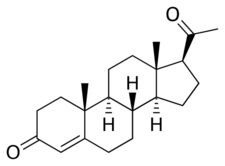
Chemistry:Progesterone
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S,3aS,3bS,9aR,9bS,11aS)-1-Acetyl-9a,11a-dimethyl-1,2,3,3a,3b,4,5,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-7H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-one | |
| Other names
P4;[1] Pregnenedione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H30O2 | |
| Molar mass | 314.469 g/mol |
| Melting point | 126 |
| log P | 4.04[4] |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | G03DA04 (WHO) |
| By mouth, topical/transdermal, vaginal, intramuscular injection, subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous implant | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| OMP: <10%[5][6] | |
| • Albumin: 80% • CBG: 18% • SHBG: <1% • Free: 1–2%[7][8] | |
| OMP: 16–18 hours[5][6][9] IM: 22–26 hours[6][10] SC: 13–18 hours[10] | |
| Renal | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species.[1][11] It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens[11] and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.[12]
In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy.[13] It was first prescribed in 1934.[14]
Biological activity
Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the nuclear progesterone receptor (nPR) (with an affinity of KD = 1 nM) the resulting effects on ribosomal transcription plays a major role in regulation of female reproduction.[11][15] In addition, progesterone is an agonist of the more recently discovered membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs),[16] of which the expression has regulation effects in reproduction function (oocyte maturation, labor, and sperm motility) and cancer although additional research is required to further define the roles.[17] It also functions as a ligand of the PGRMC1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) which impacts tumor progression, metabolic regulation, and viability control of nerve cells.[18][19][20] Moreover, progesterone is also known to be an antagonist of the sigma σ1 receptor,[21][22] a negative allosteric modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors,[12] and a potent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR).[23] Progesterone prevents MR activation by binding to this receptor with an affinity exceeding even those of aldosterone and glucocorticoids such as cortisol and corticosterone,[23] and produces antimineralocorticoid effects, such as natriuresis, at physiological concentrations.[24] In addition, progesterone binds to and behaves as a partial agonist of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), albeit with very low potency (EC50 >100-fold less relative to cortisol).[25][26]
Progesterone, through its neurosteroid active metabolites such as 5α-dihydroprogesterone and allopregnanolone, acts indirectly as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor.[27]
Progesterone and some of its metabolites, such as 5β-dihydroprogesterone, are agonists of the pregnane X receptor (PXR),[28] albeit weakly so (EC50 >10 μM).[29] In accordance, progesterone induces several hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes,[30] such as CYP3A4,[31][32] especially during pregnancy when concentrations are much higher than usual.[33] Perimenopausal women have been found to have greater CYP3A4 activity relative to men and postmenopausal women, and it has been inferred that this may be due to the higher progesterone levels present in perimenopausal women.[31]
Progesterone modulates the activity of CatSper (cation channels of sperm) voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Since eggs release progesterone, sperm may use progesterone as a homing signal to swim toward eggs (chemotaxis). As a result, it has been suggested that substances that block the progesterone binding site on CatSper channels could potentially be used in male contraception.[34][35]
Biological function
File:Estradiol and progesterone % changes across the menstrual cycle.tif
Hormonal interactions
Progesterone has a number of physiological effects that are amplified in the presence of estrogens. Estrogens through estrogen receptors (ERs) induce or upregulate the expression of the PR.[37] One example of this is in breast tissue, where estrogens allow progesterone to mediate lobuloalveolar development.[38][39][40]
Elevated levels of progesterone potently reduce the sodium-retaining activity of aldosterone, resulting in natriuresis and a reduction in extracellular fluid volume. Progesterone withdrawal, on the other hand, is associated with a temporary increase in sodium retention (reduced natriuresis, with an increase in extracellular fluid volume) due to the compensatory increase in aldosterone production, which combats the blockade of the mineralocorticoid receptor by the previously elevated level of progesterone.[41]
Early sexual differentiation
Progesterone plays a role in early human sexual differentiation.[42] Placental progesterone is the feedstock for the 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) produced via the backdoor pathway found operating in multiple non-gonadal tissues of the fetus,[43] whereas deficiencies in this pathway lead to undervirilization of the male fetus, resulting in incomplete development of the male genitalia.[44][45] DHT is a potent androgen that is responsible for the development of male genitalia, including the penis and scrotum.
During early fetal development, the undifferentiated gonads can develop into either testes or ovaries. The presence of the Y chromosome leads to the development of testes. The testes then produce testosterone, which is converted to DHT via the enzyme 5α-reductase. DHT is a potent androgen that is responsible for the masculinization of the external genitalia and the development of the prostate gland. Progesterone, produced by the placenta during pregnancy, plays a role in fetal sexual differentiation by serving as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of DHT via the backdoor pathway. In the absence of adequate levels of steroidogenic enzymes during fetal development, the backdoor pathway for DHT synthesis can become deficient, leading to undermasculinization of the male fetus. This can result in the development of ambiguous genitalia or even female genitalia in some cases. Therefore, both DHT and progesterone play crucial roles in early fetal sexual differentiation, with progesterone acting as a precursor molecule for DHT synthesis and DHT promoting the development of male genitalia.[42]
Reproductive system
Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before fertilization occurs, though the receptor(s) as yet remain unidentified.[46] Detailed characterisation of the events occurring in sperm in response to progesterone has elucidated certain events including intracellular calcium transients and maintained changes,[47] slow calcium oscillations,[48] now thought to possibly regulate motility.[49] It is produced by the ovaries.[50] Progesterone has also been shown to demonstrate effects on octopus spermatozoa.[51]
Progesterone is sometimes called the "hormone of pregnancy",[52] and it has many roles relating to the development of the fetus:
- Progesterone converts the endometrium to its secretory stage to prepare the uterus for implantation. At the same time progesterone affects the vaginal epithelium and cervical mucus, making it thick and impenetrable to sperm. Progesterone is anti-mitogenic in endometrial epithelial cells, and as such, mitigates the tropic effects of estrogen.[53] If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels will decrease, leading to menstruation. Normal menstrual bleeding is progesterone-withdrawal bleeding. If ovulation does not occur and the corpus luteum does not develop, levels of progesterone may be low, leading to anovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
- During implantation and gestation, progesterone appears to decrease the maternal immune response to allow for the acceptance of the pregnancy.[54]
- Progesterone decreases contractility of the uterine smooth muscle.[52] This effect contributes to prevention of preterm labor.[54] Studies have shown that in women who are pregnant with a single fetus, asymptomatic in the prenatal stage, and at a high risk of giving pre-term birth spontaneously, vaginal progesterone medication has been found to be effective in preventing spontaneous pre-term birth. Women who are at a high risk of giving pre-term birth spontaneously are those who have a short cervix of less than 25 mm or have previously given pre-term birth spontaneously. Although pre-term births are generally considered to be less than 37 weeks, these studies found that vaginal progesterone is associated with fewer pre-term births of less than 34 weeks.[55]
- A drop in progesterone levels is possibly one step that facilitates the onset of labor.
- In addition, progesterone inhibits lactation during pregnancy. The fall in progesterone levels following delivery is one of the triggers for milk production.
