Chemistry:Aceglutamide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
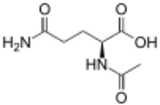
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Acetamido-5-amino-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-(Acetylamino)-glutaramidic acid
α-N-Acetylglutamine;[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | aceglutamide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 188.183 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 197 °C (387 °F; 470 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aceglutamide (brand name Neuramina), or aceglutamide aluminium (brand name Glumal), also known as acetylglutamine, is a psychostimulant, nootropic, and antiulcer agent that is marketed in Spain and Japan .[1][2][3][4] It is an acetylated form of the amino acid L-glutamine, the precursor of glutamate in the body and brain.[5] Aceglutamide functions as a prodrug to glutamine with improved potency and stability.[5]
Aceglutamide is used as a psychostimulant and nootropic, while aceglutamide aluminium is used in the treatment of ulcers.[6][7][8][9] Aceglutamide can also be used as a liquid-stable source of glutamine to prevent damage from protein energy malnutrition.[10][11][12] The drug has shown neuroprotective effects in an animal model of cerebral ischemia.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA3.
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 6–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA6.
- ↑ William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 35–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=_J2ti4EkYpkC&pg=PA35.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA3.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Neuroprotective effects of Aceglutamide on motor function in a rat model of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion". Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience 33 (5): 741–59. 2015. doi:10.3233/RNN-150509. PMID 26444640.
- ↑ "[Studies on defensive factors of experimental ulcers (2). Increasing action of aceglutamide aluminium on defensive factors in acetic acid ulcers of rats (author's transl)]". Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Folia Pharmacologica Japonica 79 (4): 327–34. April 1982. doi:10.1254/fpj.79.327. PMID 7095654.
- ↑ "Inhibitory effect of N-acetyl-L-glutamine aluminium complex (KW-110) and related compounds on gastric erosion and motility in stressed animals". Oyo Yakuri 8 (1): 1–6. 1974.
- ↑ "[Comparative study of 3 drugs (aceglutamide aluminium, zinc acexamate, and magaldrate) in the long-term maintenance treatment (1 year) of peptic ulcer]". Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas 80 (2): 91–4. August 1991. PMID 1790087.
- ↑ "Effect of N-acetyl-L-glutamine aluminium complex (KW-110), an antiulcer agent, on the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced exacerbation of gastric ulcer in rats". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 32 (2): 307–13. April 1982. doi:10.1254/jjp.32.307. PMID 7098147.
- ↑ "N-acetyl-L-glutamine, a liquid-stable source of glutamine, partially prevents changes in body weight and on intestinal immunity induced by protein energy malnutrition in pigs". Digestive Diseases and Sciences 52 (3): 650–8. March 2007. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9500-y. PMID 17253138.
- ↑ Sasaki, Kazuyuki & Toru Hayakawa, "Treating medicine for digestive organ disease", JP patent H10101576, published 1998-04-21, assigned to Nisshin Flour Milling Co Ltd.
- ↑ Baxter, Jeffrey, "Methods and compositions for providing glutamine", US patent application 2003099722, published 2003-05-29, assigned to Abbott Laboratories, abandoned during patent examination
 |

