Chemistry:Gabapentin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Neurontin, others[1] |
| Other names | CI-945; GOE-3450; DM-1796 (Gralise) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694007 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability | Low – Moderate |
| Addiction liability | Low |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Gabapentinoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 27–60% (inversely proportional to dose; a high fat meal also increases bioavailability)[4][5] |
| Protein binding | Less than 3%[4][5] |
| Metabolism | Not significantly metabolized[4][5] |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 7 hours[4][5] |
| Excretion | Kidney[4][5] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 171.240 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain.[3][6] It is commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain.[7] It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given gabapentin for diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia have a meaningful benefit.[8]
Sleepiness and dizziness are the most common side effects. Serious side effects include an increased risk of suicide, respiratory depression, and allergic reactions.[3] Lower doses are recommended in those with kidney disease.[3] Gabapentin acts by decreasing activity of a subset of calcium channels.[9][10][11]
Gabapentin was first approved for use in 1993.[12] It has been available as a generic medication in the United States since 2004.[13] In 2021, it was the tenth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 47 million prescriptions.[14][15] During the 1990s, Parke-Davis, a subsidiary of Pfizer, used a number of illegal techniques to encourage physicians in the United States to prescribe gabapentin for unapproved uses.[16] They have paid out millions of dollars to settle lawsuits regarding these activities.[17]
Medical uses
Gabapentin is recommended for use in focal seizures and neuropathic pain.[3][6] Gabapentin is widely prescribed off-label in the US and UK,[18][19] for example, for the treatment of non-neuropathic pain,[18] anxiety disorders and bipolar disorder.[20] There is concern regarding gabapentin's off-label use due to the lack of strong scientific evidence for its efficacy in multiple conditions and its proven side effects.[21][22]
Seizures
Gabapentin is approved for the treatment of focal seizures;[23] however, it is not effective for generalized epilepsy.[24]
Neuropathic pain
Gabapentin is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain by various medical authorities.[6][7][25][26] This is a general recommendation applicable to all neuropathic pain syndromes except for trigeminal neuralgia, where it may be used as a second- or third-line agent.[7][26]
In regard to the specific diagnoses, a systematic review has found evidence for gabapentin to provide pain relief for some patients with postherpetic neuralgia and diabetic neuropathy.[8] Gabapentin is approved for the former indication in the US.[3] In addition to these two neuropathies, European Federation of Neurological Societies guideline notes gabapentin effectiveness for central pain.[7] A combination of gabapentin with an opioid or nortriptyline may work better than either drug alone.[7][26]
Gabapentin shows substantial benefit (at least 50% pain relief or a patient global impression of change (PGIC) "very much improved") for neuropathic pain (postherpetic neuralgia or peripheral diabetic neuropathy) in 30–40% of subjects treated as compared to those treated with placebo.[8]
Evidence finds little or no benefit and significant risk in those with chronic low back pain or sciatica.[27][28] Gabapentin is not effective in HIV-associated sensory neuropathy[29] and neuropathic pain due to cancer.[30]
Anxiety
There is a small amount of research on the use of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety disorders.[31][32]
Gabapentin is effective for the long-term treatment of social anxiety disorder and in reducing preoperative anxiety.[21][22]
In a controlled trial of breast cancer survivors with anxiety,[32] and in a trial for social phobia,[31] gabapentin significantly reduced anxiety levels.
For panic disorder, gabapentin has produced mixed results.[32][31][22]
Sleep
Gabapentin is effective in treating sleep disorders such as insomnia and restless legs syndrome that are the result of an underlying illness, but comes with some risk of discontinuation and withdrawal symptoms after prolonged use at higher doses.[33]
Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal.[34]
Drug dependence
Gabapentin is moderately effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and associated craving.[35][36][37] The evidence in favor of gabapentin is weak in the treatment of alcoholism: it does not contribute to the achievement of abstinence, and the data on the relapse of heavy drinking and percent of days abstinent do not robustly favor gabapentin; it only decreases the percent days of heavy drinking.[38]
Gabapentin is ineffective in cocaine dependence and methamphetamine use,[39] and it does not increase the rate of smoking cessation.[40] While some studies indicate that gabapentin does not significantly reduce the symptoms of opiate withdrawal, there is increasing evidence that gabapentinoids are effective in controlling some of the symptoms during opiate detoxification. A clinical study in Iran, where heroin dependence is a significant social and public health problem, showed gabapentin produced positive results during an inpatient therapy program, particularly by reducing opioid-induced hyperalgesia and drug craving.[41][39] There is insufficient evidence for its use in cannabis dependence.[42]
Other
Gabapentin is recommended as a first-line treatment of the acquired pendular nystagmus, torsional nystagmus, and infantile nystagmus; however, it does not work in periodic alternating nystagmus.[43][44][45]
Gabapentin decreases the frequency of hot flashes in both menopausal women and patients with breast cancer. However, antidepressants have similar efficacy, and treatment with estrogen more effectively prevents hot flashes.[46]
Gabapentin reduces spasticity in multiple sclerosis and is prescribed as one of the first-line options.[47] It is an established treatment of restless legs syndrome.[48] Gabapentin alleviates itching in kidney failure (uremic pruritus)[49][50] and itching of other causes.[51] It may be an option in essential or orthostatic tremor.[52][53][54] Although the efficacy of gabapentin for insomnia has not been established, it does alleviate sleep disorder in patients with medical illness.[33]
Gabapentin does not appear to provide benefit for bipolar disorder,[22][36][55] complex regional pain syndrome,[56] post-surgical pain,[57] or tinnitus,[58] or prevent episodic migraine in adults.[59]
Contraindications
Gabapentin should be used carefully and at lower doses in people with kidney problems due to possible accumulation and toxicity. It is unclear if it is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding.[3]
Side effects
