Chemistry:Fominoben
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
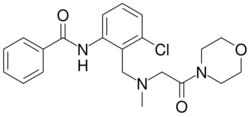 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Broncomenal, Deronyl, Finaten, Noleptan, Oleptan, Terion, Tosifar, Tussirama[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H24ClN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 401.89 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fominoben is an antitussive agent of the benzanilide class, formerly marketed under the name Noleptan.[2] It binds poorly to the sigma-1 receptor, a receptor activated by many other antitussives.[3] It is reported to have respiratory stimulant activity.[4] Other research has indicated it may be an agonist at the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.[5] It was introduced in Germany in 1973, in Italy in 1979, and in Japan in 1983.[6]
Adverse effects include appetite suppression, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, irritability, and hallucinations. Rarer side effects include somnolence, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, and urticaria.[7]
References
- ↑ Swiss Pharmaceutial Society, ed (January 2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. pp. 470. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA261.
- ↑ "FOMINOBEN". https://drugs.ncats.io/drug/TJ2KK6NYJS.
- ↑ "Dextromethorphan binding sites in the guinea pig brain". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 8 (2): 149–56. June 1988. doi:10.1007/BF00711241. PMID 3044591.
- ↑ "Effects of the antitussive fominoben (PB89) on hypoxia in chronic obstructive lung disease: comparison with dextromethorphan using a double-blind method". The Journal of International Medical Research 13 (2): 96–101. 1985. doi:10.1177/030006058501300204. PMID 3158563.
- ↑ "Anxiolytic-like properties of fominoben". European Journal of Pharmacology 97 (3–4): 277–81. January 1984. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(84)90460-6. PMID 6142823.
- ↑ William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Elsevier. pp. 1705–7. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=_J2ti4EkYpkC&pg=PA1103.
- ↑ Martín, Alfonso Velasco (2004). "Tratamiento sintomático de la tos y del resfriado común". Farmacología clínica y terapéutica médica. McGraw-Hill/Interamericana. p. 260. ISBN 9788448604271.
 |

