(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Short description: Chemical compound
Irazepine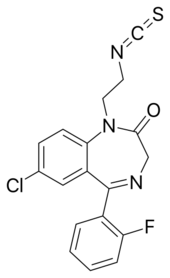 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-isothiocyanatoethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| Chemical and physical data |
|---|
| Formula | C18H13ClFN3OS |
|---|
| Molar mass | 373.83 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
C1C(=O)N(C2=C(C=C(C=C2)Cl)C(=N1)C3=CC=CC=C3F)CCN=C=S
|
InChI=1S/C18H13ClFN3OS/c19-12-5-6-16-14(9-12)18(13-3-1-2-4-15(13)20)22-10-17(24)23(16)8-7-21-11-25/h1-6,9H,7-8,10H2 Key:LTKSVYFAUMFQML-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
 N N Y (what is this?) Y (what is this?) |
Irazepine (Ro 7-1986/1) is a benzodiazepine derivative containing isothiocyanate functional group.[1] It is a non-competitive benzodiazepine binding site antagonist.[2] Irazepine and other alkylating benzodiazepines, such as kenazepine, bind to brain benzodiazepine receptors in a non-competitive (covalent) fashion in vitro, and may exert a long-lasting anticonvulsant effect.[3]
References
- ↑ Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. (1st ed.). London: Chapman & Hall. 1999. ISBN 9780412466304.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents Properties and Synonyms. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. 1999. p. 156. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ "In vivo effects of two novel alkylating benzodiazepines, irazepine and kenazepine". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 14 (4): 487–91. April 1981. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(81)90307-5. PMID 7232472.
|
|---|
| Alcohols | |
|---|
| Barbiturates | |
|---|
| Benzodiazepines | |
|---|
| Carbamates | |
|---|
| Flavonoids | |
|---|
| Imidazoles | |
|---|
| Kava constituents | |
|---|
| Monoureides | |
|---|
| Neuroactive steroids | |
|---|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
|---|
| Phenols | |
|---|
| Piperidinediones | |
|---|
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
|---|
| Quinazolinones | |
|---|
| Volatiles/gases | |
|---|
| Others/unsorted |
- 3-Hydroxybutanal
- α-EMTBL
- AA-29504
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide, potassium bromide, sodium bromide)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- DEABL
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine, dihydroergosine, dihydroergotamine, ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- DS2
- Efavirenz
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid, mefenamic acid, niflumic acid, tolfenamic acid)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Hopantenic acid
- Lanthanum
- Lavender oil
- Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol, honokiol, magnolol, obovatol)
- Loreclezole
- Menthyl isovalerate (validolum)
- Monastrol
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Org 25,435
- Phenytoin
- Propanidid
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- Safranal
- Seproxetine
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal), tetronal, trional)
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid, isovaleramide, valerenic acid, valerenol)
|
|---|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irazepine. Read more |



