Chemistry:Minaxolone
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
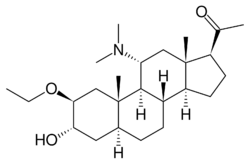
| Other names | 11α-(Dimethylamino)-2β-ethoxy-3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H43NO3 |
| Molar mass | 405.623 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Minaxolone (CCI-12923) is a neuroactive steroid which was developed as a general anesthetic but was withdrawn before registration due to toxicity seen with long-term administration in rats, and hence was never marketed.[1][2][3] It is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor,[4] as well as, less potently, a positive allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor.[4][5]
Chemistry
See also
- Alfadolone
- Alfaxolone
- Ganaxolone
- Hydroxydione
- Pregnanolone
- Renanolone
References
- ↑ Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. 21 November 1996. pp. 1358–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=A0THacd46ZsC&pg=PA1358.
- ↑ Clinical Pharmacology for Anaesthetists. W.B. Saunders. 1999. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-03707-5.50031-0. ISBN 978-0-7020-2167-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=sD1sAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "Intravenous anesthetic agents". Foundations of Anesthesia: Basic Sciences for Clinical Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2006. pp. 305–. ISBN 978-0-323-03707-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=xaXu1wHmENoC&pg=PA305.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Neurosteroid modulation of recombinant and synaptic GABAA receptor". Neurosteroids and Brain Function. Academic Press. 2001. pp. 196–. ISBN 978-0-12-366846-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=13jQfYIkwhkC&pg=PA196.
- ↑ "The interaction of anaesthetic steroids with recombinant glycine and GABAA receptors". British Journal of Anaesthesia 92 (5): 704–711. May 2004. doi:10.1093/bja/aeh125. PMID 15033889.
 |

