Chemistry:Neramexane
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
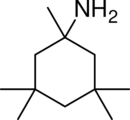 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H23N |
| Molar mass | 169.312 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Neramexane is a drug related to memantine,[1] which acts as an NMDA antagonist[2] and has neuroprotective effects.[3] It is being developed for various possible applications, including treatment of tinnitus,[4][5] Alzheimer's disease,[6] drug addiction[7] and as an analgesic.[8] Animal studies have also suggested antidepressant[9] and nootropic[10] actions, so there are a wide range of potential applications this drug may be used for. It also acts as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist.[11]
A clinical trial found that doses of 50 mg and above safely improved tinnitus scores over 16 weeks.[12]
See also
References
- ↑ "A novel class of amino-alkylcyclohexanes as uncompetitive, fast, voltage-dependent, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists--in vitro characterization". Journal of Neural Transmission 114 (12): 1529–37. 2007. doi:10.1007/s00702-007-0792-7. PMID 17728997.
- ↑ "Amino-alkyl-cyclohexanes as a novel class of uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists". Current Pharmaceutical Design 8 (10): 835–43. 2002. doi:10.2174/1381612024607117. PMID 11945134.
- ↑ "Neuroprotective potential of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists". Neurotoxicity Research 4 (2): 119–26. March 2002. doi:10.1080/10298420290015872. PMID 12829411.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00405886 for "Neramexane for Tinnitus" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00739635 for "Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Neramexane in Patients With Subjective Tinnitus" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ "Neramexane (merz pharmaceuticals/forest laboratories)". IDrugs 9 (2): 128–35. February 2006. PMID 16523403.
- ↑ "Effect of neramexane on ethanol dependence and reinforcement". European Journal of Pharmacology 503 (1–3): 95–8. October 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.09.036. PMID 15496302.
- ↑ "Antihyperalgesic and analgesic properties of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist neramexane in a human surrogate model of neurogenic hyperalgesia". European Journal of Pain 12 (1): 17–29. January 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2007.02.002. PMID 17449306.
- ↑ "Enhancement of antidepressant-like effects but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression by the novel N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist neramexane in mice". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 318 (3): 1128–36. September 2006. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.103697. PMID 16740621.
- ↑ "Enhancement of long-term spatial memory in adult rats by the noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists, memantine and neramexane". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 85 (2): 298–306. October 2006. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.08.011. PMID 17045636.
- ↑ "Inhibition of the alpha9alpha10 nicotinic cholinergic receptor by neramexane, an open channel blocker of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors". European Journal of Pharmacology 566 (1–3): 11–9. July 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.03.026. PMID 17466293.
- ↑ "A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of neramexane in patients with moderate to severe subjective tinnitus". BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 11: 1. January 2011. doi:10.1186/1472-6815-11-1. PMID 21223542.
 |