The fetus metabolizes placental progesterone in the production of adrenal steroids.[43]
Breasts
Lobuloalveolar development
Progesterone plays an important role in breast development in women. In conjunction with prolactin, it mediates lobuloalveolar maturation of the mammary glands during pregnancy to allow for milk production and thus lactation and breastfeeding of offspring following parturition (childbirth).[56] Estrogen induces expression of the PR in breast tissue and hence progesterone is dependent on estrogen to mediate lobuloalveolar development.[38][39][40] It has been found that RANKL is a critical downstream mediator of progesterone-induced lobuloalveolar maturation.[57] RANKL knockout mice show an almost identical mammary phenotype to PR knockout mice, including normal mammary ductal development but complete failure of the development of lobuloalveolar structures.[57]
Ductal development
Though to a far lesser extent than estrogen, which is the major mediator of mammary ductal development (via the ERα),[58][59] progesterone may be involved in ductal development of the mammary glands to some extent as well.[60] PR knockout mice or mice treated with the PR antagonist mifepristone show delayed although otherwise normal mammary ductal development at puberty.[60] In addition, mice modified to have overexpression of PRA display ductal hyperplasia,[57] and progesterone induces ductal growth in the mouse mammary gland.[60] Progesterone mediates ductal development mainly via induction of the expression of amphiregulin, the same growth factor that estrogen primarily induces the expression of to mediate ductal development.[60] These animal findings suggest that, while not essential for full mammary ductal development, progesterone seems to play a potentiating or accelerating role in estrogen-mediated mammary ductal development.[60]
Breast cancer risk
Progesterone also appears to be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer, though its role, and whether it is a promoter or inhibitor of breast cancer risk, has not been fully elucidated.[61][62] Most progestins, or synthetic progestogens, like medroxyprogesterone acetate, have been found to increase the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women in combination with estrogen as a component of menopausal hormone therapy.[63][62] The combination of natural oral progesterone or the atypical progestin dydrogesterone with estrogen has been associated with less risk of breast cancer than progestins plus estrogen.[64][65][66] However, this may simply be an artifact of the low progesterone levels produced with oral progesterone.[61][67] More research is needed on the role of progesterone in breast cancer.[62]
Skin health
The estrogen receptor, as well as the progesterone receptor, have been detected in the skin, including in keratinocytes and fibroblasts.[68][69] At menopause and thereafter, decreased levels of female sex hormones result in atrophy, thinning, and increased wrinkling of the skin and a reduction in skin elasticity, firmness, and strength.[68][69] These skin changes constitute an acceleration in skin aging and are the result of decreased collagen content, irregularities in the morphology of epidermal skin cells, decreased ground substance between skin fibers, and reduced capillaries and blood flow.[68][69] The skin also becomes more dry during menopause, which is due to reduced skin hydration and surface lipids (sebum production).[68] Along with chronological aging and photoaging, estrogen deficiency in menopause is one of the three main factors that predominantly influences skin aging.[68]
Hormone replacement therapy, consisting of systemic treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with a progestogen, has well-documented and considerable beneficial effects on the skin of postmenopausal women.[68][69] These benefits include increased skin collagen content, skin thickness and elasticity, and skin hydration and surface lipids.[68][69] Topical estrogen has been found to have similar beneficial effects on the skin.[68] In addition, a study has found that topical 2% progesterone cream significantly increases skin elasticity and firmness and observably decreases wrinkles in peri- and postmenopausal women.[69] Skin hydration and surface lipids, on the other hand, did not significantly change with topical progesterone.[69]
These findings suggest that progesterone, like estrogen, also has beneficial effects on the skin, and may be independently protective against skin aging.[69]
Sexuality
Libido
Progesterone and its neurosteroid active metabolite allopregnanolone appear to be importantly involved in libido in females.[70]
Homosexuality
Dr. Diana Fleischman, of the University of Portsmouth, and colleagues looked for a relationship between progesterone and sexual attitudes in 92 women. Their research, published in the Archives of Sexual Behavior found that women who had higher levels of progesterone scored higher on a questionnaire measuring homoerotic motivation. They also found that men who had high levels of progesterone were more likely to have higher homoerotic motivation scores after affiliative priming compared to men with low levels of progesterone.[71][72][73][74]
Nervous system
Progesterone, like pregnenolone and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), belongs to an important group of endogenous steroids called neurosteroids. It can be metabolized within all parts of the central nervous system.[75]
Neurosteroids are neuromodulators, and are neuroprotective, neurogenic, and regulate neurotransmission and myelination.[76] The effects of progesterone as a neurosteroid are mediated predominantly through its interactions with non-nuclear PRs, namely the mPRs and PGRMC1, as well as certain other receptors, such as the σ1 and nACh receptors.[77]
Brain damage
Previous studies have shown that progesterone supports the normal development of neurons in the brain, and that the hormone has a protective effect on damaged brain tissue. It has been observed in animal models that females have reduced susceptibility to traumatic brain injury and this protective effect has been hypothesized to be caused by increased circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone in females.[78]
Proposed mechanism
The mechanism of progesterone protective effects may be the reduction of inflammation that follows brain trauma and hemorrhage.[79][80]
Damage incurred by traumatic brain injury is believed to be caused in part by mass depolarization leading to excitotoxicity. One way in which progesterone helps to alleviate some of this excitotoxicity is by blocking the voltage-dependent calcium channels that trigger neurotransmitter release.[81] It does so by manipulating the signaling pathways of transcription factors involved in this release. Another method for reducing the excitotoxicity is by up-regulating the GABAA, a widespread inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor.[82]
Progesterone has also been shown to prevent apoptosis in neurons, a common consequence of brain injury.[83] It does so by inhibiting enzymes involved in the apoptosis pathway specifically concerning the mitochondria, such as activated caspase 3 and cytochrome c.
Not only does progesterone help prevent further damage, it has also been shown to aid in neuroregeneration.[84] One of the serious effects of traumatic brain injury includes edema. Animal studies show that progesterone treatment leads to a decrease in edema levels by increasing the concentration of macrophages and microglia sent to the injured tissue.[81][85] This was observed in the form of reduced leakage from the blood brain barrier in secondary recovery in progesterone treated rats. In addition, progesterone was observed to have antioxidant properties, reducing the concentration of oxygen free radicals faster than without.[82] There is also evidence that the addition of progesterone can also help remyelinate damaged axons due to trauma, restoring some lost neural signal conduction.[82] Another way progesterone aids in regeneration includes increasing the circulation of endothelial progenitor cells in the brain.[86] This helps new vasculature to grow around scar tissue which helps repair the area of insult.
Addiction
Progesterone enhances the function of serotonin receptors in the brain, so an excess or deficit of progesterone has the potential to result in significant neurochemical issues. This provides an explanation for why some people resort to substances that enhance serotonin activity such as nicotine, alcohol, and cannabis when their progesterone levels fall below optimal levels.[87]
- Sex differences in hormone levels may induce women to respond differently than men to nicotine. When women undergo cyclic changes or different hormonal transition phases (menopause, pregnancy, adolescence), there are changes in their progesterone levels.[88] Therefore, females have an increased biological vulnerability to nicotine's reinforcing effects compared to males and progesterone may be used to counter this enhanced vulnerability. This information supports the idea that progesterone can affect behavior.[87]
- Similar to nicotine, cocaine also increases the release of dopamine in the brain. The neurotransmitter is involved in the reward center and is one of the main neurotransmitters involved with substance abuse and reliance. In a study of cocaine users, it was reported that progesterone reduced craving and the feeling of being stimulated by cocaine. Thus, progesterone was suggested as an agent that decreases cocaine craving by reducing the dopaminergic properties of the drug.[89]
Societal
In a 2012 University of Amsterdam study of 120 women, women's luteal phase (higher levels of progesterone, and increasing levels of estrogen) was correlated with lower level of competitive behavior in gambling and math contest scenarios, while their premenstrual phase (sharply-decreasing levels of progesterone, and decreasing levels of estrogen) was correlated with a higher level of competitive behavior.[90]
Other effects
- Progesterone also has a role in skin elasticity and bone strength, in respiration, in nerve tissue and in female sexuality, and the presence of progesterone receptors in certain muscle and fat tissue may hint at a role in sexually dimorphic proportions of those.[91][infringing link?]
- During pregnancy, progesterone is said to decrease uterine irritability.[92]
- During pregnancy, progesterone helps to suppress immune responses of the mother to fetal antigens, which prevents rejection of the fetus.[92]
- Progesterone raises epidermal growth factor-1 (EGF-1) levels, a factor often used to induce proliferation, and used to sustain cultures, of stem cells.[93]
- Progesterone increases core temperature (thermogenic function) during ovulation.[94][95]
- Progesterone reduces spasm and relaxes smooth muscle. Bronchi are widened and mucus regulated. (PRs are widely present in submucosal tissue.)
- Progesterone acts as an antiinflammatory agent and regulates the immune response.
- Progesterone reduces gall-bladder activity.[96]
- Progesterone normalizes blood clotting and vascular tone, zinc and copper levels, cell oxygen levels, and use of fat stores for energy.
- Progesterone may affect gum health, increasing risk of gingivitis (gum inflammation).[97]
- Progesterone appears to prevent endometrial cancer (involving the uterine lining) by regulating the effects of estrogen.
- Progesterone plays an important role in the signaling of insulin release and pancreatic function, and may affect the susceptibility to diabetes or gestational diabetes.[98][99]
- Progesterone levels in the blood were found to be lower in women who had higher weight and higher BMI among those who became pregnant through in vitro fertilization.[100]
- Current data shows that micronized progesterone, which is chemically identical to the progesterone produced in women's bodies, in combination with estrogen in menopausal hormone therapy does not seem to have significant effects on venous thromboembolism (blood clots in veins) and ischemic stroke (lack of blood flow to the brain due to blockage of a blood vessel that supplies the brain). However, more studies need to be conducted to see whether or not micronized progesterone alone or in combined menopausal hormone therapy changes the risk of myocardial infarctions (heart attacks).[101]
- There have not been any studies done yet on the effects of micronized progesterone on hair loss due to menopause.[102]
- Despite suggestions for using hormone therapy to prevent loss of muscle mass in post-menopausal women (50 and older), menopausal hormone therapy involving either estrogen alone or estrogen and progesterone has not been found to preserve muscle mass.[103] Menopausal hormone therapy also does not result in body weight reduction, BMI reduction, or change in glucose metabolism.[104]
Biochemistry
Biosynthesis
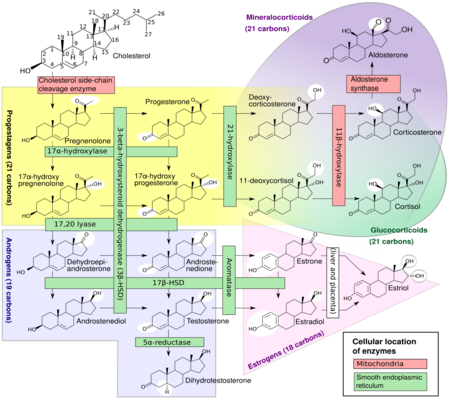
In mammals, progesterone, like all other steroid hormones, is synthesized from pregnenolone, which itself is derived from cholesterol.
