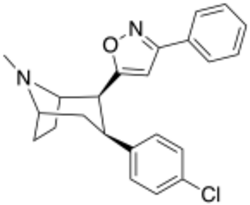
Chemistry:RTI-177
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H23ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 378.90 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
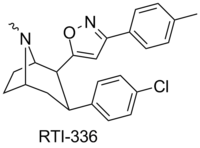
RTI(-4229)-177 (2β-(3-phenylisoxazol-5-yl)-3β-(4-chlorophenyl)tropane, β-CPPIT) is a synthetic stimulant drug from the phenyltropane family, which acts as a DRI with micromolar affinity for the SERT.[1] RTI-177 has an unusually long duration of action of 20 hours or more, substantially longer than the related compound RTI-336 from which it differs in molecular structure only by the absence of a p-methyl group.[2]
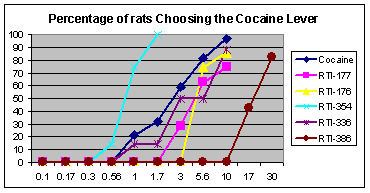
"the nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-126 and the DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-150 and RTI-336 both had a faster rate of onset (30 min) and a short duration of action (4h). In contrast, the nonselective monoamine transporter inhibitor RTI-112 had a slower rate of onset (30–60 min) and a longer duration of action (10h). The DAT-selective inhibitors RTI-171 and RTI-177 also had slower rates of onset (30–120 min), but RTI-171 had a short duration of action (2.5 h) while RTI-177 had a very long duration of action (20 h)."[3]
Update
Comparison of six MAT inhibitors
| RTI | X | R | [3H]CFT | [3H]Nisoxetine | [3H]Paroxetine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coc | — | — | 89.1 | 3298 (1986) | 1045 (45) |
| 177 | Cl | phenyl | 1.28 | 504 (304) | 2420 (220) |
| 176 | Me | phenyl | 1.58 | 398 (239) | 5110 (465) |
| 354 | Me | ethyl | 1.62 | 299 (180) | 6400 (582) |
| 336 | Cl | p-cresyl | 4.09 | 1714 (1033) | 5741 (522) |
| 386 | Me | p-anisoyl | 3.93 | 756 (450) | 4027 (380) |
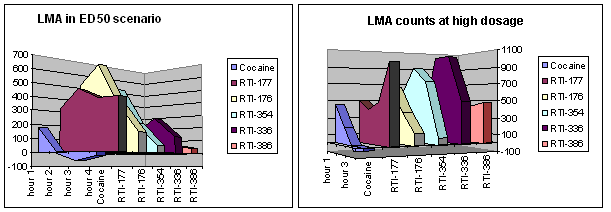
In the Lindsey paper, RTI-177 was wrongly considered to be a dual inhibitor of the NET, although this was later found out to be incorrect.[citation needed]
"In acute toxicity studies in male rats, 3β-(4-chlorophenyl)-2β-[3-(4’-methylphenyl)isoxazol-5-yl]tropane (RTI-336) possessed an LD50 of 180 mg/kg after oral administration, compared with 49 mg/kg for RTI-177 (unpublished results, Howell 2005; Table 9). These results suggested that RTI-336 was a better candidate than RTI-177 for further preclinical development."[2]
Also the potency of the heterocyclic compounds is not as great as would be predicted based on in vitro test results.
References
- ↑ "Effects of dopamine transporter inhibitors on cocaine self-administration in rhesus monkeys: relationship to transporter occupancy determined by positron emission tomography neuroimaging". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 309 (3): 959–69. June 2004. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.060293. PMID 14982963. http://research.yerkes.emory.edu/Howell/JPET309.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Development of the dopamine transporter selective RTI-336 as a pharmacotherapy for cocaine abuse". The AAPS Journal 8 (1): E196-203. March 2006. doi:10.1208/aapsj080124. PMID 16584128. PMC 2751440. http://www.aapsj.org/view.asp?art=aapsj080124.
- ↑ "Faster onset and dopamine transporter selectivity predict stimulant and reinforcing effects of cocaine analogs in squirrel monkeys". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 86 (1): 45–54. January 2007. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.12.006. PMID 17258302.
 |