(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
O-Desmethylangolensin
|
| Names
|
| IUPAC name
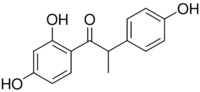
1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanone
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ChEBI
|
|
| ChemSpider
|
|
| KEGG
|
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
InChI=1S/C15H14O4/c1-9(10-2-4-11(16)5-3-10)15(19)13-7-6-12(17)8-14(13)18/h2-9,16-18H,1H3 Key: JDJPNKPFDDUBFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
CC(c1ccc(cc1)O)C(=O)c2ccc(cc2O)O
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C15H14O4
|
| Molar mass
|
258.273 g·mol−1
|
| Hazards
|
| GHS pictograms
|
  
|
| GHS Signal word
|
Danger
|
|
|
H302, H318, H410
|
|
|
P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+312, P305+351+338, P310, P330, P391, P501
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
| Infobox references
|
|
|
|
Tracking categories (test):
O-Desmethylangolensin (O-DMA) is a phytoestrogen. It is an intestinal bacterial metabolite of the soy phytoestrogen daidzein.[1] It produced in some people, deemed O-DMA producers, but not others.[1] O-DMA producers were associated with 69% greater mammographic density and 6% bone density.[1]
See also
References
|
|---|
| ER | | Agonists |
- Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
- Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
- Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estromustine
- Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
- Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
- Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
- Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
- Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, [[Chemistry:Epicateepicatechin, Chemistry:Equol|equol]], formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, Genistein|genistein]], genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, Chemistry:Liquiritigenin
|
|---|
Mixed
(SERMs) | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|---|
|
|---|
| GPER | |
|---|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/O-Desmethylangolensin. Read more |