Cholesterol undergoes double oxidation to produce 22R-hydroxycholesterol and then 20α,22R-dihydroxycholesterol. This vicinal diol is then further oxidized with loss of the side chain starting at position C22 to produce pregnenolone. This reaction is catalyzed by cytochrome P450scc.
The conversion of pregnenolone to progesterone takes place in two steps. First, the 3β-hydroxyl group is oxidized to a keto group and second, the double bond is moved to C4, from C5 through a keto/enol tautomerization reaction.[106] This reaction is catalyzed by 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/δ5-4-isomerase.
Progesterone in turn is the precursor of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone, and after conversion to 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, of cortisol and androstenedione. Androstenedione can be converted to testosterone, estrone, and estradiol, highlighting the critical role of progesterone in testosterone synthesis.
Pregnenolone and progesterone can also be synthesized by yeast.[107]
Approximately 25 mg of progesterone is secreted from the ovaries per day in women, while the adrenal glands produce about 2 mg of progesterone per day.[108]
Distribution
Progesterone binds extensively to plasma proteins, including albumin (50–54%) and transcortin (43–48%).[109] It has similar affinity for albumin relative to the PR.[15]
Metabolism
The metabolism of progesterone is rapid and extensive and occurs mainly in the liver,[110][111][112] though enzymes that metabolize progesterone are also expressed widely in the brain, skin, and various other extrahepatic tissues.[75][113] Progesterone has an elimination half-life of only approximately 5 minutes in circulation.[110] The metabolism of progesterone is complex, and it may form as many as 35 different unconjugated metabolites when it is ingested orally.[112][114] Progesterone is highly susceptible to enzymatic reduction via reductases and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases due to its double bond (between the C4 and C5 positions) and its two ketones (at the C3 and C20 positions).[112]
The major metabolic pathway of progesterone is reduction by 5α-reductase[75] and 5β-reductase into the dihydrogenated 5α-dihydroprogesterone and 5β-dihydroprogesterone, respectively.[111][112][115][116] This is followed by the further reduction of these metabolites via 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase into the tetrahydrogenated allopregnanolone, pregnanolone, isopregnanolone, and epipregnanolone.[117][111][112][115] Subsequently, 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase reduce these metabolites to form the corresponding hexahydrogenated pregnanediols (eight different isomers in total),[111][116] which are then conjugated via glucuronidation and/or sulfation, released from the liver into circulation, and excreted by the kidneys into the urine.[110][112] The major metabolite of progesterone in the urine is the 3α,5β,20α isomer of pregnanediol glucuronide, which has been found to constitute 15 to 30% of an injection of progesterone.[15][118] Other metabolites of progesterone formed by the enzymes in this pathway include 3α-dihydroprogesterone, 3β-dihydroprogesterone, 20α-dihydroprogesterone, and 20β-dihydroprogesterone, as well as various combination products of the enzymes aside from those already mentioned.[15][112][118][119] Progesterone can also first be hydroxylated (see below) and then reduced.[112] Endogenous progesterone is metabolized approximately 50% into 5α-dihydroprogesterone in the corpus luteum, 35% into 3β-dihydroprogesterone in the liver, and 10% into 20α-dihydroprogesterone.[120]
Relatively small portions of progesterone are hydroxylated via 17α-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) and 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2) into 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-deoxycorticosterone (21-hydroxyprogesterone), respectively,[114] and pregnanetriols are formed secondarily to 17α-hydroxylation.[121][122] Even smaller amounts of progesterone may be also hydroxylated via 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) and to a lesser extent via aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) into 11β-hydroxyprogesterone.[123][124][42] In addition, progesterone can be hydroxylated in the liver by other cytochrome P450 enzymes which are not steroid-specific.[125] 6β-Hydroxylation, which is catalyzed mainly by CYP3A4, is the major transformation, and is responsible for approximately 70% of cytochrome P450-mediated progesterone metabolism.[125] Other routes include 6α-, 16α-, and 16β-hydroxylation.[112] However, treatment of women with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, had minimal effects on progesterone levels, producing only a slight and non-significant increase, and this suggests that cytochrome P450 enzymes play only a small role in progesterone metabolism.[126]
Levels
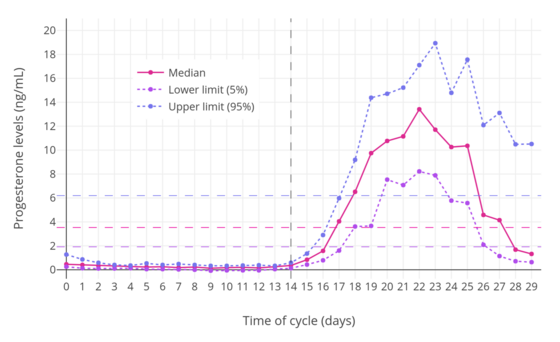
In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, rise after ovulation, and are elevated during the luteal phase, as shown in the diagram above. Progesterone levels tend to be less than 2 ng/mL prior to ovulation and greater than 5 ng/mL after ovulation. If pregnancy occurs, human chorionic gonadotropin is released, maintaining the corpus luteum and allowing it to maintain levels of progesterone. Between 7 and 9 weeks, the placenta begins to produce progesterone in place of the corpus luteum in a process called the luteal-placental shift.[128]
After the luteal-placental shift, progesterone levels start to rise further and may reach 100 to 200 ng/mL at term. Whether a decrease in progesterone levels is critical for the initiation of labor has been argued and may be species-specific. After delivery of the placenta and during lactation, progesterone levels are very low.
Progesterone levels are low in children and postmenopausal women.[129] Adult males have levels similar to those in women during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
| Group | P4 production | P4 levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prepubertal children | ND | 0.06–0.5 ng/mL | ||
| Pubertal girls Tanner stage I (childhood) Tanner stage II (ages 8–12) Tanner stage III (ages 10–13) Tanner stage IV (ages 11–14) Tanner stage V (ages 12–15) Follicular phase (days 1–14) Luteal phase (days 15–28) |
ND ND ND ND ND ND |
0.22 (<0.10–0.32) ng/mL 0.30 (0.10–0.51) ng/mL 0.36 (0.10–0.75) ng/mL 1.75 (<0.10–25.0) ng/mL 0.35 (0.13–0.75) ng/mL 2.0–25.0 ng/mL | ||
| Premenopausal women Follicular phase (days 1–14) Luteal phase (days 15–28) Oral contraceptive (anovulatory) |
0.75–5.4 mg/day 15–50 mg/day ND |
0.02–1.2 ng/mL 4–30 ng/mL 0.1–0.3 ng/mL | ||
| Postmenopausal women Oophorectomized women Oophorectomized and adrenalectomized women |
ND 1.2 mg/day <0.3 mg/day |
0.03–0.3 ng/mL 0.39 ng/mL ND | ||
| Pregnant women First trimester (weeks 1–12) Second trimester (weeks 13–26) Third trimester (weeks 27–40) Postpartum (at 24 hours) |
55 mg/day 92–100 mg/day 190–563 mg/day ND |
9–75 ng/mL 17–146 ng/mL 55–255 ng/mL 19 ng/mL | ||
| Men | 0.75–3 mg/day | 0.1–0.3 ng/mL | ||
| Notes: Mean levels are given as a single value and ranges are given after in parentheses. Sources: [130][131][132][133][134][135][136][137][138] | ||||
Ranges
Blood test results should always be interpreted using the reference ranges provided by the laboratory that performed the results. Example reference ranges are listed below.
| Person type | Reference range for blood test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower limit | Upper limit | Unit | |
| Female - menstrual cycle | (see diagram below) | ||
| Female - postmenopausal | <0.2[139] | 1[139] | ng/mL |
| <0.6[140] | 3[140] | nmol/L | |
| Female on oral contraceptives | 0.34[139] | 0.92[139] | ng/mL |
| 1.1[140] | 2.9[140] | nmol/L | |
| Males ≥16 years | 0.27[139] | 0.9[139] | ng/mL |
| 0.86[140] | 2.9[140] | nmol/L | |
| Female or male 1–9 years | 0.1[139] | 4.1[139] or 4.5[139] | ng/mL |
| 0.3[140] | 13[140] | nmol/L | |

• The ranges denoted By biological stage may be used in closely monitored menstrual cycles in regard to other markers of its biological progression, with the time scale being compressed or stretched to how much faster or slower, respectively, the cycle progresses compared to an average cycle.
