Chemistry:Testosterone enanthate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Delatestryl, Xyosted, others |
| Other names | TE; Testosterone heptanoate; Testosterone 17β-heptanoate; NSC-17591 |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection, subcutaneous injection |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: very low Intramuscular: high |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | Intramuscular: 4–5 days[1] |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H40O3 |
| Molar mass | 400.603 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Testosterone enanthate is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men.[2][3][4] It is also used in hormone therapy for transgender men.[5] It is given by injection into muscle or subcutaneously usually once every one to four weeks.[4][6][1]
Side effects of testosterone enanthate include symptoms of masculinization like acne, increased hair growth, voice changes, and increased sexual desire.[4] The drug is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[7][4] It has strong androgenic effects and moderate anabolic effects, which make it useful for producing masculinization and suitable for androgen replacement therapy.[4] Testosterone enanthate is a testosterone ester and a long-lasting prodrug of testosterone in the body.[6][2][3] Because of this, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of testosterone.[8]
Testosterone enanthate was introduced for medical use in 1954.[9][3] Along with testosterone cypionate, testosterone undecanoate, and testosterone propionate, it is one of the most widely used testosterone esters.[7][3][4] In addition to its medical use, testosterone enanthate is used to improve physique and performance.[4] The drug is a controlled substance in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit.[4]
Medical uses
Testosterone enanthate is used primarily in androgen replacement therapy.[3][10] It is the most widely used form of testosterone in androgen replacement therapy.[3] The medication is specifically approved, in the United States , for the treatment of hypogonadism in men, delayed puberty in boys, and breast cancer in women.[11] It is also used in masculinizing hormone therapy for transgender men.[5]
Side effects
Side effects of testosterone enanthate include virilization among others.[4] Approximately 10 percent of testosterone enanthate will be converted to dihydrotestosterone in normal men.[12] Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can promote masculine characteristics in both males and females. These masculine characteristics include: clitoral hypertrophy, androgenic alopecia, growth of body hair and deepening of the vocal cords. Dihydrotestosterone also plays an important role in male sexual function and may also be a contributing factor of ischemic priapism in males as shown in a study conducted on the use of finasteride to treat ischemic priapism in males. Testosterone enanthate can also lead to an increase in igf-1 and igf-bp.[13][14] Testosterone enanthate can also be converted to estradiol by aromatase,[15] which may lead to gynecomastia in males. Aromatase inhibitors can help to prevent the estrogenic activity of testosterone enanthate in the body.[15]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Medication | Ratioa |
|---|---|
| Testosterone | ~1:1 |
| Androstanolone (DHT) | ~1:1 |
| Methyltestosterone | ~1:1 |
| Methandriol | ~1:1 |
| Fluoxymesterone | 1:1–1:15 |
| Metandienone | 1:1–1:8 |
| Drostanolone | 1:3–1:4 |
| Metenolone | 1:2–1:30 |
| Oxymetholone | 1:2–1:9 |
| Oxandrolone | 1:3–1:13 |
| Stanozolol | 1:1–1:30 |
| Nandrolone | 1:3–1:16 |
| Ethylestrenol | 1:2–1:19 |
| Norethandrolone | 1:1–1:20 |
| Notes: In rodents. Footnotes: a = Ratio of androgenic to anabolic activity. Sources: See template. | |
Testosterone enanthate is a prodrug of testosterone and is an androgen and anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS). That is, it is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).
Pharmacokinetics
Testosterone enanthate has an elimination half-life of 4.5 days and a mean residence time of 8.5 days when used as a depot intramuscular injection.[1] It requires frequent administration of approximately once per week, and large fluctuations in testosterone levels result with it, with levels initially being elevated and supraphysiological.[1]
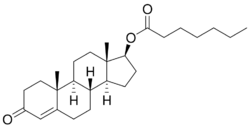
Chemistry
Testosterone enanthate, or testosterone 17β-heptanoate, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of testosterone.[16][17] It is an androgen ester; specifically, it is the C17β enanthate (heptanoate) ester of testosterone.[16][17]
History
Testosterone enanthate was described as early as 1952[18] and was first introduced for medical use in the United States in 1954 under the brand name Delatestryl.[9][3]
Society and culture
Generic names
Testosterone enanthate is the generic name of the drug and its USAN and BAN.[16][17][19][20] It has also referred to as testosterone heptanoate.[16][17][19][20]
Brand names
Testosterone enanthate is marketed primarily under the brand name Delatestryl.[16][17][19][20]
It is or has been marketed under a variety of other brand names as well, including, among others:[16][17][19][20][21]
- Andro LA
- Andropository
- Cypionat
- Cypoprime
- Depandro
- Durathate
- Everone
- Testocyp
- Testostroval
- Testrin
- Testro LA
- Xyosted
- pharmaqo labs
Availability
Testosterone enanthate is available in the United States and widely elsewhere throughout the world.[22][17][20] Testosterone enanthate (testosterone heptanoate) is often available in concentrations of 200 mg per milliliter of fluid.[23]
Legal status
Testosterone enanthate, along with other AAS, is a schedule III controlled substance in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act and a schedule IV controlled substance in Canada under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act.[24][25]
Research
As of October 2017, an auto-injection formulation of testosterone enanthate was in preregistration for the treatment of hypogonadism in the United States .[26]
Xyosted
On October 1, 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the approval of Xyosted. Xyosted, a product of Antares Pharma, Inc., is a single-use disposable auto-injector that dispenses testosterone enanthate. Xyosted is the first FDA-approved subcutaneous testosterone enanthate product for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males.[27]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "The Leydig Cell as a Target for Male Contraception". The Leydig Cell in Health and Disease. Contemporary Endocrinology. Humana Press. 2007. pp. 415–442. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-453-7_29. ISBN 978-1-58829-754-9.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Testosterone: Action, Deficiency, Substitution. Cambridge University Press. 26 July 2012. pp. 315–. ISBN 978-1-107-01290-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=MkrAPaQ4wJkC&pg=PA315.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Andrology: Male Reproductive Health and Dysfunction. Springer Science & Business Media. 13 January 2010. pp. 442–. ISBN 978-3-540-78355-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=mEgckDNkonUC&pg=PA442.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. 2011. pp. 208–211. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=afKLA-6wW0oC&pg=PT208.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Testosterone therapy for transgender men". The Lancet. Diabetes & Endocrinology 5 (4): 301–311. April 2017. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(16)00036-X. PMID 27084565.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2001. pp. 1185, 1187. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=FVfzRvaucq8C&pg=PA1185.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology 154 (3): 502–521. June 2008. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMID 18500378.
