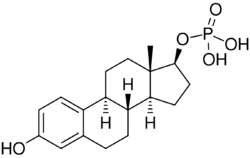
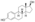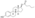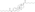Chemistry:Estradiol phosphate
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Estradiol 17β-phosphate; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate); 3-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17β-yl phosphate |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H25O5P |
| Molar mass | 352.367 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Estradiol phosphate, or estradiol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estradiol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estradiol in the body.[1][2] It is rapidly cleaved by phosphatase enzymes into estradiol upon administration.[1][2] Estradiol phosphate is contained within the chemical structures of two other estradiol esters, polyestradiol phosphate (a polymer of estradiol phosphate) and estramustine phosphate (estradiol 3-normustine 17β-phosphate), both of which have been marketed for the treatment of prostate cancer.[2][3][1]
| Estrogen | Structure | Ester(s) | Relative mol. weight |
Relative E2 contentb |
logPc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position(s) | Moiet(ies) | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Estradiol | – | – | – | – | 1.00 | 1.00 | 4.0 | ||
| Estradiol acetate | C3 | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.15 | 0.87 | 4.2 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | C3 | Benzenecarboxylic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~4–5) | 1.38 | 0.72 | 4.7 | ||
| Estradiol dipropionate | C3, C17β | Propanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 (×2) | 1.41 | 0.71 | 4.9 | ||
| Estradiol valerate | C17β | Pentanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 5 | 1.31 | 0.76 | 5.6–6.3 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate butyrate | C3, C17β | Benzoic acid, butyric acid | Mixed fatty acid | – (~6, 2) | 1.64 | 0.61 | 6.3 | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | C17β | Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6) | 1.46 | 0.69 | 6.9 | ||
| Estradiol enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | 6.7–7.3 | ||
| Estradiol dienanthate | C3, C17β | Heptanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 (×2) | 1.82 | 0.55 | 8.1–10.4 | ||
| Estradiol undecylate | C17β | Undecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.62 | 0.62 | 9.2–9.8 | ||
| Estradiol stearate | C17β | Octadecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 | 1.98 | 0.51 | 12.2–12.4 | ||
| Estradiol distearate | C3, C17β | Octadecanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 (×2) | 2.96 | 0.34 | 20.2 | ||
| Estradiol sulfate | C3 | Sulfuric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.29 | 0.77 | 0.3–3.8 | ||
| Estradiol glucuronide | C17β | Glucuronic acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.65 | 0.61 | 2.1–2.7 | ||
| Estramustine phosphated | C3, C17β | Normustine, phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.91 | 0.52 | 2.9–5.0 | ||
| Polyestradiol phosphatee | C3–C17β | Phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.23f | 0.81f | 2.9g | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative estradiol content by weight (i.e., relative estrogenic potency). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/[[hydrophobicity]]). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Also known as estradiol normustine phosphate. e = Polymer of estradiol phosphate (~13 repeat units). f = Relative molecular weight or estradiol content per repeat unit. g = logP of repeat unit (i.e., estradiol phosphate). Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Appendix: Endocrine Therapies". Textbook of Medical Oncology (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. 12 September 2009. pp. 442–. ISBN 978-0-203-09289-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=WdDKBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA442.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Clinical pharmacology of polyestradiol phosphate". The Prostate 13 (4): 299–304. 1988. doi:10.1002/pros.2990130405. PMID 3217277.
- ↑ "Treatment of prostatic cancer with diethylstilboestrol and detection of the vascular risk". Cancer of the Prostate and Kidney. Springer Science & Business Media. 29 June 2013. pp. 359–. ISBN 978-1-4684-4349-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=gtAFCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA359.
 |