• The ranges denoted Inter-cycle variability are more appropriate to use in non-monitored cycles with only the beginning of menstruation known, but where the woman accurately knows her average cycle lengths and time of ovulation, and that they are somewhat averagely regular, with the time scale being compressed or stretched to how much a woman's average cycle length is shorter or longer, respectively, than the average of the population.
• The ranges denoted Inter-woman variability are more appropriate to use when the average cycle lengths and time of ovulation are unknown, but only the beginning of menstruation is given.
Sources
Animal
Progesterone is produced in high amounts in the ovaries (by the corpus luteum) from the onset of puberty to menopause, and is also produced in smaller amounts by the adrenal glands after the onset of adrenarche in both males and females. To a lesser extent, progesterone is produced in nervous tissue, especially in the brain, and in adipose (fat) tissue, as well.
During human pregnancy, progesterone is produced in increasingly high amounts by the ovaries and placenta. At first, the source is the corpus luteum that has been "rescued" by the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) from the conceptus. However, after the 8th week, production of progesterone shifts to the placenta. The placenta utilizes maternal cholesterol as the initial substrate, and most of the produced progesterone enters the maternal circulation, but some is picked up by the fetal circulation and used as substrate for fetal corticosteroids. At term the placenta produces about 250 mg progesterone per day.
An additional animal source of progesterone is milk products. After consumption of milk products the level of bioavailable progesterone goes up.[142]
Plants
In at least one plant, Juglans regia, progesterone has been detected.[143] In addition, progesterone-like steroids are found in Dioscorea mexicana. Dioscorea mexicana is a plant that is part of the yam family native to Mexico.[144] It contains a steroid called diosgenin that is taken from the plant and is converted into progesterone.[145] Diosgenin and progesterone are also found in other Dioscorea species, as well as in other plants that are not closely related, such as fenugreek.
Another plant that contains substances readily convertible to progesterone is Dioscorea pseudojaponica native to Taiwan. Research has shown that the Taiwanese yam contains saponins — steroids that can be converted to diosgenin and thence to progesterone.[146]
Many other Dioscorea species of the yam family contain steroidal substances from which progesterone can be produced. Among the more notable of these are Dioscorea villosa and Dioscorea polygonoides. One study showed that the Dioscorea villosa contains 3.5% diosgenin.[147] Dioscorea polygonoides has been found to contain 2.64% diosgenin as shown by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.[148] Many of the Dioscorea species that originate from the yam family grow in countries that have tropical and subtropical climates.[149]
Medical use
Progesterone is used as a medication. It is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women.[114][150] It may also be used alone to treat menopausal symptoms. Studies have shown that transdermal progesterone (skin patch) and oral micronized progesterone are effective treatments for certain symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes and night sweats, which are otherwise referred to as vasomotor symptoms or VMS.[151]
It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders.[152][153][154][155] Progesterone has been shown to prevent miscarriage in women with 1) vaginal bleeding early in their current pregnancy and 2) a previous history of miscarriage.[156] Progesterone can be taken by mouth, through the vagina, and by injection into muscle or fat, among other routes.[114]
Chemistry
Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane steroid and is also known as pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione.[157][158] It has a double bond (4-ene) between the C4 and C5 positions and two ketone groups (3,20-dione), one at the C3 position and the other at the C20 position.[157][158]
Synthesis
Progesterone is commercially produced by semisynthesis. Two main routes are used: one from yam diosgenin first pioneered by Marker in 1940, and one based on soy phytosterols scaled up in the 1970s. Additional (not necessarily economical) semisyntheses of progesterone have also been reported starting from a variety of steroids. For the example, cortisone can be simultaneously deoxygenated at the C-17 and C-21 position by treatment with iodotrimethylsilane in chloroform to produce 11-keto-progesterone (ketogestin), which in turn can be reduced at position-11 to yield progesterone.[159]
Marker semisynthesis
An economical semisynthesis of progesterone from the plant steroid diosgenin isolated from yams was developed by Russell Marker in 1940 for the Parke-Davis pharmaceutical company.[160] This synthesis is known as the Marker degradation.
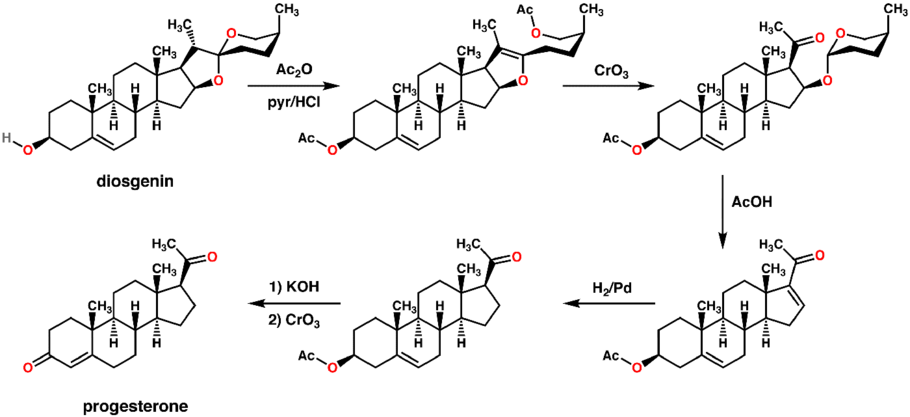
The 16-DPA intermediate is important to the synthesis of many other medically important steroids. A very similar approach can produce 16-DPA from solanine.[161]
Soy semisynthesis
Progesterone can also be made from the stigmasterol found in soybean oil also. c.f. Percy Julian.
Total synthesis

A total synthesis of progesterone was reported in 1971 by W.S. Johnson.[167] The synthesis begins with reacting the phosphonium salt 7 with phenyl lithium to produce the phosphonium ylide 8. The ylide 8 is reacted with an aldehyde to produce the alkene 9. The ketal protecting groups of 9 are hydrolyzed to produce the diketone 10, which in turn is cyclized to form the cyclopentenone 11. The ketone of 11 is reacted with methyl lithium to yield the tertiary alcohol 12, which in turn is treated with acid to produce the tertiary cation 13. The key step of the synthesis is the π-cation cyclization of 13 in which the B-, C-, and D-rings of the steroid are simultaneously formed to produce 14. This step resembles the cationic cyclization reaction used in the biosynthesis of steroids and hence is referred to as biomimetic. In the next step the enol orthoester is hydrolyzed to produce the ketone 15. The cyclopentene A-ring is then opened by oxidizing with ozone to produce 16. Finally, the diketone 17 undergoes an intramolecular aldol condensation by treating with aqueous potassium hydroxide to produce progesterone.[167]
History
George W. Corner and Willard M. Allen discovered the hormonal action of progesterone in 1929.[15][168][169][170] By 1931–1932, nearly pure crystalline material of high progestational activity had been isolated from the corpus luteum of animals, and by 1934, pure crystalline progesterone had been refined and obtained and the chemical structure of progesterone was determined.[15][169] This was achieved by Adolf Butenandt at the Chemisches Institut of Technical University in Danzig, who extracted this new compound from several thousand liters of urine.[171]
Chemical synthesis of progesterone from stigmasterol and pregnanediol was accomplished later that year.[169][172] Up to this point, progesterone, known generically as corpus luteum hormone, had been being referred to by several groups by different names, including corporin, lutein, luteosterone, and progestin.[15][173] In 1935, at the time of the Second International Conference on the Standardization of Sex Hormones in London, England, a compromise was made between the groups and the name progesterone (progestational steroidal ketone) was created.[15][174]
Veterinary use
The use of progesterone tests in dog breeding to pinpoint ovulation is becoming more widely used. There are several tests available but the most reliable test is a blood test with blood drawn by a veterinarian and sent to a lab for processing. Results can usually be obtained with 24 to 72 hours. The rationale for using progesterone tests is that increased numbers begin in close proximity to preovulatory surge in gonadotrophins and continue through ovulation and estrus. When progesterone levels reach certain levels they can signal the stage of estrus the female is. Prediction of birth date of the pending litter can be very accurate if ovulation date is known. Puppies deliver with a day or two of 9 weeks gestation in most cases. It is not possible to determine pregnancy using progesterone tests once a breeding has taken place, however. This is due to the fact that, in dogs, progesterone levels remain elevated throughout the estrus period.[175]
Pricing
Pricing for progesterone can vary depending location, insurance coverage, discount coupons, quantity, shortages, manufacturers, brand or generic versions, different pharmacies, and so on. As of currently, 30 capsules of 100 mg of the generic version, Prometrium, from CVS Pharmacy is around $40 without any discounts or insurance applied. The brand version, Progesterone, is around $450 for 30 capsules without any discounts or insurance applied.[176] In comparison, Walgreens offers 30 capsules of 100 mg in the generic version for $51 without insurance or coupons applied. The brand name costs around $431 for 30 capsules of 100 mg.[177]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 25 February 2015. p. 2179. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=xmLeBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA2179.
