Chemistry:7β-Hydroxy-DHEA
From HandWiki
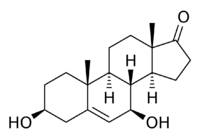
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3β,7β-Dihydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,4R,7S,9aR,9bS,11aS)-4,7-Dihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-one | |
| Other names
7β-OH-DHEA; Androst-5-en-3β,7β-diol-17-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H28O3 | |
| Molar mass | 304.430 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
7β-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone (7β-hydroxy-DHEA; 7β-OH-DHEA), also known as 3β,7β-dihydroxyandrost-5-ene-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and a metabolite of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). The major metabolic pathway of DHEA outside the liver is via 7-hydroxylation into 7α-OH-DHEA and 7β-OH-DHEA.[1] 7β-OH-DHEA has weak antiestrogenic activity, selectively antagonizing the estrogen receptor ERβ.[2]
7β-OH-DHEA is on the World Anti-Doping Agency list of prohibited substances in sporting.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Synthesis of 7alpha-hydroxy-dehydroepiandrosterone and 7beta-hydroxy-dehydroepiandrosterone". Steroids 70 (14): 970–3. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2005.07.006. PMID 16143359. "he major metabolic pathway for DHEA in extra-hepatic tissues is via 7-hydroxylation [18], [19] and [20].".
- ↑ "DHEA metabolites activate estrogen receptors alpha and beta". Steroids 78 (1): 15–25. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2012.10.002. PMID 23123738.
- ↑ "What is Prohibited". https://www.wada-ama.org/en/content/what-is-prohibited/prohibited-at-all-times/anabolic-agents.
 |

