Chemistry:Binedaline
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
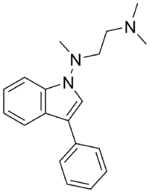
| Formula | C19H23N3 |
| Molar mass | 293.414 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Binedaline (also called binodaline or binedaline hydrochloride;[1]) is a drug that was investigated as an antidepressant in the 1980s but was never marketed.[2][3] It acts as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (Ki = 25 nM), with relatively insignificant influence on the serotonin (Ki = 847 nM) and dopamine (Ki >= 2 μM) transporters.[4] It has negligible affinity for the α-adrenergic, mACh, H1, or 5-HT2 receptors.[4]
Synthesis

Grignard reaction of 2-aminobenzophenone [2835-77-0] (1) with methylmagnesium bromide and dehydration of the tertiary carbinol gives 2-(1-phenylvinyl)aniline [64097-92-3] (2). In an example of the Widman‐Stoermer Synthesis, treatment with nitrous acid followed by basification of the diazonium species with ammonia causes an intramolecular cyclization to afford 4-phenylcinnoline [21874-06-6] (3). Hydrogenation would give 4-Phenyl-1,4-dihydrocinnoline, CID:14175750 (4). The presence of acetic acid gives (5). The reaction with Methyl p-toluenesulfonate [80-48-8] leads to CID:20337750 (6). Acid hydrolysis gives N-methyl-3-phenylindol-1-amine [57647-15-1] (7). Sodamide is then used to abstract the amine proton; alkylation of then anionic species with 2-dimethylaminoethylchloride [107-99-3] (8) then concludes the synthesis of binedaline (9).
See also
Widman‐Stoermer Synthesis also used for the synthesis of Cintazone [2056-56-6].
References
- ↑ Milne, G. W. A. (2017). "3043: Binedaline hydrochloride". Drugs: Synonyms and Properties. Routledge. ISBN 9781351755092.
- ↑ "A controlled double-blind study comparing binedaline and imipramine in the treatment of endogenous depression". Neuropsychobiology 12 (1): 34–38. 1984. doi:10.1159/000118107. PMID 6239991.
- ↑ Triggle, David J. (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=DeX7jgInYFMC&pg=PA267.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Pharmacological profile of binedaline, a new antidepressant drug". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 249 (1): 288–296. April 1989. PMID 2540319.
- ↑ "1-amino-3-phenylindoles with antidepressant activity. Binodaline hydrochloride and related substances". Arzneimittel-Forschung 30 (6): 919–923. 1980. doi:10.1002/chin.198038207. PMID 7191264.
- ↑ Fischer K, Jahn U, Schatz F, Stammbach C, Thiele K, Wagner-Jauregg T. Zirngibl L, "New Hydrazines and Methods of Manufacturing Them", DE patent 2512702, issued 23 September 1982, assigned to Siegfried AG
- ↑ Schatz F, Stammbach C, Thiele K, Theodor W. Wagner-Jauregg, Zirngibl L, Fischer J, Jahn U, "N-Amino indole derivatives having pharmacological activity", US patent 4204998, issued 27 May 1980, assigned to Siegfried AG
 |