Dizziness and somnolence are the most frequent side effects.[3] Fatigue, ataxia, peripheral edema (swelling of extremities), and nystagmus are also common.[3] Gabapentin is associated with a weight gain of 2.2 kg (4.9 lb) after 1.5 months of use.[60] Case studies indicate that it may cause anorgasmia and erectile dysfunction,[61] as well as myoclonus[62][63] that disappear after discontinuing gabapentin or replacing it with other medication. DRESS[citation needed], fever, swollen glands that do not go away, eyes or skin turning yellow, unusual bruises or bleeding, unexpected muscle pain or weakness, rash, long-lasting stomach pain which may indicate an inflamed pancreas, hallucinations, anaphylaxis, respiratory depression, and increased suicidal ideation are rare but serious side effects.[64]
Urinary incontinence associated with gabapentin was rarely reported in the literature. Noteworthy, this side effect was already verified by rechallenge.[65]
Suicide
The gabapentin label contains a warning of an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.[3] According to an insurance claims database study, gabapentin use is associated with about 40% increased risk of suicide, suicide attempt and violent death as compared with a reference anticonvulsant drug topiramate. The risk is increased for both bipolar disorder and epilepsy patients.[66] Another study has shown an approximately doubled rate of suicide attempts and self-harm in patients with bipolar disorder who are taking gabapentin versus those taking lithium.[67] A large Swedish study suggests that gabapentinoids are associated with an increased risk of suicidal behaviour, unintentional overdoses, head/body injuries, and road traffic incidents and offences.[68]
Respiratory depression
Serious breathing suppression, potentially fatal, may occur when gabapentin is taken together with opioids, benzodiazepines, or other depressants, or by people with underlying lung problems such as COPD.[69][70] Gabapentin and opioids are commonly prescribed or abused together, and research indicates that the breathing suppression they cause is additive. For example, gabapentin use before joint replacement or laparoscopic surgery increased the risk of respiratory depression by 30–60%.[69] A Canadian study showed that use of gabapentin and other gabapentinoids, whether for epilepsy, neuropathic pain or other chronic pain was associated with a 35–58% increased risk for severe exacerbation of pre-existing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[71]
Withdrawal and dependence
Withdrawal symptoms typically occur 1–2 days after abruptly stopping gabapentin (almost unambiguously due to extended use and during a very short-term rebound phenomenon) — similar to, albeit less intense than most benzodiazepines.[72] Agitation, confusion and disorientation are the most frequently reported, followed by gastrointestinal complaints and sweating, and more rare tremor, tachycardia, hypertension and insomnia.[72] In some cases, users experience withdrawal seizures after chronic or semi-chronic use in the absence of periodic cycles or breaks during repeating and consecutive use.[73] All these symptoms subside when gabapentin is re-instated[72] or tapered off gradually at an appropriate rate.[citation needed]
On its own, gabapentin appears to not have a substantial addictive power. In human and animal experiments, it shows limited to no rewarding effects. The vast majority of people abusing gabapentin are current or former abusers of opioids or sedatives.[73] In these persons, gabapentin can boost the opioid "high" as well as decrease commonly experienced opioid-withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety.[74]
Overdose
Through excessive ingestion, accidental or otherwise, persons may experience overdose symptoms including drowsiness, sedation, blurred vision, slurred speech, somnolence, uncontrollable jerking motions, and anxiety. A very high amount taken is associated with breathing suppression, coma, and possibly death, particularly if combined with alcohol or opioids.[73][75]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Gabapentin is a ligand of the α2δ calcium channel subunit.[76][77] α2δ is an auxiliary protein connected to the main α1 subunit (the channel-forming protein) of high voltage activated voltage-dependent calcium channels (L-type, N-type, P/Q type, and R-type).[9] Gabapentin is not a direct channel blocker: it exerts its actions by disrupting the regulatory function of α2δ and its interactions with other proteins. Gabapentin prevents delivery of the calcium channels to the cell membrane, reduces the activation of the channels by the α2δ subunit, decreases signaling leading to neurotransmitters release, and disrupts interactions of α2δ with NMDA receptors, neurexins, and thrombospondins.[9][10][11] Out of the four known isoforms of α2δ protein, gabapentin binds with similar high affinity to two: α2δ-1 and α2δ-2.[77] Most of the pharmacological properties of gabapentin are explained by its binding to just one isoform – α2δ-1.[77][10]
The endogenous α-amino acids L-leucine and L-isoleucine, which resemble gabapentin in chemical structure, bind α2δ with similar affinity to gabapentin and are present in human cerebrospinal fluid at micromolar concentrations.[78] They may be the endogenous ligands of the α2δ subunit, and they competitively antagonize the effects of gabapentin.[78][79] Accordingly, while gabapentin has nanomolar affinity for the α2δ subunit, its potency in vivo is in the low micromolar range, and competition for binding by endogenous L-amino acids is likely to be responsible for this discrepancy.[10]
Gabapentin is a potent activator of voltage-gated potassium channels KCNQ3 and KCNQ5, even at low nanomolar concentrations. However, this activation is unlikely to be the dominant mechanism of gabapentin's therapeutic effects.[80]
Despite the fact that gabapentin is a structural GABA analogue, and in spite of its name, it does not bind to the GABA receptors, does not convert into GABA or another GABA receptor agonist in vivo, and does not modulate GABA transport or metabolism.[76]
Pharmacokinetics
Gabapentin is absorbed from the intestines by an active transport process mediated via an amino acid transporter, presumably, LAT2.[81] As a result, the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin is dose-dependent, with diminished bioavailability and delayed peak levels at higher doses.[77]
The oral bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 80% at 100 mg administered three times daily once every 8 hours, but decreases to 60% at 300 mg, 47% at 400 mg, 34% at 800 mg, 33% at 1,200 mg, and 27% at 1,600 mg, all with the same dosing schedule.[3][82] Drugs that increase the transit time of gabapentin in the small intestine can increase its oral bioavailability; when gabapentin was co-administered with oral morphine, the oral bioavailability of a 600 mg dose of gabapentin increased by 50%.[82]
Gabapentin at a low dose of 100 mg has a Tmax (time to peak levels) of approximately 1.7 hours, while the Tmax increases to 3 to 4 hours at higher doses.[77] Food does not significantly affect the Tmax of gabapentin and increases the Cmax and area-under-curve levels of gabapentin by approximately 10%.[82]
