(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Short description: Chemical compound
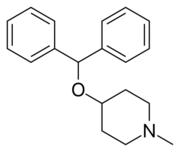
Diphenylpyraline (DPP; sold as Allergen, Arbid, Belfene, Diafen, Hispril, Histyn, Lergobine, Lyssipol, Mepiben, Neargal) is a first-generation antihistamine with anticholinergic effects of the diphenylpiperidine class.[2][3][4] It is marketed in Europe for the treatment of allergies.[2][3][5] DPP has also been found to act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor and produces hyperactivity in rodents.[6] It has been shown to be useful in the treatment of Parkinsonism.[7]
Synthesis

Diphenylpyraline synthesis via coupling of 4-hydroxy-1-methylpiperidine with benzhydrylbromide
[8][9]References
- ↑ "Half-life of diphenylpyraline in man". Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 2 (3): 191–5. June 1974. doi:10.1007/BF01059761. PMID 4156058.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. ISBN 3-88763-075-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&q=Diphenylpyraline&pg=PA358.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Diphenylpyraline (Lergobine) in the treatment of patients suffering from allergic and vasomotor rhinitis". J Int Med Res 5 (1): 37–41. 1977. doi:10.1177/030006057700500106. PMID 14039.
- ↑ "Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 43 (3): 277–82. March 1987. doi:10.1254/jjp.43.277. PMID 2884340.
- ↑ "Antihistamine Drugs". Synthesis of Essential Drugs. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 2006. ISBN 0-444-52166-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=Jjc7KYWZdOYC&q=Diphenylpyraline&pg=PA230.
- ↑ "Diphenylpyraline, a histamine H1 receptor antagonist, has psychostimulant properties". Eur J Pharmacol 506 (3): 237–40. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.11.017. PMID 15627433.
- ↑ "Diphenylpyraline-responsive parkinsonism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: long-term follow up of three patients". J Neurol Sci 182 (2): 95–7. 2001. doi:10.1016/S0022-510X(00)00441-X. PMID 11137513.
- ↑ Knox LH, Kapp R, "1-Alkylpiperidyl-4-benzhydryl ethers, acid salts thereof and their preparation", US patent 2479843, issued 23 August 1949, assigned to Nopco Chemical Company.
- ↑ Schuler WA, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von basischen Benzhydryläthern [Process for the production of basic benzhydrylethers]", DE patent 934890, issued 10 November 1955.
|
|---|
| Adamantanes | |
|---|
| Adenosine antagonists | |
|---|
| Alkylamines | |
|---|
| Ampakines | |
|---|
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
|---|
| Benzazepines | |
|---|
| Cholinergics | |
|---|
| Convulsants | |
|---|
| Eugeroics | |
|---|
| Oxazolines | |
|---|
| Phenethylamines |
- 1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane
- 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane
- 2-Fuoroamphetamine
- 2-Fuoromethamphetamine
- 2-OH-PEA
- 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane
- 2,3-MDA
- 3-Fuoroamphetamine
- 3-Fluoroethamphetamine
- 3-Fluoromethcathinone
- 3-Methoxyamphetamine
- 3-Methylamphetamine
- 3,4-DMMC
- 4-BMC
- 4-CMC
- 4-Fluoroamphetamine
- 4-Fluoromethamphetamine
- 4-MA
- 4-Methylbuphedrone
- 4-Methylcathinone
- 4-MEAP
- 4-MMA
- 4-Methylpentedrone
- 4-MTA
- 6-FNE
- AL-1095
- Alfetamine
- a-Ethylphenethylamine
- Amfecloral
- Amfepentorex
- Amfepramone
- Amidephrine
- 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
- 2-Aminoindane
- 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole
- 2-Aminotetralin
- Acridorex
- Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine)
- Amphetaminil
- Arbutamine
- β-Methylphenethylamine
- β-Phenylmethamphetamine
- Benfluorex
- Benzedrone
- Benzphetamine
- BDB
- BOH
- 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine
- BPAP
- Buphedrone
- Bupropion
- Butylone
- Camfetamine
- Cathine
- Cathinone
- Chlorphentermine
- Cilobamine
- Cinnamedrine
- Clenbuterol
- Clobenzorex
- Cloforex
- Clortermine
- Cypenamine
- D-Deprenyl
- Denopamine
- Dimethoxyamphetamine
- Dimethylamphetamine
- Dimethylcathinone
- Dobutamine
- DOPA (Dextrodopa, Levodopa)
- Dopamine
- Dopexamine
- Droxidopa
- EBDB
- Ephedrine
- Epinephrine
- Epinine
- Etafedrine
- Ethcathinone
- Ethylnorepinephrine
- Ethylone
- Etilamfetamine
- Etilefrine
- Famprofazone
- Fencamfamin
- Fencamine
- Fenethylline
- Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine, Levofenfluramine)
- Fenproporex
