Chemistry:Baclofen
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lioresal, Liofen, Gablofen, others |
| Other names | β-(4-chlorophenyl)-γ-aminobutyric acid (β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682530 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, intrathecal, transdermal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Well-absorbed |
| Protein binding | 30% |
| Metabolism | 85% excreted in urine/faeces unchanged. 15% metabolised by deamination |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 to 4 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (70–80%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 213.66 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Baclofen, sold under the brand name Lioresal among others, is a medication used to treat muscle spasticity such as from a spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis.[6][7] It may also be used for hiccups and muscle spasms near the end of life,[7] and off-label to treat alcohol use disorder[8][9] or opioid withdrawal symptoms.[10] It is taken orally (swallowed by mouth) or by intrathecal pump (delivered into the spinal canal via an implantable pump device).[6] It is also sometimes used transdermally (applied topically to the skin) in combination with gabapentin and clonidine prepared at a compounding pharmacy.[11]
Common side effects include sleepiness, weakness, and dizziness.[6] Serious side effects may occur if baclofen is rapidly stopped including seizures and rhabdomyolysis.[6] Use in pregnancy is of unclear safety while use during breastfeeding is probably safe.[12] It is believed to work by decreasing levels of certain neurotransmitters.[6] The adverse effects and safety profile associated with baclofen when it is combined with sedative drugs (for example alcohol or benzodiazepines) are unknown.[8]
Baclofen was approved for medical use in the United States in 1977.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[7][13] In 2020, it was the 108th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 6 million prescriptions.[14][15]
Medical uses
Baclofen is primarily used for the treatment of spastic movement disorders, especially in instances of spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.[16] Use in people with stroke or Parkinson's disease is not recommended.[16] Intrathecal baclofen is used for severe spasticity of spinal cord origin that is refractive to maximum doses of oral antispasmodic agents or who experience intolerable side effects.[17][18] Baclofen is also used in the treatment of sleep-related painful erections.[19]
Baclofen is sometimes used off-label as a treatment for alcohol use disorder to reduce the risk of relapse and to increase the number of days that a person can go without drinking alcohol (abstinence days).[8] It is also sometimes used for the treatment of opioid withdrawal symptoms, and may be superior for this purpose to the more-commonly used clonidine.[9][10]
Adverse drug reactions
Adverse effects include drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, headache, trouble sleeping, nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, or constipation.[1]
Withdrawal syndrome
Discontinuation of baclofen can be associated with a withdrawal syndrome which resembles benzodiazepine withdrawal and alcohol withdrawal. Withdrawal symptoms are more likely if baclofen is administered intrathecally or for long periods of time (more than a couple of months) and can occur from low or high doses.[20] The severity of baclofen withdrawal depends on the rate at which it is discontinued. Thus to minimise withdrawal symptoms, the dose should be tapered down slowly when discontinuing baclofen therapy. Abrupt withdrawal is more likely to result in severe withdrawal symptoms. Acute withdrawal symptoms can be eased or completely reversed by re-initiating therapy with baclofen.[21]
Withdrawal symptoms may include auditory hallucinations, visual hallucinations, tactile hallucinations, delusions, confusion, agitation, delirium, disorientation, fluctuation of consciousness, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, inattention, memory impairments, perceptual disturbances, itching, anxiety, depersonalization, hypertonia, hyperthermia (higher than normal temperature without infection), formal thought disorder, psychosis, mania, mood disturbances, restlessness, and behavioral disturbances, tachycardia, seizures, tremors, autonomic dysfunction, hyperpyrexia (fever), extreme muscle rigidity resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome and rebound spasticity.[21][20]
Abuse

Baclofen, at standard dosing, does not appear to possess addictive properties, and has not been associated with any degree of drug craving.[22][23] Euphoria is however listed as a common to very common side-effect of baclofen in the BNF 75.[24] There are very few cases of abuse of baclofen for reasons other than attempted suicide.[22] In contrast to baclofen, another GABAB receptor agonist, γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), has been associated with euphoria, abuse, and addiction.[25] These effects are likely mediated not by activation of the GABAB receptor, but rather by activation of the GHB receptor.[25] Baclofen possesses both sedative and anxiolytic properties.[23]
Overdose
Reports of overdose indicate that baclofen may cause symptoms including vomiting, general weakness, sedation, respiratory insufficiency, seizures, unusual pupil size[clarification needed], dizziness,[1] headaches,[1] itching, hypothermia, bradycardia, cardiac conduction abnormalities, hypertension, hyporeflexia and coma sometimes mimicking brain death.[26] Overdose may require intubation and length of mechanical ventilation required may correlate with serum baclofen levels shortly after ingestion. Symptoms may persist even after the point at which serum baclofen levels are undetectable.[27]
Pharmacology
Chemically, baclofen is a derivative of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is believed to work by activating (or agonizing) GABA receptors, specifically the GABAB receptors.[28] Its beneficial effects in spasticity result from its actions in the brain and spinal cord.[29]
Pharmacodynamics
Baclofen produces its effects by activating the GABAB receptor, similar to the drug phenibut which also activates this receptor and shares some of its effects. Baclofen is postulated to block mono-and-polysynaptic reflexes by acting as an inhibitory ligand, inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. However, baclofen does not have significant affinity for the GHB receptor, and has no known abuse potential.[30] Agonism of the GABAB receptor is responsible for baclofen's range of therapeutic properties.