Gabapentin can cross the blood–brain barrier and enter the central nervous system.[76] Gabapentin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is approximately 9–14% of its blood plasma concentration.[82] Due to its low lipophilicity,[82] gabapentin requires active transport across the blood–brain barrier.[83][76][84][85] The LAT1 is highly expressed at the blood–brain barrier[86] and transports gabapentin across into the brain.[83][76][84][85] As with intestinal absorption mediated by an amino acid transporter, the transport of gabapentin across the blood–brain barrier by LAT1 is saturable.[83] Gabapentin does not bind to other drug transporters such as P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) or OCTN2 (SLC22A5).[83] It is not significantly bound to plasma proteins (<1%).[82]
Gabapentin undergoes little or no metabolism.[77][82]
Gabapentin is eliminated renally in the urine.[82] It has a relatively short elimination half-life, with the reported average value of 5 to 7 hours.[82] Because of its short elimination half-life, gabapentin must be administered 3 to 4 times per day to maintain therapeutic levels.[87] Gabapentin XR (brand name Gralise) is taken once a day.[88]
Chemistry
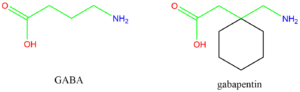
Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid.[89][90] Specifically, it is a derivative of GABA with a pentyl disubstitution at 3 position, hence, the name - gabapentin, in such a way as to form a six-membered ring. After formation of the ring, the amine and carboxylic groups are not in the same relative positions as they are in the GABA;[91] they are more conformationally constrained.[92]
Synthesis
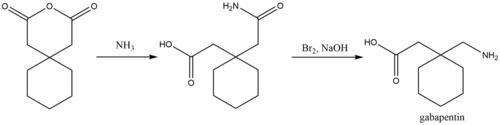
A process for chemical synthesis and isolation of gabapentin with high yield and purity[93] starts with conversion of 1,1-cyclohexanediacetic anhydride to 1,1-cyclohexanediacetic acid monoamide and is followed by a 'Hofmann' rearrangement in an aqueous solution of sodium hypobromite prepared in situ.
History
Gabapentin was designed by researchers at Parke-Davis to be an analogue of the neurotransmitter GABA that could more easily cross the blood–brain barrier and was first described in 1975 by Satzinger and Hartenstein.[91][94] Under the brand name Neurontin, it was first approved in May 1993, for the treatment of epilepsy in the United Kingdom.[95] Approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration followed in December 1993, for use as an adjuvant (effective when added to other antiseizure drugs) medication to control partial seizures in adults; that indication was extended to children in 2000.[96][3] Subsequently, gabapentin was approved in the United States for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in 2002.[97] A generic version of gabapentin first became available in the United States in 2004.[13] An extended-release formulation of gabapentin for once-daily administration, under the brand name Gralise, was approved in the United States for the treatment postherpetic neuralgia in January 2011.[98][99]
Society and culture
Legal status
United Kingdom
Effective April 2019, the United Kingdom reclassified the drug as a class C controlled substance.[100][101][102][103][104]
United States
Effective 1 July 2017, Kentucky classified gabapentin as a schedule V controlled substance statewide.[105] Effective 9 January 2019, Michigan also classified gabapentin as a schedule V controlled substance.[106] Gabapentin is scheduled V drug in other states such as West Virginia,[107] Tennessee,[108] Alabama,[109] and Virginia.[110] Gabapentin is not scheduled or considered a controlled substance (as per the Controlled Substances Act) at the federal level.
Off-label promotion
Although some small, non-controlled studies in the 1990s—mostly sponsored by gabapentin's manufacturer—suggested that treatment for bipolar disorder with gabapentin may be promising,[111] the preponderance of evidence suggests that it is not effective.[112]
Franklin v. Parke-Davis case
Subsequent to the corporate acquisition of the original patent holder, the pharmaceutical company Pfizer admitted that there had been violations of FDA guidelines regarding the promotion of unproven off-label uses for gabapentin in the Franklin v. Parke-Davis case (see below).
While off-label prescriptions are common for a number of drugs, marketing of off-label uses of a drug is not.[16] In 2004, Warner-Lambert (which subsequently was acquired by Pfizer) agreed to plead guilty for activities of its Parke-Davis subsidiary, and to pay $430 million in fines to settle civil and criminal charges regarding the marketing of Neurontin for off-label purposes. The 2004 settlement was one of the largest in U.S. history, and the first off-label promotion case brought successfully under the False Claims Act.[113]
Reuters reported on 25 March 2010, that "Pfizer Inc violated federal racketeering law by improperly promoting the epilepsy drug Neurontin ... Under federal RICO law the penalty is automatically tripled, so the finding will cost Pfizer $141 million."[114] The case stems from a claim from Kaiser Foundation Health Plan Inc. that "it was misled into believing Neurontin was effective for off-label treatment of migraines, bipolar disorder and other conditions. Pfizer argued that Kaiser physicians still recommend the drug for those uses",[115] and that "the insurer's website also still lists Neurontin as a drug for neuropathic pain."[116] The Wall Street Journal noted that Pfizer spokesman Christopher Loder said, "We are disappointed with the verdict and will pursue post-trial motions and an appeal."[117] He later added that "the verdict and the judge's rulings are not consistent with the facts and the law."[114]
Gabasync
Gabasync, a treatment consisting of a combination of gabapentin and two other medications (flumazenil and hydroxyzine) as well as therapy, is an ineffective treatment promoted for methamphetamine addiction, though it had also been claimed to be effective for dependence on alcohol or cocaine.[118] It was marketed as PROMETA. While the individual drugs had been approved by the FDA, their off-label use for addiction treatment has not.[119] Gabasync was marketed by Hythiam, Inc. which is owned by Terren Peizer, a former junk bond salesman who has since been indicted for securities fraud relative to another company.[120][121] Hythiam charges up to $15,000 per patient to license its use (of which half goes to the prescribing physician, and half to Hythiam).[122]
In November 2011, the results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study (financed by Hythiam and carried out at UCLA) were published in the peer-reviewed journal Addiction. It concluded that Gabasync is ineffective: "The PROMETA protocol, consisting of flumazenil, gabapentin and hydroxyzine, appears to be no more effective than placebo in reducing methamphetamine use, retaining patients in treatment or reducing methamphetamine craving."[123]
