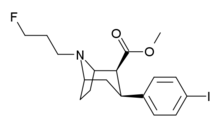
Chemistry:Ioflupane (123I)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | DaTscan |
| Other names | Ioflupane (FPCIT); [I-123] N-ω-fluoropropyl- 2β-carbomethoxy- 3β-(4-iodophenyl) nortropane |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23FINO2 |
| Molar mass | 431.290 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
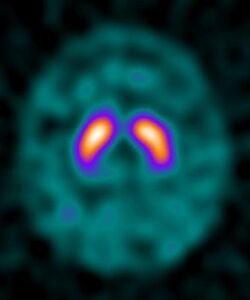
Ioflupane (123I) is the International Nonproprietary Name of a cocaine analogue which is a neuro-imaging radiopharmaceutical drug, used in nuclear medicine for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and the differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease over other disorders presenting similar symptoms. It is injected into a patient and viewed with a gamma camera in order to acquire SPECT images of the brain with particular respect to the striatum, a subcortical region of the basal ganglia.[2] The drug is sold under the tradename DaTscan and is manufactured by GE Healthcare, formerly Amersham plc. It is not marketed outside Europe and the United States.[1]
Pharmacology
Datscan is a solution of ioflupane (123I) for injection into a living test subject.
The iodine introduced during manufacture is a radioactive isotope, iodine-123, and it is the gamma decay of this isotope that is detectable to a gamma camera. 123I has a half-life of approximately 13 hours and a gamma photon energy of 159 keV making it an appropriate radionuclide for medical imaging. The solution also contains 5% ethanol to aid solubility and is supplied sterile since it is intended for intravenous use.
Ioflupane has a high binding affinity for presynaptic dopamine transporters (DAT) in the brains of mammals, in particular the striatal region of the brain. A feature of Parkinson's disease is a marked reduction in dopaminergic neurons in the striatal region. By introducing an agent that binds to the dopamine transporters a quantitative measure and spatial distribution of the transporters can be obtained.[citation needed]
Method of administration
The Datscan solution is supplied ready to inject with a certificate stating the calibration activity and time. The nominal injection activity is 185 MBq[2] and a scan should not be performed with less than 111 MBq.
Thyroid blocking via oral administration of 120 mg potassium iodide is recommended to minimize unnecessary excessive uptake of radioiodine.[3] This is typically given 1-4 hours before the injection.[2][4]
The most convenient way to administer the IV dose is via a peripheral intravenous cannula. The scan is carried out 3 to 6 hours post injection.[3][4]
Risks
Common side effects of ioflupane (123I) are headache, vertigo, increased appetite and formication. Less than 1% of patients experience pain at the injection site.[2]
The radiation risks are reported as low. The committed effective dose for a single investigation on a 70 kg individual is 4.6 mSv.[5] Pregnant patients should not undergo the test. It is not known if 123I-ioflupane is secreted in breast milk however it is recommended that breastfeeding is interrupted for three days after administration.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Removal of [123IIoflupane From Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act"]. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/rules/2015/fr0911.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "DaTSCAN Summary of Product Characteristics". GE Healthcare. 25 July 2019. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/datscan-epar-product-information_en.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "EANM procedure guidelines for brain neurotransmission SPECT using (123)I-labelled dopamine transporter ligands, version 2". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 37 (2): 443–50. February 2010. doi:10.1007/s00259-009-1267-x. PMID 19838702.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "SNM practice guideline for dopamine transporter imaging with 123I-ioflupane SPECT 1.0". Journal of Nuclear Medicine 53 (1): 154–63. January 2012. doi:10.2967/jnumed.111.100784. PMID 22159160.
- ↑ "Notes for Guidance on the Clinical Administration of Radiopharmaceuticals and Use of Sealed Radioactive Sources". Public Health England. 13 February 2019. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/arsac-notes-for-guidance.
External links
- "Ioflupane I 123". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/ioflupane%20i%20123.
 |