Chemistry:Substituted alpha-alkyltryptamine
α-Alkyltryptamines are a group of substituted tryptamines which possess an alkyl group, such as a methyl or ethyl group, attached at the alpha carbon, and in most cases no substitution on the amine nitrogen.[1][2][3] α-Alkylation of tryptamine makes it much more metabolically stable and resistant to degradation by monoamine oxidase, resulting in increased potency and greatly lengthened half-life.[3] This is analogous to α-methylation of phenethylamine into amphetamine.[3]
Many α-alkyltryptamines are drugs, acting as monoamine releasing agents, non-selective serotonin receptor agonists, and/or monoamine oxidase inhibitors,[4][5][6][7] and produce psychostimulant, entactogen, and/or psychedelic effects.[1][2][3] The most well-known of these agents are α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and α-ethyltryptamine (αET), both of which were used clinically as antidepressants for a brief period of time in the past and are abused as recreational drugs.[2][3] In accordance with its action as a dual releasing agent of serotonin and dopamine, αET has been found to produce serotonergic neurotoxicity similarly to amphetamines like MDMA and PCA, and the same is also likely to hold true for other serotonin and dopamine-releasing α-alkyltryptamines such as αMT, 5-MeO-αMT, and various others.[8]
List of substituted α-alkyltryptamines
| Structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
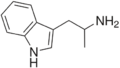
|
αMT | 1-(1H-Indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 299-26-3 |
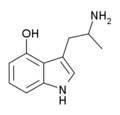
|
4-HO-αMT | 3-(2-aminopropyl)-1H-indol-4-ol | 15066-09-8 |
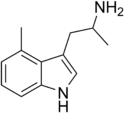
|
4-Methyl-αMT | 1-methyl-2-(4-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethylamine | 3569-29-7 |
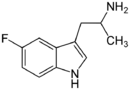
|
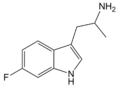
5-Fluoro-αMT | 1-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-08-3 |
|
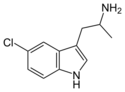
5-Chloro-αMT | 1-(5-Chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-07-2 |

|
5-HO-αMT (αMS/α-methyl-5-HT) | 3-(2-aminopropyl)-1H-indol-5-ol | 304-52-9 |
|
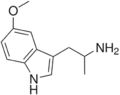
5-MeO-αMT | 1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 1137-04-8 |
|
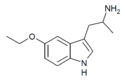
5-Ethoxy-αMT | 1-(5-ethoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 101832-83-1 |
|
6-Fluoro-αMT | 1-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-amine | 712-11-8 |
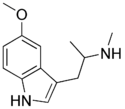
|
N-Methyl-5-MeO-αMT (α,N,O-TMS/α,N,O-trimethyl-5-HT) | [1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propan-2-yl](methyl)amine | 4822-13-3 |
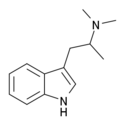
|
N,N-Dimethyl-αMT (α,N,N-TMT) | (2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)dimethylamine | |
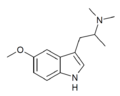
|
N,N-Dimethyl-5-MeO-αMT (5-MeO-α,N,N-TMT) | (2-(5-methoxy-1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)dimethylamine | 101831-90-7 |
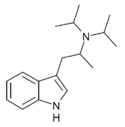
|
αMDiPT | (2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-1-methyl-ethyl)diisopropylamine | |
|
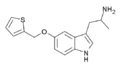
BW-723C86 | 1-[5-(2-Thienylmethoxy)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2-propanamine | 160521-72-2 |
|
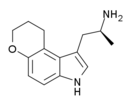
AL-37350A (4,5-dihydropyrano-αMT) | (S)-(+)-1-(2-Aminopropyl)-8,9-dihydropyrano[3,2-e]indole | 362603-40-5 |
|
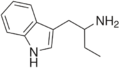
αET | 1-(1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 2235-90-7 |
|
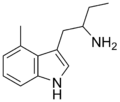
4-Methyl-αET | 1-(4-Methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 28289-30-7 |
|
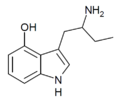
4-HO-αET | 1-(4-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 28289-28-3 |
|
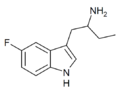
5-Fluoro-αET | 1-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 1380137-98-3 |
|
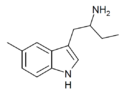
5-Methyl-αET | 1-(5-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 1380148-21-9 |
|
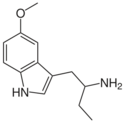
5-MeO-αET | 1-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 4765-10-0 |
|
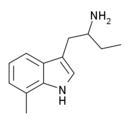
7-Methyl-αET | 1-(7-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)butan-2-amine | 13712-80-6 |
|
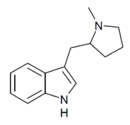
MPMI [9] | 3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | 143321-54-4 |
|
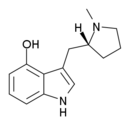
Lucigenol | (R)-3-(N-methylpyrrolidin-2-ylmethyl)-4-hydoxyindole | 250672-65-2 |
|
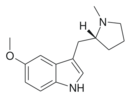
5-MeO-MPMI | 5-Methoxy-3-{[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-1H-indole | 143321-57-7 |
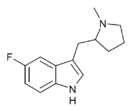
|
5-F-MPMI | 5-fluoro-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | |
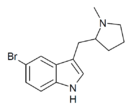
|
5-Br-MPMI | 5-bromo-3-[(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-indole | 143322-57-0 |
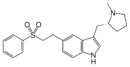
|
Eletriptan | 3-{[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl}-5-[2-(benzenesulfonyl)ethyl]-1H-indole | 143322-58-1 |
- Related compounds
A number of related compounds are known, with a similar structure but having the indole core flipped and/or replaced with related cores such as indoline, indazole or benzofuran. These similarly are primarily active as agonists at the 5-HT2 family of serotonin receptors, with applications in the treatment of glaucoma, cluster headaches or as anorectics.
| Structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
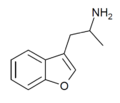
|
3-APB | 3-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran | 105909-13-5 |
|
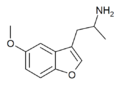
Mebfap | 3-(2-aminopropyl)-5-methoxybenzofuran | 140853-59-4 |
|
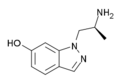
AL-34662 | 1-((S)-2-Aminopropyl)-1H-indazol-6-ol | 210580-75-9 |
|
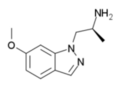
O-methyl-AL-34662 | 1-((S)-6-methoxy-2-aminopropyl)-1H-indazole | 210580-60-2 |
|
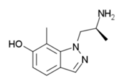
7-methyl-AL-34662 | 1-((S)-2-Aminopropyl)-7-methyl-1H-indazol-6-ol | 874668-67-4 |
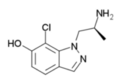
|
7-chloro-AL-34662 | 1-((S)-2-Aminopropyl)-7-chloro-1H-indazol-6-ol | 874881-86-4 |
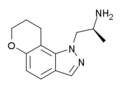
|
AL-38022A | (S)-2-(8,9-dihydro-7H-pyrano[2,3-g]indazol-1-yl)-1-methylethylamine | 478132-11-5 |
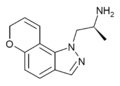
|
Example 9 [10] | (S)-α-methyl-pyrano[2,3-g]indazole-1(7H)-ethanamine | 478132-12-6 |
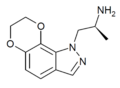
|
Example 3 [11] | (S)-7,8-dihydro-α-methyl-1H-[1,4]dioxino[2,3-g]indazole-1-ethanamine | 890087-75-9 |
|
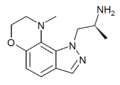
Example 1 [12] | (S)-8,9-dihydro-α,9-dimethylpyrazolo[3,4-f][1,4]benzoxazine-1(7H)-ethanamine | 1373917-69-1 |
|
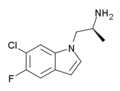
Ro60-0175 | (S)-(6-chloro-5-fluoro-1H-indol-1-yl)propan-2-amine | 169675-09-6 |
|
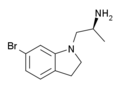
VER-3323 | (2S)-1-(6-bromo-2,3-dihydroindol-1-yl)propan-2-amine | 259857-99-3 |
|
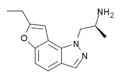
YM-348 | (2S)-1-(7-ethyl-1H-furo[2,3-g]indazol-1-yl)propan-2-amine | 372163-84-3 |
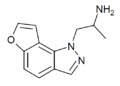
|
2-desethyl-YM-348 | (2S)-1-(1H-furo[2,3-g]indazol-1-yl)propan-2-amine |
See also
- 5-IT
- Substituted amphetamine
- Substituted benzofuran
- Substituted cathinone
- Substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ries, Richard K.; Miller, Shannon C.; Fiellin, David A. (2009). Principles of Addiction Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 216–218. ISBN 978-0-7817-7477-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=j6GGBud8DXcC&pg=PT245.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Laing, Richard R. (2003). Hallucinogens: A Forensic Drug Handbook. Academic Press. pp. 102–. ISBN 978-0-12-433951-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=l1DrqgobbcwC&pg=PA102.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Lemke, Thomas L.; Williams, David A. (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 641–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Sd6ot9ul-bUC&pg=PA641.
- ↑ "The effects of non-medically used psychoactive drugs on monoamine neurotransmission in rat brain". European Journal of Pharmacology 559 (2-3): 132–7. March 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.11.075. PMID 17223101.
- ↑ "Alpha-ethyltryptamines as dual dopamine-serotonin releasers". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 24 (19): 4754–4758. October 2014. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.07.062. PMID 25193229.
- ↑ "In vitro screening of psychoactive drugs by [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding in rat brain membranes". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 30 (12): 2328–33. December 2007. doi:10.1248/bpb.30.2328. PMID 18057721.
- ↑ "Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: nature of their interaction with rabbit pancreatic islets to alter insluin secretion". Diabetologia 11 (6): 487–94. December 1975. doi:10.1007/bf01222097. PMID 1107123.
- ↑ "Reduction in brain serotonin markers by alpha-ethyltryptamine (Monase)". European Journal of Pharmacology 200 (1): 187–90. July 1991. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90686-K. PMID 1722753.
- ↑ Macor JE, Wythes MJ. Indole derivatives. US patent 5607951
- ↑ Chen HH, May JA, Severns BS, "Pyranoindazoles and their use for the treatment of glaucoma", US patent granted 6881749, published 3 June 2004, issued 19 April 2005, assigned to Alcon, Inc.
- ↑ Chen HH, May JA, "Use of dioxindoindazoles and dioxoloindazoles for treating glaucoma", US patent granted 7425572, published 8 June 2006, issued 16 September 2008, assigned to Alcon, Inc.
- ↑ "Substituted [1,4]oxazino[2,3-g]indazoles for the treatment of glaucoma" US patent granted 7268131, published 15 December 2005, issued 11 September 2007, assigned to Alcon, Inc.
Further reading
- (Book) Tryptamines i Have Known and Loved: The Continuation, (1st. ed.). Berkeley, CA : Transform Press, ©1997.. 1997. ISBN 978-0-9630096-9-2. http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/tihkal/tihkal11.shtml. Retrieved 15 November 2013.