- ↑ Handbook of Behavioral Neurobiology Volume 7 Reproduction (1st ed.). New York: Plenum Press. 6 December 2012. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-4684-4834-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=MoDrBwAAQBAJ&q=pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione;+abbreviated+as+P4&pg=PA189. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ↑ "progesterone (CHEBI:17026)". European Molecular Biology Laboratory-EBI. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do;jsessionid=309FCC7D184C0AD58410071F3F163155?chebiId=17026&structureView=applet&viewTermLineage=.
- ↑ "Progesterone_msds". https://www.chemsrc.com/en/cas/57-83-0_1068061.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Pharmacokinetics and potency of progestins used for hormone replacement therapy and contraception". Reviews in Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders 3 (3): 211–224. September 2002. doi:10.1023/A:1020072325818. PMID 12215716.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "The absorption of oral micronized progesterone: the effect of food, dose proportionality, and comparison with intramuscular progesterone". Fertility and Sterility 60 (1): 26–33. July 1993. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(16)56031-2. PMID 8513955.
- ↑ Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 28 March 2012. pp. 44–. ISBN 978-1-4511-4847-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=KZLubBxJEwEC&pg=PA44.
- ↑ Clinical Chemistry. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2008. pp. 192–. ISBN 978-0-7234-3455-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=Gjc704GR5YEC&pg=PA192.
- ↑ Hormones in Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. 1 January 2005. p. 74. ISBN 978-81-8061-427-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=IBxBbaDjXw0C&pg=PA74.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Pharmaceutical and clinical development of a novel progesterone formulation". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 94 (Suppl 161): 28–37. November 2015. doi:10.1111/aogs.12765. PMID 26342177.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Pharmacology for Women's Health. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 25 October 2010. pp. 372–373. ISBN 978-1-4496-5800-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=E9qVyrNPsBkC&pg=PA373.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Progesterone as a neuroactive neurosteroid, with special reference to the effect of progesterone on myelination". Steroids 65 (10–11): 605–612. 2000. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(00)00173-2. PMID 11108866.
- ↑ "Progesterone Is Important for Transgender Women's Therapy-Applying Evidence for the Benefits of Progesterone in Ciswomen". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 104 (4): 1181–1186. April 2019. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01777. PMID 30608551. "Evidence has accrued that normal progesterone (and ovulation), as well as physiological estradiol levels, is necessary during ciswomen's premenopausal menstrual cycles for current fertility and long-term health; transgender women may require progesterone therapy and similar potential physiological benefits".
- ↑ Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 47X. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA47X.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 15.7 Gynecologic Endocrinology. Springer Science & Business Media. 11 November 2013. pp. 9, 25–29. ISBN 978-1-4613-2157-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=9vv2BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25.
- ↑ "Membrane progesterone receptors: evidence for neuroprotective, neurosteroid signaling and neuroendocrine functions in neuronal cells". Neuroendocrinology 96 (2): 162–171. 2012. doi:10.1159/000339822. PMID 22687885.
- ↑ "Membrane progesterone receptors in reproduction and cancer". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 434: 166–175. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2016.06.027. PMID 27368976.
- ↑ "Characterization of high affinity progesterone-binding membrane proteins by anti-peptide antiserum". Steroids 63 (2): 111–116. February 1998. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(97)00143-8. PMID 9516722.
- ↑ "Function and structural regulation of the carbon monoxide (CO)-responsive membrane protein PGRMC1". Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition 63 (1): 12–17. July 2018. doi:10.3164/jcbn.17-132. PMID 30087538.
- ↑ "Membrane Associated Progesterone Receptors: Promiscuous Proteins with Pleiotropic Functions - Focus on Interactions with Cytochromes P450". Frontiers in Pharmacology 8: 159. 27 March 2017. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00159. PMID 28396637.
- ↑ "The interaction between neuroactive steroids and the sigma1 receptor function: behavioral consequences and therapeutic opportunities". Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews 37 (1–3): 116–132. November 2001. doi:10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00112-6. PMID 11744080.
- ↑ "Antagonist action of progesterone at σ-receptors in the modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels". American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 300 (2): C328–C337. February 2011. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00383.2010. PMID 21084640.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Pharmacological and functional characterization of human mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor ligands". European Journal of Pharmacology 247 (2): 145–154. October 1993. doi:10.1016/0922-4106(93)90072-H. PMID 8282004.
- ↑ "Conception and pharmacodynamic profile of drospirenone". Steroids 68 (10–13): 891–905. November 2003. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2003.08.008. PMID 14667981.
- ↑ "Comparison of progesterone and glucocorticoid receptor binding and stimulation of gene expression by progesterone, 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate, and related progestins". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 197 (6): 599.e1–599.e7. December 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.024. PMID 18060946.
- ↑ "Progesterone acts via the nuclear glucocorticoid receptor to suppress IL-1β-induced COX-2 expression in human term myometrial cells". PLOS ONE 7 (11): e50167. 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050167. PMID 23209664. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...750167L.
- ↑ "Neuroactive steroids". FASEB Journal 6 (6): 2311–2322. March 1992. doi:10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1347506. PMID 1347506.
- ↑ "The nuclear pregnane X receptor: a key regulator of xenobiotic metabolism". Endocrine Reviews 23 (5): 687–702. October 2002. doi:10.1210/er.2001-0038. PMID 12372848.
- ↑ "The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions". The Journal of Clinical Investigation 102 (5): 1016–1023. September 1998. doi:10.1172/JCI3703. PMID 9727070.
- ↑ Tactics in Contemporary Drug Design. Springer. 8 December 2014. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-3-642-55041-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=j2HEBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA161.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Principles of Gender-specific Medicine. Gulf Professional Publishing. 2004. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-0-12-440906-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=TiLxa8nPbLkC&pg=PA146.
- ↑ "Drug Metabolism". Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 24 January 2012. p. 164. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Sd6ot9ul-bUC&pg=PA164.
- ↑ Estrogens—Advances in Research and Application: 2013 Edition: ScholarlyBrief. ScholarlyEditions. 21 June 2013. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-1-4816-7550-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=9WdGK_3ujQMC&pg=PA4.
- ↑ "The CatSper channel mediates progesterone-induced Ca2+ influx in human sperm". Nature 471 (7338): 382–386. March 2011. doi:10.1038/nature09769. PMID 21412338. Bibcode: 2011Natur.471..382S.
- ↑ "Progesterone activates the principal Ca2+ channel of human sperm". Nature 471 (7338): 387–391. March 2011. doi:10.1038/nature09767. PMID 21412339. Bibcode: 2011Natur.471..387L.
- ↑ "Women's reproductive system as balanced estradiol and progesterone actions—A revolutionary, paradigm-shifting concept in women's health". Drug Discovery Today: Disease Models 32 (Part B): 31–40. 2020. doi:10.1016/j.ddmod.2020.11.005.
- ↑ "Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B". The EMBO Journal 9 (5): 1603–1614. May 1990. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08280.x. PMID 2328727.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "Hormonal effects on the mammary gland of postmenopausal nonhuman primates". Breast Disease (IOS Press) 24: 59–70. 1 January 2006. doi:10.3233/bd-2006-24105. ISBN 978-1-58603-653-9. PMID 16917139. https://books.google.com/books?id=wGaKtDw50K0C&pg=PA61.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Essential Medical Physiology. Academic Press. 2003. pp. 770. ISBN 978-0-12-387584-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=j9e-tkdHeUoC&pg=PA770.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Anatomy and Physiology for Midwives, with Pageburst online access,3: Anatomy and Physiology for Midwives. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2011. pp. 413. ISBN 978-0-7020-3489-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=OmSKoYD-iW0C&pg=PA413.
