Chemistry:Amentoflavone
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4′,5,7-Trihydroxyflavone)-(3′→8)-(4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
8-[5-(5,7-Dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-2-yl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Didemethyl-ginkgetin
3′,8″-Biapigenin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H18O10 | |
| Molar mass | 538.464 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
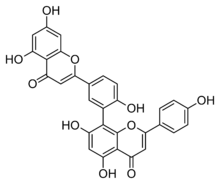
Amentoflavone is a biflavonoid (bis-apigenin coupled at 8 and 3′ positions, or 3′,8″-biapigenin) constituent of a number of plants including Ginkgo biloba, Chamaecyparis obtusa (hinoki), Biophytum sensitivum, Selaginella tamariscina,[1] Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort)[2] and Xerophyta plicata.[3]
Amentoflavone can interact with many medications by being a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, which are enzymes responsible for the metabolism of some drugs in the body.[4] It is also an inhibitor of human cathepsin B.[2]
Amentoflavone has a variety of in vitro activities including antimalarial activity,[5] anticancer activity (which may, at least in part, be mediated by its inhibition of fatty acid synthase),[6][7][8] and antagonist activity at the κ-opioid receptor (Ke = 490 nmol L−1)[9] as well as activity at the allosteric benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor as a negative allosteric modulator.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Xiong, Xifeng (22 December 2021). "Insights Into Amentoflavone: A Natural Multifunctional Biflavonoid". Frontiers in Pharmacology 12. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.768708. PMID 35002708.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Amentoflavone and its derivatives as novel natural inhibitors of human Cathepsin B". Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13 (20): 5819–5825. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.05.071. PMID 16084098.
- ↑ Williams, Christine A.; Harborne, Jeffrey B.; Tomas-Barberan A., Francisco (1987). "Biflavonoids in the primitive monocots Isophysis tasmanica and Xerophyta plicata". Phytochemistry 26 (9): 2553. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83875-3. Bibcode: 1987PChem..26.2553W.
- ↑ Kimura, Y; Ito, H; Ohnishi, R; Hatano, T (2010). "Inhibitory effects of polyphenols on human cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2C9 activity". Food Chem. Toxicol. 48 (1): 429–435. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.10.041. PMID 19883715.
- ↑ "Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum M1- Family Alanyl Aminopeptidase (M1AAP)". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assay/assay.cgi?aid=1445.
- ↑ Lee, JS; Lee, MS; Oh, WK; Sul, JY (2009). "Fatty acid synthase inhibition by amentoflavone induces apoptosis and antiproliferation in human breast cancer cells" (PDF). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32 (8): 1427–1432. doi:10.1248/bpb.32.1427. PMID 19652385. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/32/8/32_8_1427/_pdf.
- ↑ Wilsky, S; Sobotta, K; Wiesener, N; Pilas, J; Althof, N; Munder, T; Wutzler, P; Henke, A (2012). "Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by amentoflavone reduces coxsackievirus B3 replication". Arch. Virol. 157 (2): 259–269. doi:10.1007/s00705-011-1164-z. PMID 22075919.
- ↑ Lee, JS; Sul, JY; Park, JB; Lee, MS; Cha, EY; Song, IS; Kim, JR; Chang, ES (2013). "Fatty Acid Synthase Inhibition by Amentoflavone Suppresses HER2/neu(erbB2) Oncogene in SKBR3 Human Breast Cancer Cells". Phytother. Res. 27 (5): 713–720. doi:10.1002/ptr.4778. PMID 22767439.
- ↑ "Flavonoids as opioid receptor ligands: identification and preliminary structure-activity relationships". J. Nat. Prod. 70 (8): 1278–1282. 2007. doi:10.1021/np070194x. PMID 17685652.
- ↑ Hanrahan, JR; Chebib, M; Davucheron, NL; Hall, BJ; Johnston, GA (2003). "Semisynthetic preparation of amentoflavone: A negative modulator at GABA(A) receptors". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13 (14): 2281–2284. doi:10.1016/s0960-894x(03)00434-7. PMID 12824018.
External links
{{Navbox | name = GABA receptor modulators | title = GABA receptor modulators | state = collapsed | bodyclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Ionotropic | list1 = {{Navbox|subgroup | groupstyle = text-align:center | groupwidth = 5em
| group1 = GABAA | list1 =
- Agonists: (+)-Catechin
- Bamaluzole
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- BL-1020
- DAVA
- Dihydromuscimol
- GABA
- Gabamide
- GABOB
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- Homotaurine (tramiprosate, 3-APS)
- Ibotenic acid
- iso-THAZ
- iso-THIP
- Isoguvacine
- Isomuscimol
- Isonipecotic acid
- Kojic amine
- Lignans (e.g., honokiol)
- Methylglyoxal
- Monastrol
- Muscimol
- Nefiracetam
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone)
- Org 20599
- PF-6372865
- Phenibut
- Picamilon
- P4S
- Progabide
- Propofol
- Quisqualamine
- SL-75102
- TACA
- TAMP
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- ZAPA
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)<!--PMID: 9776662-->
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, [[Chemistry:Cholecholesterol]], THDOC)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., [[abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, [[Chemistry:Diethyl diethyl ether, Parparaldehyde]], sevoflurane)
- Antagonists: Bicuculline
- Coriamyrtin
- Dihydrosecurinine
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Hydrastine
- Hyenachin (mellitoxin)
- PHP-501
- Pitrazepin
- Securinine
- Sinomenine
- SR-42641
- SR-95103
- Thiocolchicoside
- Tutin
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., [[apalutamide, [[Chemistry:Bicalutbicalutamide, Enzalutenzalutamide, Chemistry:Flutamide|flut]]amide]], nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
| group2 = GABAA-ρ | list2 =
- Agonists: BL-1020
- CACA
- CAMP
- Homohypotaurine
- GABA
- GABOB
- Ibotenic acid
- Isoguvacine
- Muscimol
- N4-Chloroacetylcytosine arabinoside
- Picamilon
- Progabide
- TACA
- TAMP
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- Positive modulators: Allopregnanolone
- Alphaxolone
- ATHDOC
- Lanthanides
- Antagonists: (S)-2-MeGABA
- (S)-4-ACPBPA
- (S)-4-ACPCA
- 2-MeTACA
- 3-APMPA
- 4-ACPAM
- 4-GBA
- cis-3-ACPBPA
- CGP-36742 (SGS-742)
- DAVA
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- I4AA
- Isonipecotic acid
- Loreclezole
- P4MPA
- P4S
- SKF-97541
- SR-95318
- SR-95813
- TPMPA
- trans-3-ACPBPA
- ZAPA
- Negative modulators: 5α-Dihydroprogesterone
- Bilobalide
- Loreclezole
- Picrotoxin (picrotin, picrotoxinin)
- Pregnanolone
- ROD-188
- THDOC
- Zinc
}}
| group2 = Metabotropic
| list2 =
| below =
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- GABAA receptor positive modulators
- GABA metabolism/transport modulators
}}
 |

