(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Short description: Antihypertensive drug of the calcium channel blocker class
Nicardipine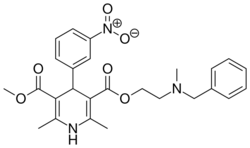 |
| Clinical data |
|---|
| Trade names | Cardene |
|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
|---|
| MedlinePlus | a695032 |
|---|
Routes of
administration | Oral, intravenous |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
| Legal status |
|---|
| Legal status |
- In general: ℞ (Prescription only)
|
|---|
| Pharmacokinetic data |
|---|
| Protein binding | >95% |
|---|
| Elimination half-life | 8.6 hours |
|---|
| Identifiers |
|---|
2-[benzyl(methyl)amino]ethylmethyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
|---|
| DrugBank | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEBI | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| Chemical and physical data |
|---|
| Formula | C26H29N3O6 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 479.533 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
| Melting point | 136–138 °C (277–280 °F) |
|---|
O=C(OCCN(Cc1ccccc1)C)\C2=C(\N/C(=C(/C(=O)OC)C2c3cccc([N+]([O-])=O)c3)C)C
|
InChI=1S/C26H29N3O6/c1-17-22(25(30)34-4)24(20-11-8-12-21(15-20)29(32)33)23(18(2)27-17)26(31)35-14-13-28(3)16-19-9-6-5-7-10-19/h5-12,15,24,27H,13-14,16H2,1-4H3  Y YKey:ZBBHBTPTTSWHBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y
|
| (verify) |
Nicardipine (Cardene) is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and angina. It belongs to the dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blockers (CCBs). It is also used for Raynaud's phenomenon. It is available in by mouth and intravenous formulations. It has been used in percutaneous coronary intervention.[1]
Its mechanism of action and clinical effects closely resemble those of nifedipine and the other dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (amlodipine, felodipine), except that nicardipine is more selective for cerebral and coronary blood vessels. It is primarily a peripheral arterial vasodilator, thus unlike the nitrovasodilators (nitroglycerin and nitroprusside), cardiac preload is minimally affected. It has the longest duration among parenteral CCBs. [2][3] As its use may lead to reflex tachycardia, it is advisable to use it in conjunction with a beta-blocker.[3][2]
It was patented in 1973 and approved for medical use in 1981.[4]
Nicardipine was approved by the FDA in December 1988. The patent for both Cardene and Cardene SR expired in October 1995.[5]
See also
References
|
|---|
{{Navbox
| name = GABA receptor modulators
| title = GABA receptor modulators
| state = collapsed
| bodyclass = hlist
| groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Ionotropic
| list1 = {{Navbox|subgroup
| groupstyle = text-align:center
| groupwidth = 5em
| group1 = GABAA
| list1 =
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)<!--PMID: 9776662-->
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, [[Chemistry:Cholecholesterol]], THDOC)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., [[abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, [[Chemistry:Diethyl diethyl ether, Parparaldehyde]], sevoflurane)
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., [[apalutamide, [[Chemistry:Bicalutbicalutamide, Enzalutenzalutamide, Chemistry:Flutamide|flut]]amide]], nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
| group2 = GABAA-ρ
| list2 =
}}
| group2 = Metabotropic
| list2 =
| below =
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- GABAA receptor positive modulators
- GABA metabolism/transport modulators
}}
|
|---|
Receptor
(ligands) | | GlyR |
- Positive modulators: Alcohols (e.g., brometone, chlorobutanol (chloretone), ethanol (alcohol), tert-butanol (2M2P), tribromoethanol, trichloroethanol, trifluoroethanol)
- Alkylbenzene sulfonate
- Anandamide
- Barbiturates (e.g., pentobarbital, sodium thiopental)
- Chlormethiazole
- D12-116
- Dihydropyridines (e.g., nicardipine)
- Etomidate
- Ginseng constituents (e.g., ginsenosides (e.g., ginsenoside-Rf))
- Glutamic acid (glutamate)
- Ivermectin
- Ketamine
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., alfaxolone, pregnenolone (eltanolone), pregnenolone acetate, minaxolone, ORG-20599)
- Nitrous oxide
- Penicillin G
- Propofol
- Tamoxifen
- Tetrahydrocannabinol
- Triclofos
- Tropeines (e.g., atropine, bemesetron, cocaine, LY-278584, tropisetron, zatosetron)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, desflurane, diethyl ether (ether), enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane, sevoflurane, toluene, trichloroethane (methyl chloroform), trichloroethylene)
- Xenon
- Zinc
- Antagonists: 2-Aminostrychnine
- 2-Nitrostrychnine
- 4-Phenyl-4-formyl-N-methylpiperidine
- αEMBTL
- Bicuculline
- Brucine
- Cacotheline
- Caffeine
- Colchicine
- Colubrine
- Cyanotriphenylborate
- Dendrobine
- Diaboline
- Endocannabinoids (e.g., 2-AG, anandamide (AEA))
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- Gelsemine
- iso-THAZ
- Isobutyric acid
- Isonipecotic acid
- Isostrychnine
- Laudanosine
- N-Methylbicuculline
- N-Methylstrychnine
- N,N-Dimethylmuscimol
- Nipecotic acid
- Pitrazepin
- Pseudostrychnine
- Quinolines (e.g., 4-hydroxyquinoline, 4-hydroxyquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, 5,7-CIQA, 7-CIQ, 7-TFQ, 7-TFQA)
- RU-5135
- Sinomenine
- Strychnine
- Thiocolchicoside
- Tutin
|
|---|
| NMDAR | |
|---|
|
|---|
Transporter
(blockers) | |
|---|
|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicardipine. Read more |



