(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Short description: Chemical compound
Cyclopentobarbital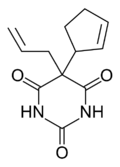 |
| Clinical data |
|---|
| Other names | Allylpental, Cyclopental, 5-Allyl-5-Δ2-Cyclopentenyl Barbituric Acid |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
| Legal status |
|---|
| Legal status |
|
|---|
| Identifiers |
|---|
5-(1-cyclopent-2-enyl)-5-prop-2-enyl-1,3-
diazinane-2,4,6-trione
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| Chemical and physical data |
|---|
| Formula | C12H14N2O3 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 234.255 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1(C2/C=C\CC2)C\C=C
|
InChI=1S/C12H14N2O3/c1-2-7-12(8-5-3-4-6-8)9(15)13-11(17)14-10(12)16/h2-3,5,8H,1,4,6-7H2,(H2,13,14,15,16,17)  Y YKey:XOVJAYNMQDTIJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y
|
| (verify) |
Cyclopentobarbital sodium (Cyclopal, Dormisan) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s.[1] It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine.[2] Cyclopal is considered similar in effects to phenobarbital but lasts almost three times as long, and is considered a long-acting barbiturate with a fairly slow onset of action.
See also
References
- ↑ "Psychopharmacological agents.". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. December 2000. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1619250313011820.a01. ISBN 0471238961.
- ↑ "A Pharmacologic Study of 5-Allyl-5-Cyclopentenyl Barbituric Acid (Cyclopal).". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 80 (2): 119–125. 1944.
|
|---|
| Alcohols | |
|---|
| Barbiturates | |
|---|
| Benzodiazepines | |
|---|
| Carbamates | |
|---|
| Flavonoids | |
|---|
| Imidazoles | |
|---|
| Kava constituents | |
|---|
| Monoureides | |
|---|
| Neuroactive steroids | |
|---|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
|---|
| Phenols | |
|---|
| Piperidinediones | |
|---|
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
|---|
| Quinazolinones | |
|---|
| Volatiles/gases | |
|---|
| Others/unsorted |
- 3-Hydroxybutanal
- α-EMTBL
- AA-29504
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide, potassium bromide, sodium bromide)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- DEABL
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine, dihydroergosine, dihydroergotamine, ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- DS2
- Efavirenz
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid, mefenamic acid, niflumic acid, tolfenamic acid)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Hopantenic acid
- Lanthanum
- Lavender oil
- Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol, honokiol, magnolol, obovatol)
- Loreclezole
- Menthyl isovalerate (validolum)
- Monastrol
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Org 25,435
- Phenytoin
- Propanidid
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- Safranal
- Seproxetine
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal), tetronal, trional)
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid, isovaleramide, valerenic acid, valerenol)
|
|---|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclopentobarbital. Read more |