- ↑ "The metabolic effects of progesterone in man". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 15 (10): 1194–1215. October 1955. doi:10.1210/jcem-15-10-1194. PMID 13263410.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 "Alternative androgen pathways". WikiJournal of Medicine 10: X. 2023. doi:10.15347/WJM/2023.003.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "Alternative (backdoor) androgen production and masculinization in the human fetus". PLOS Biology 17 (2): e3000002. February 2019. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000002. PMID 30763313.
- ↑ "Steroidogenesis of the testis -- new genes and pathways". Annales d'Endocrinologie 75 (2): 40–47. May 2014. doi:10.1016/j.ando.2014.03.002. PMID 24793988.
- ↑ "Prismatic cases: 17,20-desmolase (17,20-lyase) deficiency". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 81 (2): 457–459. February 1996. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.2.8636249. PMID 8636249.
- ↑ "Non-genomic steroid actions in human spermatozoa. "Persistent tickling from a laden environment"". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 25 (3): 208–219. May 2007. doi:10.1055/s-2007-973433. PMID 17447210.
- ↑ "Biphasic elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) in individual human spermatozoa exposed to progesterone". Developmental Biology 222 (2): 326–335. June 2000. doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9729. PMID 10837122.
- ↑ "Slow calcium oscillations in human spermatozoa". The Biochemical Journal 378 (Pt 3): 827–832. March 2004. doi:10.1042/BJ20031368. PMID 14606954.
- ↑ "Stimulation of human spermatozoa with progesterone gradients to simulate approach to the oocyte. Induction of [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations and cyclical transitions in flagellar beating". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (44): 46315–46325. October 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401194200. PMID 15322137.
- ↑ Anatomy & physiology. Benjamin-Cummings. 2013. p. 903. ISBN 9780321887603.
- ↑ "Progesterone induces activation in Octopus vulgaris spermatozoa". Molecular Reproduction and Development 59 (1): 97–105. May 2001. doi:10.1002/mrd.1011. PMID 11335951.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "Placental Hormones". 6 August 2000. http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/reprod/placenta/endocrine.html.
- ↑ "Role of nuclear progesterone receptor isoforms in uterine pathophysiology". Human Reproduction Update 21 (2): 155–173. 2014. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmu056. PMID 25406186.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 "Progesterone in normal and pathological pregnancy". Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation 27 (1): 35–48. July 2016. doi:10.1515/hmbci-2016-0038. PMID 27662646.
- ↑ "Interventions to prevent spontaneous preterm birth in women with singleton pregnancy who are at high risk: systematic review and network meta-analysis". BMJ 376: e064547. February 2022. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-064547. PMID 35168930.
- ↑ "Mammary gland development". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Developmental Biology 1 (4): 533–557. 2012. doi:10.1002/wdev.35. PMID 22844349.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 57.2 "Minireview: Progesterone Regulation of Proliferation in the Normal Human Breast and in Breast Cancer: A Tale of Two Scenarios?". Molecular Endocrinology 29 (9): 1230–1242. September 2015. doi:10.1210/me.2015-1152. PMID 26266959.
- ↑ "The Breast". Yen and Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. 13 September 2013. pp. 236–. ISBN 978-1-4557-2758-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=KZ95AAAAQBAJ&pg=PA236.
- ↑ "GPER mediates estrogen-induced signaling and proliferation in human breast epithelial cells and normal and malignant breast". Hormones & Cancer 5 (3): 146–160. June 2014. doi:10.1007/s12672-014-0174-1. PMID 24718936.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 60.2 60.3 60.4 "Amphiregulin mediates progesterone-induced mammary ductal development during puberty". Breast Cancer Research 15 (3): R44. May 2013. doi:10.1186/bcr3431. PMID 23705924.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 "Progesterone--promoter or inhibitor of breast cancer". Climacteric 16 (Suppl 1): 54–68. August 2013. doi:10.3109/13697137.2013.768806. PMID 23336704.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 62.2 "Progesterone and Breast Cancer". Endocrine Reviews 41 (2): 320–344. April 2020. doi:10.1210/endrev/bnz001. PMID 31512725.
- ↑ Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer (September 2019). "Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence". Lancet 394 (10204): 1159–1168. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31709-X. PMID 31474332.
- ↑ "The impact of micronized progesterone on breast cancer risk: a systematic review". Climacteric 21 (2): 111–122. April 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2017.1421925. PMID 29384406.
- ↑ "Progesterone vs. synthetic progestins and the risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Systematic Reviews 5 (1): 121. July 2016. doi:10.1186/s13643-016-0294-5. PMID 27456847.
- ↑ "Progesterone, progestins and the breast in menopause treatment". Climacteric 21 (4): 326–332. August 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1476483. PMID 29852797.
- ↑ "Menopausal hormone therapy: a better and safer future". Climacteric 21 (5): 454–461. October 2018. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1439915. PMID 29526116.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 68.2 68.3 68.4 68.5 68.6 68.7 "Skin aging and menopause : implications for treatment". American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 4 (6): 371–378. 2003. doi:10.2165/00128071-200304060-00001. PMID 12762829.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 69.3 69.4 69.5 69.6 69.7 "Effects and side-effects of 2% progesterone cream on the skin of peri- and postmenopausal women: results from a double-blind, vehicle-controlled, randomized study". The British Journal of Dermatology 153 (3): 626–634. September 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06685.x. PMID 16120154.
- ↑ Neurosteroids and the Nervous System. Springer Science & Business Media. 9 November 2012. pp. 44–46. ISBN 978-1-4614-5559-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=D1fOTC6CP3kC&pg=PA44.
- ↑ "Testing the Affiliation Hypothesis of Homoerotic Motivation in Humans: The Effects of Progesterone and Priming". Archives of Sexual Behavior 44 (5): 1395–1404. July 2015. doi:10.1007/s10508-014-0436-6. PMID 25420899. https://researchportal.port.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/testing-the-affiliation-hypothesis-of-homoerotic-motivation-in-humans(d1eb5448-5664-4d2d-8694-18f970836cbb).html.
- ↑ "Homosexuality may help us bond". UoP News. https://uopnews.port.ac.uk/2014/11/25/homosexuality-may-help-us-bond/.
- ↑ "Having homosexual thoughts 'is an essential part of human evolution' study suggests". 25 November 2014. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/science/11251206/Having-homosexual-thoughts-is-an-essential-part-of-human-evolution-study-suggests.html.
- ↑ "New Study Identifies Evolutionary Basis Of Homosexuality". 26 November 2014. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/homosexuality-evolution-social-bonding_n_6218406.
- ↑ 75.0 75.1 75.2 "Progesterone metabolism in the pineal, brain stem, thalamus and corpus callosum of the female rat". Brain Research 125 (2): 313–324. April 1977. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(77)90624-2. PMID 558037. https://zenodo.org/record/890908.
- ↑ "Local synthesis and dual actions of progesterone in the nervous system: neuroprotection and myelination". Growth Hormone & IGF Research 14 (Suppl A): S18–S33. June 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ghir.2004.03.007. PMID 15135772.
- ↑ "Non-genomic mechanisms of progesterone action in the brain". Frontiers in Neuroscience 7: 159. September 2013. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00159. PMID 24065876.
- ↑ "Gender differences in acute CNS trauma and stroke: neuroprotective effects of estrogen and progesterone". Journal of Neurotrauma 17 (5): 367–388. May 2000. doi:10.1089/neu.2000.17.367. PMID 10833057.
- ↑ "Inhibitory effect of progesterone on inflammatory factors after experimental traumatic brain injury". Biomedical and Environmental Sciences 20 (5): 432–438. October 2007. PMID 18188998.
- ↑ "Progesterone exerts neuroprotective effects and improves long-term neurologic outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage in middle-aged mice". Neurobiology of Aging 42: 13–24. June 2016. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.02.029. PMID 27143417.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 "Progesterone inhibition of neuronal calcium signaling underlies aspects of progesterone-mediated neuroprotection". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 131 (1–2): 30–36. August 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.11.002. PMID 22101209.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 "Progesterone exerts neuroprotective effects after brain injury". Brain Research Reviews 57 (2): 386–397. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.06.012. PMID 17826842.
- ↑ "The role of progesterone in traumatic brain injury". The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 26 (6): 497–499. 2011. doi:10.1097/HTR.0b013e31823088fa. PMID 22088981.
- ↑ "Progesterone Changes VEGF and BDNF Expression and Promotes Neurogenesis After Ischemic Stroke". Molecular Neurobiology 54 (1): 571–581. January 2016. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9651-y. PMID 26746666.
- ↑ "Sex, sex steroids, and brain injury". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 27 (3): 229–239. May 2009. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216276. PMID 19401954.