- ↑ "Compounded Bioidentical Hormones in Endocrinology Practice: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 101 (4): 1318–1343. April 2016. doi:10.1210/jc.2016-1271. PMID 27032319.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Testosterone Enanthate". p. 35t. https://books.google.com/books?id=_J2ti4EkYpkC&pg=PAPA3171. in William Andrew Publishing (2007). "T". Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. pp. 1t–242t. doi:10.1016/B978-0-8155-1526-5.50024-6. ISBN 978-0-8155-1526-5.
- ↑ "Testosterone Enanthate raw powder (CAS 315-37-7) ≥98% | AASraw" (in en-US). aasraw. https://www.aasraw.com/products/testosterone-enanthate/.
- ↑ "DELATESTRYL Package Insert". Indevus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/009165s031lbl.pdf.
- ↑ "DHT (dihydrotestosterone): What is DHT's role in baldness?". 28 July 2017. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/68082.php.
- ↑ "Testosterone increases insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein". Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science 25 (5): 381–388. 1995. PMID 7486812.
- ↑ "Management of Recurrent Ischemic Priapism 2014: A Complex Condition with Devastating Consequences". Sexual Medicine Reviews 3 (1): 24–35. March 2015. doi:10.1002/smrj.37. PMID 27784569.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Aromatase-independent testosterone conversion into estrogenic steroids is inhibited by a 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 98 (2–3): 133–138. February 2006. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.09.004. PMID 16386416.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 641–642. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA641.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 1002–1004. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA1002.
- ↑ "Über protrahiert wirksame Androgene". Festschrift zum 75. Geburtstag. Springer. 1952. pp. 85–92. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-49902-9_11. ISBN 978-3-642-49610-3.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 "Testosterone". Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. p. 270. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA270.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 "Testosterone". October 1, 2018. https://www.drugs.com/international/testosterone.html.
- ↑ "Testosterone cypionate profile and most popular brands in USA" (in en). http://downsizefitness.com/rankings/testosterone-cypionate/.
- ↑ "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/.
- ↑ "Testosterone enanthate". Drugbank. https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB13944.
- ↑ Drug Abuse Handbook, Second Edition. CRC Press. 21 December 2006. pp. 30–. ISBN 978-1-4200-0346-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZjrMBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA30.
- ↑ Pharmacology for Canadian Health Care Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. 5 August 2016. pp. 50–. ISBN 978-1-77172-066-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=dNgoDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA50.
- ↑ "Testosterone enanthate auto-injection - Antares Pharma". February 5, 2018. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800037740.
- ↑ "Antares Receives Fda Approval of Xyostedtm (Testosterone Enanthate) Injection for Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Adult Males". https://www.antarespharma.com/application/files/2715/3835/7488/XYOSTED_FDA_Approval_Final.pdf.
{{Navbox
| name = Androgens and antiandrogens | title = Androgens and antiandrogens | state = collapsed | listclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Androgens
(incl. AAS)
| list1 =
| group2 = Antiandrogens | list2 = {{Navbox|child | groupstyle = text-align:center; | groupwidth = 9em;
| group1 = AR antagonists | list1 =
- Steroidal: Abiraterone acetate
- Canrenone
- Chlormadinone acetate
- Cyproterone acetate
- Delmadinone acetate
- Dienogest
- Drospirenone
- Medrogestone
- Megestrol acetate
- Nomegestrol acetate
- Osaterone acetate
- Oxendolone
- Potassium canrenoate
- Spironolactone
- Nonsteroidal: Apalutamide
- Bicalutamide
- Cimetidine
- Darolutamide
- Enzalutamide
- Flutamide
- Ketoconazole
- Nilutamide
- Seviteronel†
- Topilutamide (fluridil)
| group2 = Steroidogenesis| list2 =
inhibitors
| 5α-Reductase | |
|---|---|
| Others |
| group3 = Antigonadotropins | list3 =
- D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
- Estrogens (e.g., bifluranol, [[diethylstilbestrol, estradiol, estradiol esters, ethinylestradiol, ethinylestradiol sulfonate, paroxypropione)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin)
- GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix)
- Progestogens (incl., chlormadinone acetate, [[cyproterone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, gestonorone caproate, [[Chemistry:Medroxyprogesterone medroxyprogesterone acetate, Chemistry:Megestrol acetate|megestrol acetate]])
| group4 = Others | list4 =
- Androstenedione immunogens: Androvax (androstenedione albumin)
- Ovandrotone albumin (Fecundin)
}}
| liststyle = background:#DDDDFF;| list3 =
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
- See also
- Androgen receptor modulators
- Estrogens and antiestrogens
- Progestogens and antiprogestogens
- List of androgens/anabolic steroids
}}
 |
