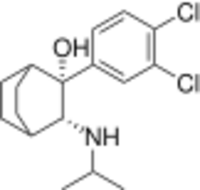
Chemistry:Cilobamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H23Cl2NO |
| Molar mass | 328.28 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Cilobamine is a drug which acts as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and has stimulant and antidepressant effects.[1][2]
It can clearly be seen that the structure is based on dichloroisoprenaline that has been fused onto the bicycloalkane scaffold.
Synthesis

An intramolecular Dieckmann cyclization on methyl 4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylate [1401222-79-4] (3) with sodium hydride base gives reaction Methyl 3-oxobicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2-carboxylate [30144-30-0] (4). Treatment with sodium nitrite introduces an isonitroso group adjacent to the ketone, giving 3-Hydroxyiminobicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-one, CID:131066320 (5). Addition of the aryl Grignard reagent, and reduction of the oxime gives CID:154108204 (6). A reductive amination of the primary amino group with acetone then completed the synthesis of cilobamine (7).
See also
- Fencamfamine
- Manifaxine
References
- ↑ "Dose related induction of the drug metabolizing enzymes of rat liver by cilobamine". Fundamental and Applied Toxicology 4 (2 Pt 1): 261–9. April 1984. doi:10.1016/0272-0590(84)90127-1. PMID 6724198.
- ↑ "Cilobamine in the treatment of atypical depression". Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental 3 (3): 201–205. 1988. doi:10.1002/hup.470030308.
- ↑ DE2003744 idem Jules Freedman, U.S. Patent 3,651,142 (1970 to Colgate Palmolive Co).
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| α1 |
|
|---|---|
| α2 |
|
| β |
|
| D1-like |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||
 | 0.00      (0 votes) (0 votes) |