- ↑ "Progesterone increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells and induces neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury in aged rats". Journal of Neurotrauma 29 (2): 343–353. January 2012. doi:10.1089/neu.2011.1807. PMID 21534727.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 "Role of progesterone in nicotine addiction: evidence from initiation to relapse". Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 18 (6): 451–461. December 2010. doi:10.1037/a0021265. PMID 21186920.
- ↑ "Sex differences in availability of β2*-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in recently abstinent tobacco smokers". Archives of General Psychiatry 69 (4): 418–427. April 2012. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1465. PMID 22474108.
- ↑ "Effects of progesterone and testosterone on cocaine self-administration and cocaine discrimination by female rhesus monkeys". Neuropsychopharmacology 36 (11): 2187–2199. October 2011. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.130. PMID 21796112.
- ↑ "The impact of the menstrual cycle and hormonal contraceptives on competitiveness". Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization. Gender Differences in Risk Aversion and Competition 83 (1): 1–10. 1 June 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jebo.2011.06.006. ISSN 0167-2681. https://dare.uva.nl/personal/pure/en/publications/the-impact-of-the-menstrual-cycle-and-hormonal-contraceptives-on-competitiveness(701b996f-ef86-45a1-a05f-794918dd68e2).html.
- ↑ Medicinal Chemistry. New Delhi: Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd.. 2007. p. 432. ISBN 978-81-317-0031-0.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 Maternal, Fetal, & Neonatal Physiology. Elsevier Health Sciences. 14 April 2014. pp. 92–. ISBN 978-0-323-29296-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=RNLsAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA92.
- ↑ "Progesterone receptors upregulate Wnt-1 to induce epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation and c-Src-dependent sustained activation of Erk1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells". Molecular and Cellular Biology 27 (2): 466–480. January 2007. doi:10.1128/MCB.01539-06. PMID 17074804.
- ↑ "Section 5/5ch9/s5ch9_13". Essentials of Human Physiology. http://humanphysiology.tuars.com/program/section5/5ch9/s5ch9_13.htm.
- ↑ "The Physiologic Basis for the Temperature Raising Effect of Progesterone" (in en), Metabolic Effects of Gonadal Hormones and Contraceptive Steroids (Boston, MA: Springer US): pp. 668–675, 1969, doi:10.1007/978-1-4684-1782-1_49, ISBN 978-1-4684-1782-1, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-1782-1_49, retrieved 22 March 2021
- ↑ "Progesterone receptors regulate gallbladder motility". The Journal of Surgical Research 45 (6): 505–512. December 1988. doi:10.1016/0022-4804(88)90137-0. PMID 3184927.
- ↑ "Hormones and Oral Health". http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/hormones-oral-health.
- ↑ "Progesterone receptor knockout mice have an improved glucose homeostasis secondary to beta -cell proliferation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (24): 15644–15648. November 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.202612199. PMID 12438645.
- ↑ "Progesterone in gestational diabetes mellitus: guilty or not guilty?". Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 14 (2): 54–56. March 2003. doi:10.1016/S1043-2760(03)00003-1. PMID 12591170.
- ↑ "The effect of weight and body mass index on serum progesterone values and live birth rate in cryopreserved in vitro fertilization cycles". F&S Reports 2 (2): 195–200. June 2021. doi:10.1016/j.xfre.2021.02.005. PMID 34278354.
- ↑ "The impact of micronized progesterone on cardiovascular events - a systematic review". Climacteric 25 (4): 327–336. August 2022. doi:10.1080/13697137.2021.2022644. PMID 35112635.
- ↑ "Impact of progesterone on skin and hair in menopause - a comprehensive review". Climacteric 24 (3): 229–235. June 2021. doi:10.1080/13697137.2020.1838476. PMID 33527841.
- ↑ "Association Between Hormone Therapy and Muscle Mass in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Network Open 2 (8): e1910154. August 2019. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.10154. PMID 31461147.
- ↑ "Impact of micronized progesterone on body weight, body mass index, and glucose metabolism: a systematic review". Climacteric 22 (2): 148–161. April 2019. doi:10.1080/13697137.2018.1514003. PMID 30477366.
- ↑ "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (1). 2014. doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.005. ISSN 2002-4436.
- ↑ Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. New York: Wiley. 2002. pp. 244. ISBN 0-471-49641-3.
- ↑ "Self-sufficient biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in engineered yeast". Nature Biotechnology 16 (2): 186–189. February 1998. doi:10.1038/nbt0298-186. PMID 9487528.
- ↑ "Women's Health". Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 24 January 2012. pp. 1397–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Sd6ot9ul-bUC&pg=PA1397.
- ↑ Progesterone - Drugs.com, https://www.drugs.com/pro/progesterone.html, retrieved 23 August 2015
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 110.2 Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2007. pp. 22–. ISBN 978-0-323-03309-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=fOPtaEIKvcIC&pg=PA22.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 111.2 111.3 Reproduction in Domestic Animals. Elsevier. 20 February 1991. pp. 101–. ISBN 978-0-08-057109-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=bbb-ow0N7K4C&pg=PA101.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 112.2 112.3 112.4 112.5 112.6 112.7 112.8 "All progestins are not created equal". Steroids 68 (10–13): 879–890. November 2003. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2003.08.003. PMID 14667980.
- ↑ Pharmacology and Therapeutics for Dentistry. Elsevier Health Sciences. 3 September 2016. pp. 448–. ISBN 978-0-323-44595-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=6xT7DAAAQBAJ&pg=PA448.
- ↑ 114.0 114.1 114.2 114.3 "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric 8 (Suppl 1): 3–63. August 2005. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 Knobil and Neill's Physiology of Reproduction. Academic Press. 15 November 2014. pp. 304–. ISBN 978-0-12-397769-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=I1ACBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA304.
- ↑ 116.0 116.1 Amenorrhea: A Case-Based, Clinical Guide. Springer Science & Business Media. 11 September 2010. pp. 13–. ISBN 978-1-60327-864-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=4836MLkPoIYC&pg=PA13.
- ↑ "Neurosteroids". Sex Differences in the Human Brain, their Underpinnings and Implications. Progress in Brain Research. 186. Elsevier. 2010. pp. 113–37. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53630-3.00008-7. ISBN 9780444536303.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 Hormones: From Molecules to Disease. Springer Science & Business Media. 30 November 1990. pp. 401–. ISBN 978-0-412-02791-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=Seddp4-dulIC&pg=PA401.
- ↑ "Progestins as inhibitors of the human 20-ketosteroid reductases, AKR1C1 and AKR1C3". Chemico-Biological Interactions 191 (1–3): 227–233. May 2011. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.12.012. PMID 21182831.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics of estrogen and progesterone in chronic kidney disease". Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease 11 (4): 357–360. October 2004. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2004.07.001. PMID 15492972.
- ↑ Integrative Therapies for Depression: Redefining Models for Assessment, Treatment and Prevention. CRC Press. 27 April 2016. pp. 201–. ISBN 978-1-4987-0230-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=GpHwCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA201.
- ↑ Reproductive Biology of the Great Apes: Comparative and Biomedical Perspectives. Elsevier. 2 December 2012. pp. 179–. ISBN 978-0-323-14971-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=iUA0CdGhYksC&pg=PA179.
- ↑ "Structural insights into aldosterone synthase substrate specificity and targeted inhibition". Molecular Endocrinology 27 (2): 315–324. February 2013. doi:10.1210/me.2012-1287. PMID 23322723.
- ↑ "The in vitro metabolism of 11β-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-ketoprogesterone to 11-ketodihydrotestosterone in the backdoor pathway". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 178: 203–212. April 2018. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.12.014. PMID 29277707.
- ↑ 125.0 125.1 Regulation of Steroid Metabolism and the Hepatic Transcriptome by Estradiol and Progesterone. 2008. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-1-109-04632-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=2nlbQ12QrSsC&pg=PA24.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Effects of ketoconazole in hirsute women". Acta Endocrinologica 124 (1): 19–22. January 1991. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1240019. PMID 1825737.
- ↑ "Establishment of detailed reference values for luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, estradiol, and progesterone during different phases of the menstrual cycle on the Abbott ARCHITECT analyzer". Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 44 (7): 883–887. 2006. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2006.160. PMID 16776638.
- ↑ "Effects of luteectomy and progesterone replacement therapy in early pregnant patients". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 115 (6): 759–765. March 1973. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(73)90517-6. PMID 4688578.
- ↑ NIH Clinical Center (16 August 2004). "Progesterone Historical Reference Ranges". United States National Institutes of Health. http://cclnprod.cc.nih.gov/dlm/testguide.nsf/Index/CB26894E1EB28DEF85256BA5005B000E?OpenDocument.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid945344 - ↑ Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 31 October 2012. pp. 908–. ISBN 978-1-4557-4502-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=dWHYcOJK-cgC&pg=PA908.