Barrons, in a November 2005 article entitled "Curb Your Cravings For This Stock", wrote "If the venture works out for patients and the investing public, it'll be a rare success for Peizer, who's promoted a series of disappointing small-cap medical or technology stocks ... since his days at Drexel".[124] Journalist Scott Pelley said to Peizer in 2007: "Depending and who you talk to, you're either a revolutionary or a snake oil salesman."[125][124] 60 Minutes, NBC News, and The Dallas Morning News criticized Peizer after the company bypassed clinical studies and government approval when bringing to market Prometa; the addiction drug proved to be completely ineffective.[126][127][118][128] Journalist Adam Feuerstein opined: "most of what Peizer says is dubious-sounding hype".[129]
Brand names
Gabapentin was originally marketed under the brand name Neurontin. Since it became generic, it has been marketed worldwide using over 300 different brand names.[1] An extended-release formulation of gabapentin for once-daily administration was introduced in 2011, for postherpetic neuralgia under the brand name Gralise.[130]
Related drugs
Parke-Davis developed a drug called pregabalin, which is related in structure to gabapentin, as a successor to gabapentin.[131] Another similar drug atagabalin has been unsuccessfully tried by Pfizer as a treatment for insomnia.[132] A prodrug form (gabapentin enacarbil)[133] was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Recreational use
Gabapentin when taken in excess, can induce euphoria, a sense of calm, a marijuana-like high, improved sociability, and reduced alcohol or cocaine cravings.[134][135][136] Also known on the streets as "Gabbies",[137] gabapentin is increasingly abused and misused for these euphoric effects.[138][139] About 1 percent of the responders to an Internet poll and 22 percent of those attending addiction facilities had a history of abuse of gabapentin.[72][140] Gabapentin misuse, toxicity, and use in suicide attempts among adults in the US increased from 2013 to 2017.[141]
After Kentucky's implementation of stricter legislation regarding opioid prescriptions in 2012, there was an increase in gabapentin-only and multi-drug use in 2012–2015. The majority of these cases were from overdose in suspected suicide attempts. These rates were also accompanied by increases in abuse and recreational use.[142]
Withdrawal symptoms, often resembling those of benzodiazepine withdrawal, play a role in the physical dependence some users experience.[73] Its misuse predominantly coincides with the usage of other CNS depressant drugs, namely opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol.[143]
Veterinary use
In cats, gabapentin can be used as an analgesic in multi-modal pain management,[144] anxiety medication to reduce stress in cats for travel or vet visits,[145] and anticonvulsant.[146] Veterinarians may prescribe gabapentin as an anticonvulsant and pain reliever in dogs. It is also used to treat chronic pain-associated nerve inflammation in horses and dogs. Side effects include tiredness and loss of coordination but they generally go away within 24 hours of starting the medication.[147][146]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "International listings for Gabapentin". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/international/gabapentin.html.
- ↑ "Gabapentin Use During Pregnancy". 2 December 2019. https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/gabapentin.html.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 "Neurontin- gabapentin capsule Neurontin- gabapentin tablet, film coated Neurontin- gabapentin solution". 11 April 2019. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=ee9ad9ed-6d9f-4ee1-9d7f-cfad438df388.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. http://reference.medscape.com/drug/neurontin-gralise-gabapentin-343011#showall.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "Gabapentin. A review of its pharmacological properties and clinical potential in epilepsy". Drugs 46 (3): 409–427. September 1993. doi:10.2165/00003495-199346030-00007. PMID 7693432.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "1 Recommendations | Neuropathic pain in adults: pharmacological management in non-specialist settings | Guidance". 20 November 2013. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg173/chapter/1-Recommendations.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 "EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision". European Journal of Neurology 17 (9): 1113–1e88. September 2010. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x. PMID 20402746.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 6 (6): CD007938. June 2017. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub4. PMID 28597471.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 "Emerging roles for α2δ subunits in calcium channel function and synaptic connectivity". Current Opinion in Neurobiology 63: 162–169. August 2020. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2020.04.007. PMID 32521436.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 "The diverse therapeutic actions of pregabalin: is a single mechanism responsible for several pharmacological activities?". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 34 (6): 332–339. June 2013. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2013.04.001. PMID 23642658.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Analgesia with Gabapentin and Pregabalin May Involve N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors, Neurexins, and Thrombospondins". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 374 (1): 161–174. July 2020. doi:10.1124/jpet.120.266056. PMID 32321743.
- ↑ Models of Seizures and Epilepsy. Burlington: Elsevier. 2005. p. 539. ISBN 978-0-08-045702-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=Qw6KqLjwtZQC&pg=PA539.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 The Other End of the Stethoscope: The Physician's Perspective on the Health Care Crisis. AuthorHouse. 2 March 2012. pp. 63–. ISBN 978-1-4685-4410-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=HkICcDDz0qQC&pg=PA63.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2021". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Gabapentin – Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Gabapentin.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Safeguarding patient welfare: who's in charge?". Annals of Internal Medicine 145 (4): 305–307. August 2006. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-145-4-200608150-00013. PMID 16908923.
- ↑ "Pfizer to pay $325 million in Neurontin settlement". Reuters. 2 June 2014. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-pfizer-neurontin-settlement/pfizer-to-pay-325-million-in-neurontin-settlement-idUSKBN0ED1IS20140602.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Trends in First Gabapentin and Pregabalin Prescriptions in Primary Care in the United Kingdom, 1993-2017". JAMA 320 (20): 2149–2151. November 2018. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.12358. PMID 30480717.
