Chemistry:Arfendazam
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
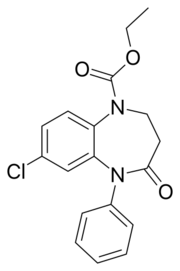
| Formula | C18H17ClN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 344.792 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Arfendazam (INN)[1] is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. Arfendazam is a 1,5-benzodiazepine, with the nitrogen atoms located at positions 1 and 5 of the diazepine ring, and so is most closely related to other 1,5-benzodiazepines such as clobazam.
Arfendazam has sedative and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, but is a partial agonist at GABAA receptors, so the sedative effects are relatively mild and it produces muscle relaxant effects only at very high doses.[2][3]
Arfendazam produces an active metabolite lofendazam, which is thought to be responsible for part of its effects.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances. Proposed International Nonproprietary Names (Prop. INN): List 39. Supplement to WHO Chronicle". World Health Organization. March 1978. p. 3. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/PL39.pdf.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine receptor interactions of arfendazam, a novel 1, 5-benzodiazepine.". Pharmacopsychiatry 18 (1): 10–1. January 1985. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1017288.
- ↑ "In vitro and in vivo studies of the mechanism of action of arfendazam, a novel 1, 5-benzodiazepine.". Pharmacopsychiatry 19 (4): 314–315. July 1986. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1017251.
- ↑ The Pharmacology of Sleep.. Springer Science & Business Media. December 2012. ISBN 978-3-540-58961-7.
 |