- ↑ Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2001. pp. 889, 940. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=FVfzRvaucq8C&pg=PA940.
- ↑ Gynecologic Endocrinology. Springer Science & Business Media. 11 November 2013. pp. 9, 25–29, 139. ISBN 978-1-4613-2157-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=9vv2BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25.
- ↑ The Premenstrual Syndrome: Proceedings of a workshop held during the Sixth International Congress of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynecology, Berlin, September 1980. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-94-011-6255-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=0IAJBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA51.
- ↑ Yen and Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2009. pp. 807–. ISBN 978-1-4160-4907-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=NudwnhxY8kYC&pg=PA807.
- ↑ Berman's Pediatric Decision Making. Elsevier Health Sciences. 1 January 2011. pp. 160–. ISBN 978-0-323-05405-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=NPhnHrDQ1_kC&pg=PA160.
- ↑ "Natürliche und Synthetische Sexualhormone – Biologische Grundlagen und Behandlungsprinzipien" (in de). Grundlagen und Klinik der Menschlichen Fortpflanzung. Walter de Gruyter. 1988. pp. 229–306. ISBN 978-3110109689. OCLC 35483492. https://books.google.com/books?id=v4HvAQAACAAJ.
- ↑ Little, A. B., & Billiar, R. B. (1983). Progestagens. In Endocrinology of Pregnancy, 3rd Edition (pp. 92–111). Harper and Row Philadelphia. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=2512291948467467634
- ↑ 139.0 139.1 139.2 139.3 139.4 139.5 139.6 139.7 139.8 Progesterone Reference Ranges, Performed at the Clinical Center at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda MD, 03Feb09
- ↑ 140.0 140.1 140.2 140.3 140.4 140.5 140.6 140.7 Converted from mass values using molar mass of 314.46 g/mol
- ↑ "Reference ranges for estradiol, progesterone, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone during the menstrual cycle". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (1). 2014. doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.001. ISSN 2002-4436.
- ↑ "Milk products are a source of dietary progesterone". 30th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium. 13 December 2007. pp. abstract # 2028. http://www.docguide.com/news/content.nsf/news/852571020057CCF6852573B1007803AD.
- ↑ "Occurrence of progesterone and related animal steroids in two higher plants". Journal of Natural Products 73 (3): 338–345. March 2010. doi:10.1021/np9007415. PMID 20108949.
- ↑ "Steroids". Chemical Week 104: 57–72. May 1969. PMID 12255132.
- ↑ "Metabolism of tomato steroidal glycosides in humans". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54 (9): 1312–1314. September 2006. doi:10.1248/cpb.54.1312. PMID 16946542.
- ↑ "Isolation and identification of steroidal saponins in Taiwanese yam cultivar (Dioscorea pseudojaponica Yamamoto)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 51 (22): 6438–6444. October 2003. doi:10.1021/jf030390j. PMID 14558759. http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/189462/1/58.pdf.
- ↑ "Final report of the amended safety assessment of Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) root extract". International Journal of Toxicology 23 (Suppl 2): 49–54. 2004. doi:10.1080/10915810490499055. PMID 15513824.
- ↑ "Diosgenin quantification by HPLC in a Dioscorea polygonoides tuber collection from colombian flora". Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 18 (5): 1073–1076. 2007. doi:10.1590/S0103-50532007000500030.
- ↑ "Properties of starches in yam (Dioscorea spp.) tuber". Current Topics in Food Science and Technology: 105–114. 2005. ISBN 81-308-0003-9.
- ↑ "Hormonal and Surgical Treatment Options for Transgender Women and Transfeminine Spectrum Persons". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America 40 (1): 99–111. March 2017. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2016.10.006. PMID 28159148.
- ↑ "Efficacy of progestin-only treatment for the management of menopausal symptoms: a systematic review". Menopause 28 (2): 217–224. November 2020. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001676. PMID 33109992.
- ↑ "Systemic progesterone therapy--oral, vaginal, injections and even transdermal?". Maturitas 79 (3): 248–255. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.07.009. PMID 25113944.
- ↑ "Clinical roles and applications of progesterone in reproductive medicine: an overview". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 94 (Suppl 161): 3–7. November 2015. doi:10.1111/aogs.12791. PMID 26443945.
- ↑ "Clinical use of progesterone in infertility and assisted reproduction". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 94 (Suppl 161): 17–27. November 2015. doi:10.1111/aogs.12770. PMID 26345161.
- ↑ "Use of progesterone supplement therapy for prevention of preterm birth: review of literatures". Obstetrics & Gynecology Science 60 (5): 405–420. September 2017. doi:10.5468/ogs.2017.60.5.405. PMID 28989916.
- ↑ "Progesterone to prevent miscarriage in women with early pregnancy bleeding: the PRISM RCT" (in EN). Health Technology Assessment 24 (33): 1–70. June 2020. doi:10.3310/hta24330. PMID 32609084.
- ↑ 157.0 157.1 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 1024–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA1024.
- ↑ 158.0 158.1 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 880–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA880.
- ↑ "Regiospecific deoxygenation of the dihydroxyacetone moiety at C-17 of corticoid steroids with iodotrimethylsilane". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 34 (9): 3722–3726. September 1986. doi:10.1248/cpb.34.3722. PMID 3815593.
- ↑ 160.0 160.1 "Sterols. CXII. Sapogenins. XLI. The Preparation of Trillin and its Conversion to Progesterone". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 (12): 3349–3350. 1940. doi:10.1021/ja01869a023.
- ↑ "A One-Pot Efficient Process for 16-Dehydropregnenolone Acetate". Organic Process Research & Development 7 (3): 306–308. 1 May 2003. doi:10.1021/op0200625.
- ↑ "Progesterone from 3-Acetoxybisnor-5-cholenaldehyde and 3-Ketobisnor-4-cholenaldehyde". Journal of the American Chemical Society 72 (6): 2617–2619. 1950. doi:10.1021/ja01162a076.
- ↑ "Ozonolysis. II. 1 The Effect of Pyridine on the Ozonolysis of 4,22-Stigmastadien-3-one 2". Journal of the American Chemical Society 80 (4): 915–921. 1958. doi:10.1021/ja01537a041.
- ↑ "A convenient synthesis of progesterone from stigmasterol". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 42 (22): 3633–3634. October 1977. doi:10.1021/jo00442a044. PMID 915584.
- ↑ "Nova Transcripts: Forgotten Genius". PBS.org. 6 February 2007. https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/transcripts/3402_julian.html.
- ↑ "Giants of the Past". lipidlibrary.aocs.org. http://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/history/Julian/index.htm.
- ↑ 167.0 167.1 167.2 "Acetylenic bond participation in biogenetic-like olefinic cyclizations. II. Synthesis of dl-progesterone". Journal of the American Chemical Society 93 (17): 4332–4334. August 1971. doi:10.1021/ja00746a062. PMID 5131151.
- ↑ "Physiology of the corpus luteum". American Journal of Physiology. Legacy Content 88 (2): 326–339. 1 March 1929. doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1929.88.2.326. ISSN 0002-9513. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajplegacy.1929.88.2.326.
- ↑ 169.0 169.1 169.2 Is Menstruation Obsolete?. Oxford University Press. 1999. pp. 31–. ISBN 978-0-19-513021-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=1ZzmCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA31.
- ↑ The Menstrual Cycle. Routledge. 7 March 2008. pp. 49–. ISBN 978-1-134-71411-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=7HQBAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA49.
- ↑ "Adolf Butenandt und sein Wirken an der Technischen Hochschule Danzig". Chemkon 10 (3): 135–138. 2003. doi:10.1002/ckon.200390038.
- ↑ Premenstrual Syndrome: Ethical and Legal Implications in a Biomedical Perspective. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 274–. ISBN 978-1-4684-5275-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=HTLoBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA274.
- ↑ The Endocrine Organs in Health and Disease: With an Historical Review. Oxford University Press, H. Milford. 1936. p. 406. https://books.google.com/books?id=tkgbAAAAIAAJ.
- ↑ "Progesterone: how did the name originate?". Southern Medical Journal 63 (10): 1151–1155. October 1970. doi:10.1097/00007611-197010000-00012. PMID 4922128.
- ↑ "Interpretation of Serum Progesterone Results for Management of Breeding in Dogs". Webcd.endo.ref. February 2009. https://www.dcpah.msu.edu/sections/endocrinology/Progesterone_Guidelines.pdf.
- ↑ "Progesterone Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". https://www.goodrx.com/progesterone.
- ↑ "Progesterone Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". https://www.goodrx.com/progesterone.
External links
- Progesterone MS Spectrum
- Progesterone at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- "Progesterone". Kimball's Biology Pages. 27 May 2007. http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/P/Progesterone.html.
 |



