grundriss der modernen Arzneistoff-Synthese. Stuttgart: Verlag Ferd. Enke. 1931.
- ↑ H. P. Kaufmann, Arzneimittel-Synthese (Berlin, 1953).
 |