Similarly to phenibut (β-phenyl-GABA), as well as pregabalin (β-isobutyl-GABA), which are close analogues of baclofen, baclofen (β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA) has been found to block α2δ subunit-containing voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs).[31] However, it is weaker relative to phenibut in this action (Ki = 23 and 39 μM for R- and S-phenibut and 156 μM for baclofen).[31] Moreover, baclofen is in the range of 100-fold more potent by weight as an agonist of the GABAB receptor in comparison to phenibut, and in accordance, is used at far lower relative dosages. As such, the actions of baclofen on α2δ subunit-containing VGCCs are likely not clinically relevant.[31]
For drug-reward and addiction, baclofen's mechanism of action is thought to be through its affect on the mesolimbic dopamine pathway, specifically leading to a decrease in dopamine release associated with alcohol.[8] GABAB receptor activation (GABAB receptor agonist activity) may decrease or inhibit alcohol's ability to activate or fire dopaminergic neurons following exposure to alcohol. Baclofen's mechanism of action is not thought to be mediated through its muscle-relaxing or sedative properties, however there is evidence to suggest that the GABAB receptor-activation in the limbus may also reduce feelings of anxiety in people with alcohol use disorder.[8]
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and is widely distributed throughout the body. Biotransformation is low: the drug is predominantly excreted unchanged by the kidneys.[32] The half-life of baclofen is roughly 2–4 hours; it therefore needs to be administered frequently throughout the day to control spasticity appropriately.
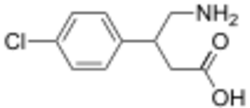
Chemistry
Baclofen is a white (or off-white) mostly odorless crystalline powder, with a molecular weight of 213.66 g/mol. It is slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, and insoluble in chloroform.
History
Historically, baclofen was designed as a drug for treating epilepsy. It was first made at Ciba-Geigy, by the Swiss chemist Heinrich Keberle, in 1962.[33][34] Its effect on epilepsy was disappointing, but it was found that in certain people, spasticity decreased. In 1971, it was introduced as a treatment for certain form of spasticity. It approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1977.[35]
Intrathecal baclofen was first introduced in 1984 to treat severe spinal spasticity. This administration route aimed to avoid supraspinal side effects.[36][37]
In his 2008 book, Le Dernier Verre (translated literally as The Last Glass or The End of my Addiction), French-American cardiologist Olivier Ameisen described how he treated his alcoholism with baclofen. Inspired by this book, an anonymous donor gave $750,000 to the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands to initiate a clinical trial of high-dose baclofen, which Ameisen had called for since 2004.[38] The trial concluded, "In summary, the current study did not find evidence of a positive effect of either low or high doses of baclofen in AD patients. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that baclofen is an effective medication for the treatment of severe, heavy drinking AD patients not responding to or not accepting routine psychosocial interventions."[39]
Society and culture
Routes of administration
Baclofen can be administered, orally, intrathecally (directly into the cerebral spinal fluid) using a pump implanted under the skin, or transdermally as part of a pain-relieving and muscle-relaxing topical cream mix (also containing gabapentin and clonidine) prepared at a compounding pharmacy.[11][40]
Intrathecal pumps offer much lower doses of baclofen because they are designed to deliver the medication directly to the spinal fluid rather than going through the digestive and blood system first. A drug concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid more than 10 times greater than when given orally is achieved with this route versus. At the same time the blood concentration levels are almost undetectable, thus minimizing side effects.[40]
Besides those with spasticity, intrathecal administration is also used in patients with cerebral palsy[40] or multiple sclerosis who have severe painful spasms which are not controllable by oral baclofen.[citation needed] With pump administration, a test dose is first injected into the spinal fluid to assess the effect, and if successful in relieving spasticity, a chronic intrathecal catheter is inserted from the spine through the abdomen and attached to the pump which is implanted under the abdomen's skin, usually by the ribcage.[citation needed] The pump is computer-controlled for automatic dosage and its reservoir can be replenished by percutaneous injection.[citation needed] The pump also has to be replaced every five years or so when the battery is changed.[citation needed]
Other names
Synonyms include chlorophenibut. Brand names include Beklo, Baclodol, Flexibac, Gablofen, Kemstro, Liofen, Lioresal, Lyflex, Clofen, Muslofen, Bacloren, Baklofen, Sclerofen, Pacifen and others.