- Feprosidnine
- Flephedrone
- Fludorex
- Formetorex
- Furfenorex
- Gepefrine
- Hexapradol
- Hexedrone
- HMMA
- Hordenine
- 4-Hydroxyamphetamine
- 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane
- Ibopamine
- Indanylamphetamine
- Iofetamine
- Isoetarine
- Isoethcathinone
- Isoprenaline
- L-Deprenyl (Selegiline)
- Lefetamine
- Lisdexamfetamine
- Lophophine
- MBDB
- MDA (tenamfetamine)
- MDBU
- MDEA
- MDMA (midomafetamine)
- MDMPEA
- MDOH
- MDPR
- MDPEA
- Mefenorex
- Mephedrone
- Mephentermine
- Metanephrine
- Metaraminol
- Mesocarb
- Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine)
- Methoxamine
- Methoxyphenamine
- MMA
- Methcathinone
- Methedrone
- Methoxyphenamine
- Methylenedioxycathinone
- Methylone
- Mexedrone
- MMDA
- MMDMA
- MMMA
- Morforex
- N,alpha-Diethylphenylethylamine
- N-Ethylbuphedrone
- N-Ethylhexedrone
- N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine
- Naphthylamphetamine
- Nisoxetine
- Norepinephrine
- Norfenefrine
- Norfenfluramine
- Normetanephrine
- L-Norpseudoephedrine
- Octopamine (drug)
- Orciprenaline
- Ortetamine
- Oxifentorex
- Oxilofrine
- PBA
- PCA
- PCMA
- PHA
- Pentorex
- Pentedrone
- Pentylone
- Phenatine
- Phenpromethamine
- Phentermine
- Phenylalanine
- Phenylephrine
- Phenylpropanolamine
- Pholedrine
- PIA
- PMA
- PMEA
- PMMA
- PPAP
- Phthalimidopropiophenone
- Prenylamine
- Propylamphetamine
- Pseudoephedrine
- Ropinirole
- Salbutamol (Levosalbutamol)
- Sibutramine
- Solriamfetol
- Synephrine
- Theodrenaline
- Tiflorex
- Tranylcypromine
- Tyramine
- Tyrosine
- Xylopropamine
- Zylofuramine
|
|---|
| Phenylmorpholines | |
|---|
| Piperazines | |
|---|
| Piperidines | |
|---|
| Pyrrolidines | |
|---|
| Racetams | |
|---|
| Tropanes | |
|---|
| Tryptamines | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| mAChRs | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate
- 4-DAMP
- Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol)
- Abediterol
- AF-DX 250
- AF-DX 384
- Ambutonium bromide
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine, buclizine, captodiame, chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine), cinnarizine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, [[Chemistry:Dimetdimetindene, Diphenhydramine|diphenhydramine]], doxylamine, meclizine, mepyramine (pyrilamine), mequitazine, perlapine, phenindamine, pheniramine, Phenyltoloxamine|Phenyltoloxamine]]]], promethazine, propiomazine, triprolidine)
- AQ-RA 741
- Atropine
- Atropine methonitrate
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine, Chemistry:Fluperlapine
|
|---|
|
|---|
Precursors
(and prodrugs) | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| nAChRs | Agonists
(and PAMs) |
- 5-HIAA
- A-84,543
- A-366,833
- A-582,941
- A-867,744
- ABT-202
- ABT-418
- ABT-560
- ABT-894
- Acetylcholine
- Altinicline
- Anabasine
- Anatoxin-a
- AR-R17779
- Bephenium hydroxynaphthoate
- Butinoline
- Butyrylcholine
- Carbachol
- Choline
- Cotinine
- Cytisine
- Decamethonium
- Desformylflustrabromine
- Dianicline
- Dimethylphenylpiperazinium
- Epibatidine
- Epiboxidine
- Ethanol (alcohol)
- Ethoxysebacylcholine
- EVP-4473
- EVP-6124
- Galantamine
- GTS-21
- Ispronicline
- Ivermectin
- JNJ-39393406
- Levamisole
- Lobeline
- MEM-63,908 (RG-3487)
- Morantel
- Nicotine (tobacco)
- NS-1738
- PHA-543,613
- PHA-709,829
- PNU-120,596
- PNU-282,987
- Pozanicline
- Pyrantel
- Rivanicline
- RJR-2429
- Sazetidine A
- SB-206553
- Sebacylcholine
- SIB-1508Y
- SIB-1553A
- SSR-180,711
- Suberyldicholine
- Suxamethonium (succinylcholine)
- Suxethonium (succinyldicholine)
- TC-1698
- TC-1734
- TC-1827
- TC-2216
- TC-5214
- TC-5619
- TC-6683
- Tebanicline
- Tribendimidine
- Tropisetron
- UB-165
- Varenicline
- WAY-317,538
- XY-4083
|
|---|
Antagonists
(and NAMs) | |
|---|
|
|---|
Precursors
(and prodrugs) | |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
DAT
(DRIs) | |
|---|
NET
(NRIs) | | | | | | |
- Others: Antihistamines (e.g., brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine)
- Antipsychotics (e.g., loxapine, ziprasidone)
- Arylcyclohexylamines (e.g., ketamine, phencyclidine)
- Dopexamine
- Ephenidine
- Ginkgo biloba
- Indeloxazine
- Nefazodone
- Opioids (e.g., Desmetramadol|Desmetramadol]]]], methadone, pethidine (meperidine), tapentadol, tramadol, Levorphanol
|
|
|---|
SERT
(SRIs) | |
|---|
| VMATs | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diphenylpyraline. Read more |





 (0 votes)
(0 votes)
