Chemistry:Rosonabant
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
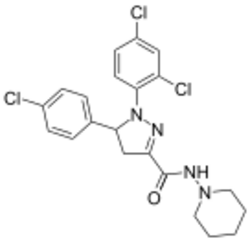 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H21Cl3N4O |
| Molar mass | 451.78 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rosonabant (INN; E-6776) is a drug acting as a CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist that was under investigation by Esteve as an appetite suppressant for the treatment of obesity.[1][2] Development of the drug for clinical use was apparently halted shortly after the related CB1 antagonist rimonabant was discontinued in November 2008,[when?] due to the reports of severe psychiatric adverse effects such as anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation associated with it and with similarly acting agents.[3][4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Cannabinoid receptor antagonists: pharmacological opportunities, clinical experience, and translational prognosis". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs 14 (1): 43–65. March 2009. doi:10.1517/14728210902736568. PMID 19249987.
- ↑ "Preclinical Developments in Antiobesity Drugs". Appetite and Body Weight: Integrative Systems and the Development of Anti-Obesity Drugs. Academic Press. 2007. p. 325. ISBN 978-0-12-370633-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=YO3BUp3nicMC&pg=PA325. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- ↑ "Regulatory challenges for new drugs to treat obesity and comorbid metabolic disorders". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 68 (6): 861–874. December 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03549.x. PMID 20002080.
- ↑ "The current status and future perspectives of studies of cannabinoid receptor 1 antagonists as anti-obesity agents". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 9 (6): 482–503. 2009. doi:10.2174/156802609788897844. PMID 19689362. http://www.benthamdirect.org/pages/content.php?CTMC/2009/00000009/00000006/0003R.SGM.
- ↑ "The psychiatric side-effects of rimonabant". Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria 31 (2): 145–153. June 2009. doi:10.1590/S1516-44462009000200012. PMID 19578688.
 |