Research
Baclofen is being studied for the treatment of alcoholism.[22] Evidence as of 2019 is not conclusive enough to recommend its use for this purpose.[22][41] In 2014, the French drug agency ANSM issued a three-year temporary recommendation allowing the use of baclofen in alcoholism.[42] In 2018, baclofen received a Marketing Authorization for use in alcoholism treatment from the agency if all other treatments are not effective.[43]
It is being studied along with naltrexone and sorbitol for Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT), a hereditary disease that causes peripheral neuropathy.[44] It is also being studied for cocaine addiction.[45] Baclofen and other muscle relaxants are being studied for potential use for persistent hiccups.[46][47]
From 2014 to 2017 baclofen misuse, toxicity and use in suicide attempts among adults in the US increased.[48]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Gablofen- baclofen injection injection, solution". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=00d3e846-dd92-448d-9ab8-6a07be823cc1.
- ↑ "Lioresal- baclofen injection". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=351cde63-00fa-404a-92df-cb055e991840.
- ↑ "Ozobax- baclofen solution". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=92153f69-bc9b-4bef-9a8e-751effde5c7e.
- ↑ "Lyvispah- baclofen granule". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=a7d2dc58-e167-4ebc-ac1d-932f000fb412.
- ↑ "Fleqsuvy- baclofen suspension". 4 February 2022. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=9076d6ce-bbc2-4a9f-9cb9-2de1b675b9aa.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 "Baclofen Monograph for Professionals" (in en). American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/baclofen.html.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 1092. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 "Baclofen for alcohol use disorder". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1 (1): CD012557. January 2023. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd012557.pub3. PMID 36637087.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Baclofen versus clonidine in the treatment of opiates withdrawal, side-effects aspect: a double-blind randomized controlled trial". Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 26 (1): 67–71. February 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2710.2001.00325.x. PMID 11286609.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Baclofen for maintenance treatment of opioid dependence: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial [ISRCTN32121581"]. BMC Psychiatry 3: 16. November 2003. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-3-16. PMID 14624703.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Baclofen 2%, Gabapentin 6%, and Clonidine Hydrochloride 0.1% in Pluronic Lecithin Organogel". Jobson Medical Information LLC. 17 November 2010. https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/baclofen-2-gabapentin-6-and-clonidine-hydrochloride-01-in-pluronic-lecithin-organogel.
- ↑ "Baclofen Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/baclofen.html.
- ↑ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". 29 June 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/generic-drugs/competitive-generic-therapy-approvals.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Baclofen - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Baclofen.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Baclofen". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/baclofen.html.
- ↑ "Baclofen". StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. May 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526037/.
- ↑ "Pharmacotherapy". CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.. McGraw Hill. 2014. ISBN 978-0-07-179329-2. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=1180§ionid=70377149.