- ↑ "A Clinical Overview of Off-label Use of Gabapentinoid Drugs". JAMA Internal Medicine 179 (5): 695–701. May 2019. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0086. PMID 30907944.
- ↑ Successful Psychopharmacology: Evidence-Based Treatment Solutions for Achieving Remission. W. W. Norton. 5 November 2012. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-393-70857-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=dnAlO_Veu2QC&pg=PA124.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Review finds little evidence to support gabapentinoid use in bipolar disorder or insomnia" (in en). NIHR Evidence (National Institute for Health and Care Research). 17 October 2022. doi:10.3310/nihrevidence_54173. https://evidence.nihr.ac.uk/alert/review-finds-little-evidence-support-gabapentinoid-use-bipolar-disorder-or-insomnia/.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "Gabapentin and pregabalin in bipolar disorder, anxiety states, and insomnia: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and rationale". Molecular Psychiatry 27 (3): 1339–1349. March 2022. doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01386-6. PMID 34819636.
- ↑ "Management of focal-onset seizures: an update on drug treatment". Drugs 66 (13): 1701–1725. 2006. doi:10.2165/00003495-200666130-00004. PMID 16978035.
- ↑ "Pharmacotherapy for tonic-clonic seizures". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 15 (10): 1417–1426. July 2014. doi:10.1517/14656566.2014.915029. PMID 24798217.
- ↑ "Pharmacological management of chronic neuropathic pain - consensus statement and guidelines from the Canadian Pain Society". Pain Research & Management 12 (1): 13–21. 2007. doi:10.1155/2007/730785. PMID 17372630.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 "Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet. Neurology 14 (2): 162–173. February 2015. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0. PMID 25575710.
- ↑ "Benefits and safety of gabapentinoids in chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". PLOS Medicine 14 (8): e1002369. August 2017. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002369. PMID 28809936.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". CMAJ 190 (26): E786–E793. July 2018. doi:10.1503/cmaj.171333. PMID 29970367.
- ↑ "Pharmacological treatment of painful HIV-associated sensory neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". PLOS ONE 5 (12): e14433. December 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014433. PMID 21203440. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...514433P.
- ↑ "Gabapentin for Chronic Neuropathic Pain". JAMA 319 (8): 818–819. February 2018. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.21547. PMID 29486015.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 "The role of anticonvulsant drugs in anxiety disorders: a critical review of the evidence". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 27 (3): 263–272. June 2007. doi:10.1097/jcp.0b013e318059361a. PMID 17502773.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 "Gabapentin and Pregabalin for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development 7 (3): 228–232. March 2018. doi:10.1002/cpdd.446. PMID 29579375.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Efficacy and Tolerability of Gabapentin in Adults with Sleep Disturbance in Medical Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Frontiers in Neurology 8: 316. 2017. doi:10.3389/fneur.2017.00316. PMID 28769860.
- ↑ "Treatment effects of gabapentin for primary insomnia". Clinical Neuropharmacology 33 (2): 84–90. 2010. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181cda242. PMID 20124884.
- ↑ "Outpatient management of alcohol withdrawal syndrome". American Family Physician 88 (9): 589–595. November 2013. PMID 24364635.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Gabapentin Therapy in Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 17 (5). 2015. doi:10.4088/PCC.15r01821. PMID 26835178.
- ↑ "Effectiveness of Gabapentin in Reducing Cravings and Withdrawal in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Review". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 21 (4). August 2019. doi:10.4088/PCC.19r02465. PMID 31461226.
- ↑ "A meta-analysis of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder". Addiction 114 (9): 1547–1555. September 2019. doi:10.1111/add.14655. PMID 31077485.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 27 (1): 113–124. January 2018. doi:10.1080/13543784.2018.1417383. PMID 29241365.
- ↑ "Gabapentin for smoking cessation". Nicotine & Tobacco Research 12 (3): 300–304. March 2010. doi:10.1093/ntr/ntp195. PMID 20081039.
- ↑ "Gabapentin Effect on Pain Associated with Heroin Withdrawal in Iranian Crack: a Randomized Double-blind Clinical Trial". Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 11 (3): 979–983. 2012. PMID 24250527.
- ↑ "Pharmacotherapies for cannabis dependence". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1 (1): CD008940. January 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008940.pub3. PMID 30687936.
- ↑ "The pharmacological treatment of nystagmus: a review". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 10 (11): 1805–1816. August 2009. doi:10.1517/14656560902978446. PMID 19601699.
- ↑ "Treatment of nystagmus". Current Treatment Options in Neurology 14 (1): 60–72. February 2012. doi:10.1007/s11940-011-0154-5. PMID 22072056.
- ↑ "The pharmacological treatment of acquired nystagmus". Practical Neurology 12 (3): 147–153. June 2012. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2011-000181. PMID 22661344.
- ↑ "Efficacy and safety of gabapentin and pregabalin in patients with vasomotor symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 222 (6): 564–579.e12. June 2020. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2019.12.011. PMID 31870736.
- ↑ "Pharmacological management of spasticity in multiple sclerosis: Systematic review and consensus paper". Multiple Sclerosis 22 (11): 1386–1396. October 2016. doi:10.1177/1352458516643600. PMID 27207462. https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1496196/.
- ↑ "Treatment of restless legs syndrome: Evidence-based review and implications for clinical practice (Revised 2017)§". Movement Disorders 33 (7): 1077–1091. July 2018. doi:10.1002/mds.27260. PMID 29756335.
- ↑ "Pruritus and renal failure". Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 30 (2): 99–100. June 2011. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2011.04.005. PMID 21767770.
- ↑ "Interventions for itch in people with advanced chronic kidney disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020 (12): CD011393. December 2020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011393.pub2. PMID 33283264.
- ↑ "Gabapentin for pruritus in palliative care". The American Journal of Hospice & Palliative Care 30 (2): 192–196. March 2013. doi:10.1177/1049909112445464. PMID 22556282.
