(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Short description: Typical antipsychotic
Butaperazine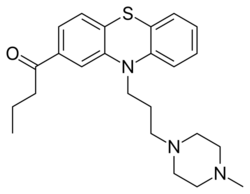 |
| Clinical data |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
| Legal status |
|---|
| Legal status |
- BR: Class C1 (Other controlled substances)
|
|---|
| Identifiers |
|---|
1-[10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazin-2-yl]butan-1-one
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| DrugBank | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEBI | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| Chemical and physical data |
|---|
| Formula | C24H31N3OS |
|---|
| Molar mass | 409.59 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O=C(c2cc1N(c3c(Sc1cc2)cccc3)CCCN4CCN(C)CC4)CCC
|
InChI=1S/C24H31N3OS/c1-3-7-22(28)19-10-11-24-21(18-19)27(20-8-4-5-9-23(20)29-24)13-6-12-26-16-14-25(2)15-17-26/h4-5,8-11,18H,3,6-7,12-17H2,1-2H3  Y YKey:DVLBYTMYSMAKHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y
|
| (verify) |
Butaperazine (Repoise, Tyrylen) is a typical antipsychotic of the phenothiazine class.[1] It was approved in 1967, and possibly discontinued in the 1980s.
Synthesis
2-Butyrylphenothiazine [25244-91-1] (1) is the requisite starting material for carrying out the procedure. It is prepared in a manner that is synonymous with the method used in the propiomazine and propiopromazine already discussed.
The 1-(γ-chloropropyl)-4-methylpiperazine [104-16-5] (2) is prepared in the conventional way from alkylating 1-methylpiperazine and 1-Bromo-3-chloropropane.
Sodamide is used to extract the 10-H thereby facilitating the nucleophilic substitution reaction. And completing the instalment of the sidechain.
See also
References
|
|---|
|
|---|
| mAChRs | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate
- 4-DAMP
- Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol)
- Abediterol
- AF-DX 250
- AF-DX 384
- Ambutonium bromide
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine, buclizine, captodiame, chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine), cinnarizine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, [[Chemistry:Dimetdimetindene, Diphenhydramine|diphenhydramine]], doxylamine, meclizine, mepyramine (pyrilamine), mequitazine, perlapine, phenindamine, pheniramine, Phenyltoloxamine|Phenyltoloxamine]]]], promethazine, propiomazine, triprolidine)
- AQ-RA 741
- Atropine
- Atropine methonitrate
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine, Chemistry:Fluperlapine
|
|---|
|
|---|
Precursors
(and prodrugs) | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| nAChRs | Agonists
(and PAMs) |
- 5-HIAA
- A-84,543
- A-366,833
- A-582,941
- A-867,744
- ABT-202
- ABT-418
- ABT-560
- ABT-894
- Acetylcholine
- Altinicline
- Anabasine
- Anatoxin-a
- AR-R17779
- Bephenium hydroxynaphthoate
- Butinoline
- Butyrylcholine
- Carbachol
- Choline
- Cotinine
- Cytisine
- Decamethonium
- Desformylflustrabromine
- Dianicline
- Dimethylphenylpiperazinium
- Epibatidine
- Epiboxidine
- Ethanol (alcohol)
- Ethoxysebacylcholine
- EVP-4473
- EVP-6124
- Galantamine
- GTS-21
- Ispronicline
- Ivermectin
- JNJ-39393406
- Levamisole
- Lobeline
- MEM-63,908 (RG-3487)
- Morantel
- Nicotine (tobacco)
- NS-1738
- PHA-543,613
- PHA-709,829
- PNU-120,596
- PNU-282,987
- Pozanicline
- Pyrantel
- Rivanicline
- RJR-2429
- Sazetidine A
- SB-206553
- Sebacylcholine
- SIB-1508Y
- SIB-1553A
- SSR-180,711
- Suberyldicholine
- Suxamethonium (succinylcholine)
- Suxethonium (succinyldicholine)
- TC-1698
- TC-1734
- TC-1827
- TC-2216
- TC-5214
- TC-5619
- TC-6683
- Tebanicline
- Tribendimidine
- Tropisetron
- UB-165
- Varenicline
- WAY-317,538
- XY-4083
|
|---|
Antagonists
(and NAMs) | |
|---|
|
|---|
Precursors
(and prodrugs) | |
|---|
|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Butaperazine. Read more |







 (0 votes)
(0 votes)