- ↑ "Sleep-Related Painful Erections-A Case Series of 24 Patients Regarding Diagnostics and Treatment Options". Sexual Medicine 5 (4): e237–e243. December 2017. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2017.09.001. PMID 29066083.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "[Severe hyperthermia caused by sudden withdrawal of continuous intrathecal administration of baclofen]". Annales Françaises d'Anesthésie et de Réanimation 15 (5): 659–662. 1996. doi:10.1016/0750-7658(96)82130-7. PMID 9033759.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Delirium associated with baclofen withdrawal: a review of common presentations and management strategies". Psychosomatics 46 (6): 503–507. Nov–Dec 2005. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.46.6.503. PMID 16288128.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "Effectiveness and safety of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependent patients". CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets 9 (1): 33–44. March 2010. doi:10.2174/187152710790966614. PMID 20201813.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Efficacy and tolerability of baclofen in substance use disorders: a systematic review". European Addiction Research 19 (6): 325–345. 2013. doi:10.1159/000347055. PMID 23775042.
- ↑ "BNF is only available in the UK". https://www.nice.org.uk/bnf-uk-only.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 "The distribution of gamma-hydroxybutyrate-induced Fos expression in rat brain: comparison with baclofen". Neuroscience 158 (2): 441–455. January 2009. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.10.011. PMID 18996447.
- ↑ "Toxicologic Confounders of Brain Death Determination: A Narrative Review". Neurocritical Care 34 (3): 1072–1089. June 2021. doi:10.1007/s12028-020-01114-y. PMID 33000377.
- ↑ "Baclofen overdose: drug experimentation in a group of adolescents". Pediatrics 101 (6): 1045–1048. June 1998. doi:10.1542/peds.101.6.1045. PMID 9606233.
- ↑ "Product Information Clofen". Millers Point, Australia: Alphapharm Pty Limited. 7 June 2017. https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-04975-3.
- ↑ "Baclofen: Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference". London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. 9 January 2017. https://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/martindale/current/5702-z.htm.
- ↑ "Behavioral analyses of GHB: receptor mechanisms". Pharmacology & Therapeutics 121 (1): 100–114. January 2009. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.10.003. PMID 19010351.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 "R-phenibut binds to the α2-δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels and exerts gabapentin-like anti-nociceptive effects". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 137: 23–29. October 2015. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2015.07.014. PMID 26234470.
- ↑ "Plasma and urinary excretion kinetics of oral baclofen in healthy subjects". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 37 (2): 181–184. 1989. doi:10.1007/BF00558228. PMID 2792173.
- ↑ "Chemistry and Pharmacology of GABAb Receptor Ligands". GABAb Receptor Pharmacology – A Tribute to Norman Bowery. Advances in Pharmacology. 58. 2010. pp. 19–62. doi:10.1016/S1054-3589(10)58002-5. ISBN 978-0-12-378647-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=_iMDQOA2UIsC&pg=PA19.
- ↑ "An update on GABA analogs for CNS drug discovery". Recent Patents on CNS Drug Discovery 1 (1): 113–118. January 2006. doi:10.2174/157488906775245291. PMID 18221197. http://www.bentham.org/rpcn/samples/rpcn1-1/Yogeeswari.pdf.
- ↑ "Baclofen therapeutics, toxicity, and withdrawal: A narrative review". SAGE Open Medicine 9: 20503121211022197. 2021. doi:10.1177/20503121211022197. PMID 34158937.
- ↑ "Intrathecal baclofen". Baillière's Clinical Neurology 2 (1): 73–86. April 1993. PMID 8143075.
- ↑ "[Intrathecal baclofen. Experimental and pharmacokinetic studies]" (in French). Neuro-Chirurgie 49 (2-3 Pt 2): 271–5. May 2003. PMID 12746702.
- ↑ "Addiction research. Anonymous alcoholic bankrolls trial of controversial therapy". Science 332 (6030): 653. May 2011. doi:10.1126/science.332.6030.653. PMID 21551041. Bibcode: 2011Sci...332..653E.
- ↑ "Efficacy and safety of high-dose baclofen for the treatment of alcohol dependence: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind controlled trial". European Neuropsychopharmacology 26 (12): 1950–1959. December 2016. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.10.006. PMID 27842939.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 "Intrathecal baclofen use in adults with cerebral palsy". Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 51 (Suppl 4): 106–12. October 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03422.x. PMID 19740217.
- ↑ "Baclofen for alcohol withdrawal". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019 (11). November 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008502.pub6. PMID 31689723.
- ↑ "Une recommandation temporaire d'utilisation (RTU) est accordée pour le baclofène – Point d'information". L'Agence nationale de sécurité du médicament et des produits de santé (ANSM). 14 March 2014. http://ansm.sante.fr/S-informer/Points-d-information-Points-d-information/Une-recommandation-temporaire-d-utilisation-RTU-est-accordee-pour-le-baclofene-Point-d-information.