- ↑ "The treatment of tremor". Neurotherapeutics 11 (1): 128–138. January 2014. doi:10.1007/s13311-013-0230-5. PMID 24142589.
- ↑ "Evidence-based guideline update: treatment of essential tremor: report of the Quality Standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology 77 (19): 1752–1755. November 2011. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318236f0fd. PMID 22013182.
- ↑ "Pharmacological management of essential tremor". Drugs 70 (17): 2215–2228. December 2010. doi:10.2165/11538180-000000000-00000. PMID 21080739.
- ↑ "A Systematic Review of the Clinical Use of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Bipolar Disorder". Pharmaceuticals 14 (9): 834. August 2021. doi:10.3390/ph14090834. PMID 34577534.
- ↑ "Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: a review of the evidence". Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 57 (2): 149–166. February 2010. doi:10.1007/s12630-009-9237-0. PMID 20054678.
- ↑ "A Meta-Analysis on the Use of Gabapentinoids for the Treatment of Acute Postoperative Pain Following Total Knee Arthroplasty". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 98 (16): 1340–1350. August 2016. doi:10.2106/jbjs.15.01202. PMID 27535436. https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:cbe29197-14a9-47dc-b961-2ad3e24fd1c0. Retrieved 22 August 2020.
- ↑ "Gabapentin for tinnitus: a systematic review". American Journal of Audiology 20 (2): 151–158. December 2011. doi:10.1044/1059-0889(2011/10-0041). PMID 21940981.
- ↑ "Gabapentin or pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013 (6): CD010609. June 2013. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010609. PMID 23797675.
- ↑ "Clinical review: Drugs commonly associated with weight change: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 100 (2): 363–370. February 2015. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-3421. PMID 25590213.
- ↑ "Sexual dysfunction related to antiepileptic drugs in patients with epilepsy". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety 15 (1): 31–42. January 2016. doi:10.1517/14740338.2016.1112376. PMID 26559937.
- ↑ "Negative myoclonus induced by gabapentin and pregabalin: A case series and systematic literature review". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 382: 36–39. November 2017. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2017.09.019. PMID 29111014.
- ↑ "Gabapentin or pregabalin induced myoclonus: A case series and literature review". Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 61: 225–234. March 2019. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2018.09.019. PMID 30381161.
- ↑ "Side effects of gabapentin". National Health Service. https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/gabapentin/side-effects-of-gabapentin/.
- ↑ "Gabapentin-Associated Urinary Incontinence: A Case Verified by Rechallenge". Clinical Neuropharmacology 42 (3): 91–93. May 2019. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000334. PMID 30844853.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsant medications and the risk of suicide, attempted suicide, or violent death". JAMA 303 (14): 1401–1409. April 2010. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.410. PMID 20388896.
- ↑ "The association between gabapentin and suicidality in bipolar patients". International Clinical Psychopharmacology 34 (1): 27–32. January 2019. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000242. PMID 30383553.
- ↑ "Associations between gabapentinoids and suicidal behaviour, unintentional overdoses, injuries, road traffic incidents, and violent crime: population based cohort study in Sweden". BMJ 365: l2147. June 2019. doi:10.1136/bmj.l2147. PMID 31189556.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 "FDA warns about serious breathing problems with seizure and nerve pain medicines gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR)". 19 December 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-warns-about-serious-breathing-problems-seizure-and-nerve-pain-medicines-gabapentin-neurontin.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "FDA warns about serious breathing problems with seizure and nerve pain medicines gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR) When used with CNS depressants or in patients with lung problems" (PDF). 19 December 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/133681/download.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ Rahman, Alvi A. (16 Jan 2024). "Gabapentinoids and Risk for Severe Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease : A Population-Based Cohort Study". Annals of Internal Medicine (Online ahead of print). doi:10.7326/M23-0849. PMID 38224592. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38224592/. Retrieved 26 January 2024.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 72.3 "Gabapentin: Abuse, Dependence, and Withdrawal". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 50 (3): 229–233. March 2016. doi:10.1177/1060028015620800. PMID 26721643.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 73.2 73.3 "How addictive are gabapentin and pregabalin? A systematic review". European Neuropsychopharmacology 27 (12): 1185–1215. December 2017. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.08.430. PMID 28988943.
- ↑ "On the addictive power of gabapentinoids: a mini-review". Psychiatria Danubina 30 (2): 142–149. June 2018. doi:10.24869/psyd.2018.142. PMID 29930223. http://www.psychiatria-danubina.com/UserDocsImages/pdf/dnb_vol30_no2/dnb_vol30_no2_142.pdf.
- ↑ R.C. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 677–8. ISBN:978-0-9626523-7-0.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 76.2 76.3 76.4 "The mechanisms of action of gabapentin and pregabalin". Current Opinion in Pharmacology 6 (1): 108–113. February 2006. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2005.11.003. PMID 16376147.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 77.2 77.3 77.4 77.5 "Alpha2delta ligands, gabapentin, pregabalin and mirogabalin: a review of their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 16 (11): 1263–1277. November 2016. doi:10.1080/14737175.2016.1202764. PMID 27345098.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 "Ca2+ channel alpha2delta ligands: novel modulators of neurotransmission". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 28 (2): 75–82. February 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2006.12.006. PMID 17222465.
- ↑ "Functional biology of the alpha(2)delta subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 28 (5): 220–228. May 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2007.03.005. PMID 17403543.
- ↑ "Gabapentin Is a Potent Activator of KCNQ3 and KCNQ5 Potassium Channels". Molecular Pharmacology 94 (4): 1155–1163. October 2018. doi:10.1124/mol.118.112953. PMID 30021858.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetic role of L-type amino acid transporters LAT1 and LAT2". European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 35 (3): 161–174. October 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2008.06.015. PMID 18656534.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 82.3 82.4 82.5 82.6 82.7 82.8 "A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 49 (10): 661–669. October 2010. doi:10.2165/11536200-000000000-00000. PMID 20818832.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 83.3 "Transport of gabapentin by LAT1 (SLC7A5)". Biochemical Pharmacology 85 (11): 1672–1683. June 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.03.022. PMID 23567998.
