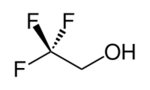
Chemistry:2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2,2-Trifluoroethan-1-ol | |
| Other names
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1733203 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| 2532 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3F3O | |
| Molar mass | 100.04 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.325±0.06 g/mL @ 20 °C, 760 Torr liquid |
| Melting point | −43.5 °C (−46.3 °F; 229.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 74.0 °C (165.2 °F; 347.1 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility in ethanol | Miscible |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.46±0.10 Most Acidic Temp: 25 °C |
| Viscosity | 0.9 cSt @ 37.78 °C |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
-886.6 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H301, H312, H315, H318, H331, H332, H335, H360, H373 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+310, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P310, P311, P312 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related alcohols
|
Hexafluoro-2-propanol |
Related compounds
|
1,1,1-Trifluoroethane Trifluoroacetic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol is the organic compound with the formula CF3CH2OH. Also known as TFE or trifluoroethyl alcohol, this colourless, water-miscible liquid has a smell reminiscent of ethanol. Due to the electronegativity of the trifluoromethyl group, this alcohol exhibits a stronger acidic character compared to ethanol.
Synthesis
Trifluoroethanol is produced industrially by hydrogenation or the hydride reduction of derivatives of trifluoroacetic acid, such as the esters or acyl chloride.[1]
TFE can also be prepared by hydrogenolysis of compounds of generic formula CF3−CHOH−OR (where R is hydrogen or an alkyl group containing from one to eight carbon atoms), in the presence of a palladium containing catalyst deposited on activated charcoal.[citation needed] As a co-catalyst for this conversion tertiary aliphatic amines like triethylamine are commonly employed.
Properties
Trifluoroethanol is used as a specialized solvent in organic chemistry.[2][3] Oxidations of sulfur compounds using hydrogen peroxide are effectively conducted in TFE.[4]
It competitively inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase for example.[5]
TFE forms complexes with Lewis bases such as THF or pyridine through hydrogen bonding, yielding 1:1 adducts.[6] It is classified as a hard Lewis acid and its acceptor properties are discussed in the ECW model yielding EA = 2.07 and CA = 1.06.
TFE can be used in biochemical experiments to stabilize alpha helix.[7][8] There are also stable beta sheets in TFE, suggesting that TFE stabilizes the secondary structure the sequence has a preference for.[8]
Reactions
Oxidation of trifluoroethanol yields trifluoroacetic acid. It also serves as a source of the trifluoroethoxy group for various chemical reactions (Still-Gennari modification of HWE reaction).
2,2,2-Trifluoroethyl vinyl ether, an inhaled drug introduced clinically under the tradename Fluoromar, features a vinyl ether of trifluorethanol. This species was prepared by the reaction of trifluoroethanol with acetylene.[1]
Safety
Trifluoroethanol is classified as toxic to blood, the reproductive system, bladder, brain, upper respiratory tract and eyes.[9] Research has shown it to be a testicular toxicant in rats and dogs.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Fluorine Compounds, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. 2000. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349. ISBN 3527306730.
- ↑ "Fluorinated Alcohols: A New Medium for Selective and Clean Reaction". Synlett (1): 18–29. 2004. doi:10.1055/s-2003-44973.
- ↑ "Fluorinated Alcohols as Solvents, Cosolvents and Additives in Homogeneous Catalysis". Synthesis 2007 (19): 2925–2943. 2007. doi:10.1055/s-2007-983902.
- ↑ "Mild and Selective Oxidation of Sulfur Compounds in Trifluorethanol: Diphenyl Disulfide and Methyl Phenyl Sulfoxide". Organic Syntheses 80: 184. 2003. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.080.0184. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=v80p0184.
- ↑ "The competitive inhibition of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase by 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol". Biochemical Education 26 (3): 239–242. 1998. doi:10.1016/s0307-4412(98)00073-9.
- ↑ "Linear enthalpy-spectral shift correlations for 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol". Journal of Physical Chemistry 74 (19): 3535–3543. 1970. doi:10.1021/j100713a017.
- ↑ "Trifluoroethanol direct interactions with protein backbones destabilize α-helices". Journal of Molecular Liquids 365: 120209. 2022-11-01. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120209. ISSN 0167-7322. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167732222017482.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Environment affects amino acid preference for secondary structure". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89 (10): 4462–4465. May 1992. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.10.4462. PMID 1584778. Bibcode: 1992PNAS...89.4462Z.
- ↑ "Sciencelab MSDS". http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9925323.
- ↑ Fischer Scientific MSDS
External links
- Halocarbon Fluorochemicals
- United States Patent number 4,647,706 "Process for the synthesis of 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol and 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoroisopropanol"
 |