- ↑ "Autorisation du baclofène: des conditions d'utilisation trop restrictives ? - A la une" (in fr-FR). L'Agence nationale de sécurité du médicament et des produits de santé (ANSM). 25 October 2018. https://destinationsante.com/autorisation-du-baclofene-des-conditions-dutilisation-trop-restrictives.html.
- ↑ "An exploratory randomised double-blind and placebo-controlled phase 2 study of a combination of baclofen, naltrexone and sorbitol (PXT3003) in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 9 (1): 199. December 2014. doi:10.1186/s13023-014-0199-0. PMID 25519680.
- ↑ "New medications for the treatment of cocaine dependence". Psychiatry 2 (12): 44–48. December 2005. PMID 21120115.
- ↑ "What Is the Latest on Treatment for Hiccups?". Medscape. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/844420.
- ↑ "Baclofen, a treatment for chronic hiccup". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 16 (2): 125–132. August 1998. doi:10.1016/S0885-3924(98)00039-6. PMID 9737104.
- ↑ "Trends in gabapentin and baclofen exposures reported to U.S. poison centers". Clinical Toxicology 58 (7): 763–772. July 2020. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1687902. PMID 31786961.
External links
- "Baclofen". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/baclofen.
{{Navbox | name = GABA receptor modulators | title = GABA receptor modulators | state = collapsed | bodyclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Ionotropic | list1 = {{Navbox|subgroup | groupstyle = text-align:center | groupwidth = 5em
| group1 = GABAA | list1 =
- Agonists: (+)-Catechin
- Bamaluzole
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- BL-1020
- DAVA
- Dihydromuscimol
- GABA
- Gabamide
- GABOB
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- Homotaurine (tramiprosate, 3-APS)
- Ibotenic acid
- iso-THAZ
- iso-THIP
- Isoguvacine
- Isomuscimol
- Isonipecotic acid
- Kojic amine
- Lignans (e.g., honokiol)
- Methylglyoxal
- Monastrol
- Muscimol
- Nefiracetam
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone)
- Org 20599
- PF-6372865
- Phenibut
- Picamilon
- P4S
- Progabide
- Propofol
- Quisqualamine
- SL-75102
- TACA
- TAMP
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- ZAPA
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)<!--PMID: 9776662-->
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, [[Chemistry:Cholecholesterol]], THDOC)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., [[abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, [[Chemistry:Diethyl diethyl ether, Parparaldehyde]], sevoflurane)
- Antagonists: Bicuculline
- Coriamyrtin
- Dihydrosecurinine
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Hydrastine
- Hyenachin (mellitoxin)
- PHP-501
- Pitrazepin
- Securinine
- Sinomenine
- SR-42641
- SR-95103
- Thiocolchicoside
- Tutin
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., [[apalutamide, [[Chemistry:Bicalutbicalutamide, Enzalutenzalutamide, Chemistry:Flutamide|flut]]amide]], nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
| group2 = GABAA-ρ | list2 =
- Agonists: BL-1020
- CACA
- CAMP
- Homohypotaurine
- GABA
- GABOB
- Ibotenic acid
- Isoguvacine
- Muscimol
- N4-Chloroacetylcytosine arabinoside
- Picamilon
- Progabide
- TACA
- TAMP
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- Positive modulators: Allopregnanolone
- Alphaxolone
- ATHDOC
- Lanthanides
- Antagonists: (S)-2-MeGABA
- (S)-4-ACPBPA
- (S)-4-ACPCA
- 2-MeTACA
- 3-APMPA
- 4-ACPAM
- 4-GBA
- cis-3-ACPBPA
- CGP-36742 (SGS-742)
- DAVA
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- I4AA
- Isonipecotic acid
- Loreclezole
- P4MPA
- P4S
- SKF-97541
- SR-95318
- SR-95813
- TPMPA
- trans-3-ACPBPA
- ZAPA
- Negative modulators: 5α-Dihydroprogesterone
- Bilobalide
- Loreclezole
- Picrotoxin (picrotin, picrotoxinin)
- Pregnanolone
- ROD-188
- THDOC
- Zinc
}}
| group2 = Metabotropic
| list2 =
| below =
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- GABAA receptor positive modulators
- GABA metabolism/transport modulators
}}
 |