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 "Molecular determinants of blood-brain barrier permeation". Therapeutic Delivery 6 (8): 961–971. 2015. doi:10.4155/tde.15.32. PMID 26305616.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 "Prodrug approaches for enhancing the bioavailability of drugs with low solubility". Chemistry & Biodiversity 6 (11): 2071–2083. November 2009. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200900114. PMID 19937841.
- ↑ "Selective expression of the large neutral amino acid transporter at the blood-brain barrier". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96 (21): 12079–12084. October 1999. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.21.12079. PMID 10518579. Bibcode: 1999PNAS...9612079B.
- ↑ "Gabapentin enacarbil - clinical efficacy in restless legs syndrome". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 6: 151–158. May 2010. doi:10.2147/NDT.S5712. PMID 20505847.
- ↑ Pharmacology, An Issue of Anesthesiology Clinics E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 5 June 2017. pp. 98–. ISBN 978-0-323-52998-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=lsUmDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT98.
- ↑ Wyllie's Treatment of Epilepsy: Principles and Practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 17 February 2012. p. 423. ISBN 978-1-4511-5348-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=j9t6Qg0kkuUC&pg=RA1-PA423.
- ↑ Practical Management of Pain. Elsevier Health Sciences. 11 September 2013. p. 1006. ISBN 978-0-323-17080-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=kfcDAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA1006.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. 2005. pp. 219–220. ISBN 978-0-470-01552-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=jglFsz5EJR8C&pg=PA219.
- ↑ "Conformationally restricted GABA analogs: from rigid carbocycles to cage hydrocarbons". Future Medicinal Chemistry 3 (2): 223–241. February 2011. doi:10.4155/fmc.10.287. PMID 21428817.
- ↑ "Process For Synthesis Of Gabapentin". https://patents.google.com/patent/US20080103334A1/en.
- ↑ The Art of Drug Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. 26 February 2013. pp. 13–. ISBN 978-1-118-67846-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=zvruBDAulWEC&pg=SA13-PA41.
- ↑ "Drug Profile: Gabapentin". Adis Insight. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800002421.
- ↑ "Examination of the evidence for off-label use of gabapentin". Journal of Managed Care Pharmacy 9 (6): 559–568. 2003. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2003.9.6.559. PMID 14664664. PMC 10437292. http://www.amcp.org/data/jmcp/Contemporary%20Subject-559-568.pdf. Retrieved 15 August 2006.
- ↑ "Once-daily gastroretentive gabapentin for the management of postherpetic neuralgia: an update for clinicians". Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease 3 (5): 211–218. September 2012. doi:10.1177/2040622312452905. PMID 23342236.
- ↑ "Yabba Dabba Gabapentin: Are Gralise and Horizant Worth the Cost?". GoodRx, Inc.. 31 May 2013. https://www.goodrx.com/blog/yabba-dabba-gabapentin-are-gralise-and-horizant-worth-the-cost/.
- ↑ "Gabapentin controlled release – Depomed". Adis Insight. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800019682.
- ↑ "Pregabalin and gabapentin will become controlled drugs in April" (in en-GB). 17 October 2018. https://nursingnotes.co.uk/pregabalin-gabapentin-will-become-controlled-drugs-april/.
- ↑ "Re: Pregabalin and Gabapentin advice". 14 January 2016. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/491854/ACMD_Advice_-_Pregabalin_and_gabapentin.pdf.
- ↑ "Pregabalin and gabapentin: proposal to schedule under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001". 10 November 2017. https://www.gov.uk/government/consultations/pregabalin-and-gabapentin-proposal-to-schedule-under-the-misuse-of-drugs-regulations-2001.
- ↑ "Pregabalin and gabapentin become controlled drugs to cut deaths from misuse". BMJ 363: k4364. October 2018. doi:10.1136/bmj.k4364. PMID 30327316.
- ↑ "Pregabalin and gabapentin to be controlled as Class C drugs". 15 October 2018. https://www.gov.uk/government/news/pregabalin-and-gabapentin-to-be-controlled-as-class-c-drugs.
- ↑ "Important Notice: Gabapentin Becomes a Schedule 5 Controlled Substance in Kentucky". March 2017. https://pharmacy.ky.gov/Documents/Gabapentin%20-%20Schedule%20V%20Controlled%20Substance.pdf.
- ↑ "Gabapentin Scheduled as Controlled Substance to help with State's Opioid Epidemic". https://www.michigan.gov/lara/0,4601,7-154-11472-487050--,00.html.
- ↑ "WV Code 212". http://www.wvlegislature.gov/WVCODE/ChapterEntire.cfm?chap=60a&art=2§ion=212.
- ↑ "Gabapentin will be a Schedule V controlled substance in Tennessee effective July 1, 2018". https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/health/healthprofboards/New%20Statue%20Gabapentin%2006-18.pdf.
- ↑ "Pharmacy Division". http://www.alabamapublichealth.gov/pharmacy/.
- ↑ "Scheduling of Gabapentin". Virginia Department of Health Professions. http://www.dhp.virginia.gov/Pharmacy/docs/gabapentin06172019.pdf.
- ↑ "Examination of the evidence for off-label use of gabapentin". Journal of Managed Care Pharmacy 9 (6): 559–568. 2003. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2003.9.6.559. PMID 14664664.
- ↑ "A systematic review on the role of anticonvulsants in the treatment of acute bipolar depression". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 16 (2): 485–496. March 2013. doi:10.1017/S1461145712000491. PMID 22575611.
- ↑ "Huge penalty in drug fraud, Pfizer settles felony case in Neurontin off-label promotion". San Francisco Chronicle: p. C-1. 14 May 2004. http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/c/a/2004/05/14/BUGKK6L0LB1.DTL.
- ↑ 114.0 114.1 "US jury's Neurontin ruling to cost Pfizer $141 mln". Reuters. 25 March 2010. https://www.reuters.com/article/pfizer-neurontin-idUSN259778920100325.
- ↑ "Pfizer faces $142M in damages for drug fraud". Bloomberg Businessweek. 25 March 2010. http://www.businessweek.com/ap/financialnews/D9ELVKG80.htm.
- ↑ "Pfizer Told to Pay $142.1 Million for Neurontin Marketing Fraud". 26 March 2010. https://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=email_en&sid=a_9aVylZQGjU.
- ↑ "Jury Rules Against Pfizer in Marketing Case". The Wall Street Journal. 25 March 2010. https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424052748704094104575144223583428414.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 "Prescription For Addiction". 60 Minutes (CBS News). 9 December 2007. http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2007/12/07/60minutes/main3590535.shtml..
- ↑ "Prometa Founder's Spotty Background Explored". 3 November 2006. http://www.drugfree.org/join-together/prometa-founders-spotty-background-explored/.
- ↑ "UNITED STATES V. TERREN S. PEIZER". 1 March 2023. https://www.justice.gov/criminal-vns/case/united-states-v-terren-s-peizer.
- ↑ Prescription For Addiction, 60 Minutes' Scott Pelley Reports On A New Addiction Treatment, 7 December 2007, http://www.cbsnews.com/news/prescription-for-addiction/
- ↑ "Prometa under fire in Washington drug court program". Alcoholism & Drug Abuse Weekly 20 (3). 21 January 2008. doi:10.1002/adaw.20121. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adaw.20121.
- ↑ "Double-blind placebo-controlled evaluation of the PROMETA™ protocol for methamphetamine dependence". Addiction 107 (2): 361–369. February 2012. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03619.x. PMID 22082089.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 "Curb Your Cravings For This Stock". The Wall Street Journal. 7 November 2005. https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB113115427427989094.
- ↑ "Prescription For Addiction". 7 December 2007. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/prescription-for-addiction/.
- ↑ Kari Huus (5 February 2007). "Unproven meth, cocaine 'remedy' hits market". http://www.nbcnews.com/health/health-news/unproven-meth-cocaine-remedy-hits-market-flna1C9444547.
- ↑ "The Rise and Fall of a "Miracle Cure" for Drug Addiction". Washington Monthly. 24 January 2012. http://washingtonmonthly.com/2012/01/24/the-rise-and-fall-of-a-miracle-cure-for-drug-addiction/.
- ↑ "Texas' Prometa program for treating meth addicts draws skeptics". Dallas Morning News. 20 January 2008. https://www.dallasnews.com/sharedcontent/dws/dn/latestnews/stories/012108dntexprometa.2c2f801.html.
- ↑ "Hythiam, Shire, Genentech; Talk is proving cheap at Hythiam". Biotech Notebook. TheStreet. 13 November 2007. https://www.thestreet.com/investing/stocks/biotech-notebook-hythiam-shire-genentech-10389850.
- ↑ "Gralise Approval History". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/history/gralise.html.
- ↑ "The mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs 7 (1): 33–39. January 2006. PMID 16425669.
- ↑ "Modeling sleep data for a new drug in development using markov mixed-effects models". Pharmaceutical Research 28 (10): 2610–2627. October 2011. doi:10.1007/s11095-011-0490-x. PMID 21681607.
- ↑ "Modifications of antiepileptic drugs for improved tolerability and efficacy". Perspectives in Medicinal Chemistry 2: 21–39. February 2008. doi:10.1177/1177391X0800200001. PMID 19787095.
- ↑ "Substance misuse of gabapentin". The British Journal of General Practice 62 (601): 406–407. August 2012. doi:10.3399/bjgp12X653516. PMID 22867659.
- ↑ "Gabapentin abuse and overdose: a case report". J Subst Abus Alcohol 2: 1018. 2014. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9bab/627065e943e1508057231c865569bf20f5d3.pdf.
- ↑ "A Call for Caution in Prescribing Gabapentin to Individuals With Concurrent Polysubstance Abuse: A Case Report". Journal of Psychiatric Practice 25 (4): 308–312. July 2019. doi:10.1097/PRA.0000000000000403. PMID 31291212.
- ↑ Oxford Textbook of Correctional Psychiatry. Oxford University Press. April 2015. p. 167. ISBN 978-0199360574.
- ↑ "Gabapentin and Pregabalin for Pain - Is Increased Prescribing a Cause for Concern?". The New England Journal of Medicine 377 (5): 411–414. August 2017. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1704633. PMID 28767350.
- ↑ "Abuse and Misuse of Pregabalin and Gabapentin". Drugs 77 (4): 403–426. March 2017. doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0700-x. PMID 28144823.
- ↑ "[On the risk of dependence on gabapentinoids]" (in de). Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie 86 (2): 82–105. February 2018. doi:10.1055/s-0043-122392. PMID 29179227.
- ↑ "Trends in gabapentin and baclofen exposures reported to U.S. poison centers". Clinical Toxicology 58 (7): 763–772. July 2020. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1687902. PMID 31786961.
- ↑ "Trending gabapentin exposures in Kentucky after legislation requiring use of the state prescription drug monitoring program for all opioid prescriptions". Clinical Toxicology 57 (6): 398–403. June 2019. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1538518. PMID 30676102.
- ↑ "Gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion: a systematic review". Addiction 111 (7): 1160–1174. July 2016. doi:10.1111/add.13324. PMID 27265421.
- ↑ "Gabapentin as part of multi-modal analgesia in two cats suffering multiple injuries". Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia 38 (5): 518–520. September 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2995.2011.00638.x. PMID 21831060.
- ↑ "Effects of a single preappointment dose of gabapentin on signs of stress in cats during transportation and veterinary examination". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 251 (10): 1175–1181. November 2017. doi:10.2460/javma.251.10.1175. PMID 29099247.
- ↑ 146.0 146.1 "Gabapentin". https://www.plumbsveterinarydrugs.com/#!/veterinarymedicationguides.
- ↑ "Gabapentin for Dogs: Uses and Side Effects" (in en). https://www.akc.org/expert-advice/health/gabapentin-for-dogs/.
External links
 |